Study on the Gelation of a No-Flow Underfill Through Monte Carlo Simulation
Abstract
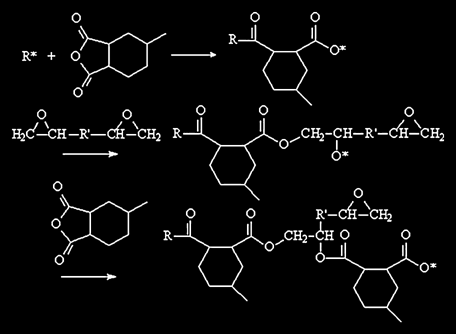
Summary: The gelation behavior of an epoxy/anhydride system was studied using the differential scanning calorimeter (DSC) and a stress rheometer. It was found that the gelation was dependent on the curing temperature. At a higher curing temperature, the resin tended to gel at lower degree of cure (DOC). Monte Carlo (MC) simulation was performed, to investigate the effect of curing kinetics on the network formation and the gelation. Both the effects of the propagation rate and the catalyst concentration was studied. The temperature dependent gelation was related to the change of propagation/initiation ratio with temperature according to the simulation results.