Effects of Fusion Temperature and Metal Ion Variation on Crystallization of Lightly Ionized Poly(butylene succinate)
Kazuki Ishida
Department of Biomolecular Engineering, Tokyo Institute of Technology, 4259-B55 Nagatsuta-cho, Midori-ku, Yokohama 226-8501, Japan
Search for more papers by this authorSang-Il Han
Department of Fiber and Polymer Engineering, Hanyang University, 17 Haengdang-dong, Seongdong-gu, Seoul 133-791, Korea
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Seung-Soon Im
Department of Fiber and Polymer Engineering, Hanyang University, 17 Haengdang-dong, Seongdong-gu, Seoul 133-791, Korea
Seung-Soon Im, Department of Fiber and Polymer Engineering, Hanyang University, 17 Haengdang-dong, Seongdong-gu, Seoul 133-791, Korea. Fax: (+82) 2 2297 5859
Yoshio Inoue, Department of Biomolecular Engineering, Tokyo Institute of Technology, 4259-B55 Nagatsuta-cho, Midori-ku, Yokohama 226-8501, Japan. Fax: (+81) 45 924 5827
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Yoshio Inoue
Department of Biomolecular Engineering, Tokyo Institute of Technology, 4259-B55 Nagatsuta-cho, Midori-ku, Yokohama 226-8501, Japan
Seung-Soon Im, Department of Fiber and Polymer Engineering, Hanyang University, 17 Haengdang-dong, Seongdong-gu, Seoul 133-791, Korea. Fax: (+82) 2 2297 5859
Yoshio Inoue, Department of Biomolecular Engineering, Tokyo Institute of Technology, 4259-B55 Nagatsuta-cho, Midori-ku, Yokohama 226-8501, Japan. Fax: (+81) 45 924 5827
Search for more papers by this authorKazuki Ishida
Department of Biomolecular Engineering, Tokyo Institute of Technology, 4259-B55 Nagatsuta-cho, Midori-ku, Yokohama 226-8501, Japan
Search for more papers by this authorSang-Il Han
Department of Fiber and Polymer Engineering, Hanyang University, 17 Haengdang-dong, Seongdong-gu, Seoul 133-791, Korea
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Seung-Soon Im
Department of Fiber and Polymer Engineering, Hanyang University, 17 Haengdang-dong, Seongdong-gu, Seoul 133-791, Korea
Seung-Soon Im, Department of Fiber and Polymer Engineering, Hanyang University, 17 Haengdang-dong, Seongdong-gu, Seoul 133-791, Korea. Fax: (+82) 2 2297 5859
Yoshio Inoue, Department of Biomolecular Engineering, Tokyo Institute of Technology, 4259-B55 Nagatsuta-cho, Midori-ku, Yokohama 226-8501, Japan. Fax: (+81) 45 924 5827
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Yoshio Inoue
Department of Biomolecular Engineering, Tokyo Institute of Technology, 4259-B55 Nagatsuta-cho, Midori-ku, Yokohama 226-8501, Japan
Seung-Soon Im, Department of Fiber and Polymer Engineering, Hanyang University, 17 Haengdang-dong, Seongdong-gu, Seoul 133-791, Korea. Fax: (+82) 2 2297 5859
Yoshio Inoue, Department of Biomolecular Engineering, Tokyo Institute of Technology, 4259-B55 Nagatsuta-cho, Midori-ku, Yokohama 226-8501, Japan. Fax: (+81) 45 924 5827
Search for more papers by this authorAbstract
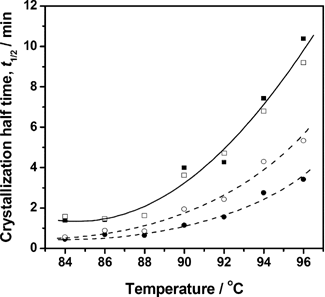
Crystallization behavior was investigated for poly(butylene succinate)-based ionomers (PBSIs) with very small amounts of metal sulfosuccinate units. The PBSI samples, precipitated by adding their chloroform solutions into an excess volume of hexane, showed not only higher overall crystallization rates than the parent PBS but also strong fusion temperature dependences of the crystallization kinetics. In the early stage of film-hydrolysis experiments, the center region of PBSI spherulites was found to be easily eroded. A putative internal structure of PBSI spherulites, that is, relatively ion-rich centers and ion-poor outskirts, was proposed. PBSIs with K ions were found to show higher crystallization temperatures than those with Na ions in the non-isothermal crystallization from the melts. These results indicate that the crystallization behavior of PBSIs is dominated by the ionic aggregates which induce the crystal nucleation around themselves.
References
- 1 M. R. Tant, K. A. Mauritz, G. L. Wilkes, “ Ionomers; Synthesis, Structure, Properties and Applications”, Blackie, London 1982.
- 2 A. Eisenberg, J. S. Kim, “ Introduction to Ionomers”, John Wiley & Sons, New York 1989.
- 3 R. Longworth, D. J. Vaughan, Nature 1968, 218, 85.
- 4 A. Eisenberg, Macromolecules 1970, 3, 147.
- 5 T. D. Gierke, G. E. Munn, F. C. Wilson, J. Polym. Sci., Polym. Phys. 1981, 19, 1687.
- 6 M. Fujimura, T. Hashimoto, H. Kawai, Macromolecules 1981, 14, 1309.
- 7 D. J. Yarusso, S. L. Cooper, Macromolecules 1983, 16, 1871.
- 8 D. J. Yarusso, S. L. Cooper, Polymer 1985, 26, 371.
- 9 K. A. Mauritz, J. Macromol. Sci., Rev. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 1988, C28(1), 65.
- 10 A. Eisenberg, B. Hird, R. B. Moore, Macromolecules 1990, 23, 4099.
- 11 D. J. Quiram, R. A. Register, A. J. Ryan, Macromolecules 1998, 31, 1432.
- 12 E. B. Orler, D. J. Yontz, R. B. Moore, Macromolecules 1993, 26, 5157.
- 13 Y.-T. Yoo, B.-J. Lee, S.-I. Han, S.-S. Im, D.-K. Kim, Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2003, 79, 257.
- 14 E. B. Orler, B. H. Calhoun, R. B. Moore, Macromolecules 1996, 29, 5965.
- 15 B. Hird, A. Eisenberg, Macromolecules 1992, 25, 6466.
- 16 P. K. Agarwal, H. S. Makowaki, R. D. Lundberg, Macromolecules 1980, 13, 1679.
- 17 S.-I. Han, S.-S. Im, D.-K. Kim, Polymer 2003, 44, 7165.
- 18 S.-I. Han, W.-D. Lee, D.-K. Kim, S.-S. Im, Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2004, 25, 753.
- 19 S.-I. Han, Y.-T. Yoo, D.-K. Kim, S.-S. Im, Macromol. Biosci. 2004, 4, 199.
- 20 S.-I. Han, S.-W. Kang, B.-S. Kim, S.-S. Im, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2005, 15, 367.
- 21 K. Ishida, S.-I. Han, Y. Inoue, S.-S. Im, Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2005, 206, 1028.
- 22 M. Vert, Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 538.
- 23 A. N. Gent, J. Polym. Sci. 1955, 18, 321.
- 24 L. Mandelkern, “ Crystallization in Polymers”, McGraw-Hill, New York 1964.
- 25 T. Miyata, T. Masuko, Polymer 1998, 39, 1399.
- 26 Z. Gan, H. Abe, H. Kurokawa, Y. Doi, Biomacromolecules 2001, 2, 605.
- 27 M. Wunderlich, “ Macromolecular Physics: Crystal Nucleation, Growth, Annealing”, Academic Press 1973, Vol. 2, Chapter VI, pp. 115–347.
- 28 T. Dong, K.-M. Shin, B. Zhu, Y. Inoue, Macromolecules 2006, 39, 2427.
- 29 M. Avrami, J. Chem. Phys. 1939, 7, 1103.
- 30 M. Avrami, J. Chem. Phys. 1940, 8, 212.
- 31 M. Avrami, J. Chem. Phys. 1941, 9, 177.
- 32 M. Mochizuki, M. Hirami, Polym. Adv. Technol. 1997, 8, 203.
- 33 E. A. Moelwyn-Hughes, “ Physical Chemistry”, 2nd edition, Pergamon Press, New York 1961.
- 34
L. Pauling,
Proc. R. Soc. London
1927,
A114,
181.
10.1098/rspa.1927.0035 Google Scholar