Electrical Conduction Mechanisms of Nitrogenated Amorphous Carbon Films Deposited by High-Density Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition
Abstract
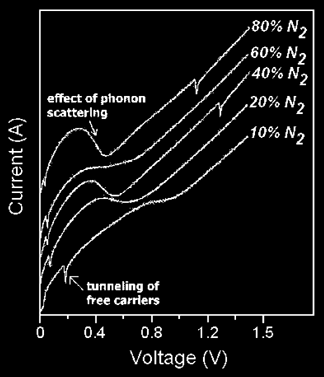
Summary: In this work, we study the electrical conduction mechanisms of nitrogenated amorphous carbon (a-C:H:N) films, which were deposited by a high-density plasma chemical vapor deposition (HDP-CVD) technique. The plasma was inductively coupled by an external planar coil. Mixtures of methane and nitrogen at different concentrations were used in the depositions. The working pressure process was 15 mTorr and the RF power was 250 W. An analysis focused on the influence of the precursor gases and plasma parameters on the conduction mechanisms of the a-C:H:N films is reported. Current-voltage (I-V) curves were used to study the conduction mechanisms of the a-C:H:N films. As a result of these studies we observed that the main electrical conduction mechanism found in the I-V characteristics of our a-C:H:N films was the Poole-Frenkel emission. I-V curves were also obtained in the range of 0–100 V and they were used to determine the electrical resistivity of the films.