Structurally Distinct Hybrid Polymer/Lipid Nanoconstructs Harboring a Type-I Ribotoxin as Cellular Imaging and Glioblastoma-Directed Therapeutic Vectors
M. Sheikh Mohamed
Bio Nano Electronics Research Center, Graduate School of Interdisciplinary New Science Toyo University, Kawagoe, Saitama, 350-8585 Japan
Search for more papers by this authorSrivani Veeranarayanan
Bio Nano Electronics Research Center, Graduate School of Interdisciplinary New Science Toyo University, Kawagoe, Saitama, 350-8585 Japan
Search for more papers by this authorAnkur Baliyan
Bio Nano Electronics Research Center, Graduate School of Interdisciplinary New Science Toyo University, Kawagoe, Saitama, 350-8585 Japan
Search for more papers by this authorAby Cheruvathoor Poulose
Bio Nano Electronics Research Center, Graduate School of Interdisciplinary New Science Toyo University, Kawagoe, Saitama, 350-8585 Japan
Search for more papers by this authorYutaka Nagaoka
Bio Nano Electronics Research Center, Graduate School of Interdisciplinary New Science Toyo University, Kawagoe, Saitama, 350-8585 Japan
Search for more papers by this authorHiroaki Minegishi
Bio Nano Electronics Research Center, Graduate School of Interdisciplinary New Science Toyo University, Kawagoe, Saitama, 350-8585 Japan
Search for more papers by this authorSeiki Iwai
Bio Nano Electronics Research Center, Graduate School of Interdisciplinary New Science Toyo University, Kawagoe, Saitama, 350-8585 Japan
Search for more papers by this authorYasuhiro Shimane
Bio Nano Electronics Research Center, Graduate School of Interdisciplinary New Science Toyo University, Kawagoe, Saitama, 350-8585 Japan
Search for more papers by this authorYasuhiko Yoshida
Bio Nano Electronics Research Center, Graduate School of Interdisciplinary New Science Toyo University, Kawagoe, Saitama, 350-8585 Japan
Search for more papers by this authorToru Maekawa
Bio Nano Electronics Research Center, Graduate School of Interdisciplinary New Science Toyo University, Kawagoe, Saitama, 350-8585 Japan
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
D. Sakthi Kumar
Bio Nano Electronics Research Center, Graduate School of Interdisciplinary New Science Toyo University, Kawagoe, Saitama, 350-8585 Japan
Search for more papers by this authorM. Sheikh Mohamed
Bio Nano Electronics Research Center, Graduate School of Interdisciplinary New Science Toyo University, Kawagoe, Saitama, 350-8585 Japan
Search for more papers by this authorSrivani Veeranarayanan
Bio Nano Electronics Research Center, Graduate School of Interdisciplinary New Science Toyo University, Kawagoe, Saitama, 350-8585 Japan
Search for more papers by this authorAnkur Baliyan
Bio Nano Electronics Research Center, Graduate School of Interdisciplinary New Science Toyo University, Kawagoe, Saitama, 350-8585 Japan
Search for more papers by this authorAby Cheruvathoor Poulose
Bio Nano Electronics Research Center, Graduate School of Interdisciplinary New Science Toyo University, Kawagoe, Saitama, 350-8585 Japan
Search for more papers by this authorYutaka Nagaoka
Bio Nano Electronics Research Center, Graduate School of Interdisciplinary New Science Toyo University, Kawagoe, Saitama, 350-8585 Japan
Search for more papers by this authorHiroaki Minegishi
Bio Nano Electronics Research Center, Graduate School of Interdisciplinary New Science Toyo University, Kawagoe, Saitama, 350-8585 Japan
Search for more papers by this authorSeiki Iwai
Bio Nano Electronics Research Center, Graduate School of Interdisciplinary New Science Toyo University, Kawagoe, Saitama, 350-8585 Japan
Search for more papers by this authorYasuhiro Shimane
Bio Nano Electronics Research Center, Graduate School of Interdisciplinary New Science Toyo University, Kawagoe, Saitama, 350-8585 Japan
Search for more papers by this authorYasuhiko Yoshida
Bio Nano Electronics Research Center, Graduate School of Interdisciplinary New Science Toyo University, Kawagoe, Saitama, 350-8585 Japan
Search for more papers by this authorToru Maekawa
Bio Nano Electronics Research Center, Graduate School of Interdisciplinary New Science Toyo University, Kawagoe, Saitama, 350-8585 Japan
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
D. Sakthi Kumar
Bio Nano Electronics Research Center, Graduate School of Interdisciplinary New Science Toyo University, Kawagoe, Saitama, 350-8585 Japan
Search for more papers by this authorAbstract
A nanoformulation composed of a ribosome inactivating protein-curcin and a hybrid solid lipid nanovector has been devised against glioblastoma. The structurally distinct nanoparticles were highly compatible to human endothelial and neuronal cells. A sturdy drug release from the particles, recorded upto 72 h, was reflected in the time-dependent toxicity. Folate-targeted nanoparticles were specifically internalized by glioma, imparting superior toxicity and curbed an aggressively proliferating in vitro 3D cancer mass in addition to suppressing the anti-apoptotic survivin and cell matrix protein vinculin. Combined with the imaging potential of the encapsulated dye, the nanovector emanates as a multifunctional anti-cancer system.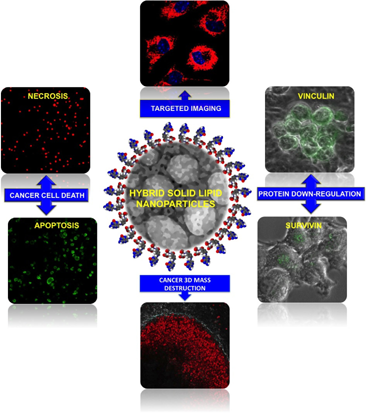
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| mabi201400248-sm-0001-SuppFig-S1.docx276.4 KB |
Figure S1. Quantitative analysis of VNT-HSLNs uptake by cells pre-treated with specific endocytosis inhibitors. Though all the cells, showed significant levels of particle uptake, it was noteworthy that cytochalasin D, which inhibits the macropinocytosis and cavelolae mediated endocytosis, seemed to be somewhat restrictive to the HSLNs. Overall it seems that the particle exploit multiple pathways to access the cellular compartments. Figure S2. Quantification of cells exhibiting apoptosis/necrosis or both signals, post treatment with CT-HSLNs and stained with annexin/PPI. It is evident that the CT-HSLNs preferentially induced apoptosis and necrosis in the cancer cell line with a considerable percentage of cells exhibiting both symptoms. The normal cells on the other hand were immune to the toxic effects of encapsulated curcin as the particles did not gain entry into them. Figure S3. Corrected total cell florescence of survivin expression on exposure to CT-HSLNs. As evident from the plot, the level of survivin expression in glioma was highly diminished on treatment with CT-HSLNs, when compared to the normal cells. The significant loss of survivin expression in gliomas made them extremely vulnerable to chemotherapeutic agents as curcin. Figure S4. Corrected total cell florescence of vinculin expression on exposure to CT-HSLNs. As evident from the plot, the level of vinculin expression in glioma was greatly diminished on treatment with CT-HSLNs, when compared to the normal cells signifying the loss of cell-cell and cell-matrix adherent ability of the cancer cell line. |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1 T. N. Seyfried, P. Mukherjee, Nutr. Metab. 2005, 2, 30.
- 2 J. T. Huse, E. C. Holland, Nat. Rev. Cancer 2010, 10, 319.
- 3 C. L. Gladson, R. A. Prayson, W. M. Liu, Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2010, 5, 33.
- 4 M. J. Binning, J. K. Liu, J. R. Kestle, D. L. Brockmeyer, M. L. Walker, Neurosurg. Focus 2007, 23, E2.
- 5 M. Jansen, S. Yip, D. N. Louis, Lancet Neurol. 2010, 9, 717.
- 6 D. Karkan, C. Pfeifer, T. Z. Vitalis, G. Arthur, M. Ujiie, Q. Chen, S. Tsai, G. Koliatis, R. Gabathuler, W. A. Jefferies, PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2469.
- 7 D. J. Begley, Pharmacol. Ther. 2004, 104, 29.
- 8 S. P. Mathupala, Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2009, 19, 137.
- 9 M. Smola, T. Vandamme, A. Sokolowski, Int. J. Nanomed. 2008, 3, 1.
- 10 D. Peer, J. M. Karp, S. Hong, O. C. Farokhzad, R. Margalit, R. Langer, Nat. Nanotechnol. 2007, 2, 751.
- 11 K. Hadinoto, A. Sundaresan, W. S. Cheow, Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2013, 85, 427.
- 12 L. Zhang, J. M. Chan, F. X. Gu, J. W. Rhee, A. Z. Wang, A. F. Radovic-Moreno, F. Alexis, R. Langer, O. C. Farokhzad, ACS Nano 2008, 2, 1696.
- 13 R. H. Fang, S. Aryal, C.-M. J. Hu, L. Zhang, Langmuir 2010, 26, 16958.
- 14 Z. Mühlen, C. Schwarz, W. Mehnert, Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 1998, 45, 149.
- 15 E. H. Gocke, E. Korkmaz, E. Dellera, G. Sandri, M. C. Bonferoni, O. Ozer, Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 1841.
- 16 A. Bunge, M. Loew, P. Pescador, A. Arbuzova, N. Brodersen, J. Kang, L. Dahne, J. Liebscher, A. Herrmann, G. Stengel, D. Huster, J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 16425.
- 17 J. Du, W.-L. Lu, X. Ying, Y. Liu, P. Du, W. Tian, Y. Men, J. Guo, Y. Zhang, R.-J. Li, J. Zhou, J.-N. Lou, J.-C. Wang, X. Zhang, Q. Zhang, Mol. Pharm. 2009, 6, 905.
- 18 Z. Pang, H. Gao, Y. Yu, L. Guo, J. Chen, S. Pan, J. Ren, Z. Wen, X. Jiang, Bioconjug. Chem. 2011, 22, 1171.
- 19 L. Juan, Y. Fang, T. Lin, C. Fang, Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2003, 24, 241.
- 20 J. Lin, X. Zhou, J. Wang, P. Jiang, K. Tang, Prep. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2010, 40, 107.
- 21 M. S. Mohamed, S. Veeranarayanan, H. Minegishi, Y. Sakamoto, Y. Shimane, Y. Nagaoka, A. Aki, A. C. Poulose, A. Echigo, Y. Yoshida, T. Maekawa, D. S. Kumar, Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5747.
- 22 M. H. Kang, M. J. Park, H. J. Yoo, K. Y. Hyuk, S. G. Lee, S. R. Kim, D. W. Yeorn, M. J. Kang, Y. W. Choi, Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2014, 87, 489.
- 23 Z. Peng, C. Wang, E. Fang, X. Lu, G. Wang, Q. Tong, PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e92924.
- 24 Z. Urban-Morlan, A. Ganem-Rondero, L. M. Melgoza-Contreras, J. J. Escobar-Chavez, M. G. Nava-Aezaluz, D. Quintanar-Guerrero, Int. J. Nanomed. 2010, 5, 611.
- 25 A. Aravind, P. Jeyamohan, R. Nair, S. Veeranarayanan, Y. Nagaoka, Y. Yoshida, T. Maekawa, D. S. Kumar, Biotechnol. Bioengg. 2012, 109, 2920.
- 26 A. C. Poulose, S. Veeranarayanan, M. S. Mohamed, S. Raveendran, Y. Nagaoka, Y. Yoshida, T. Maekawa, D. S. Kumar, J. Fluoresc. 2012, 22, 931.
- 27 S. Veeranarayanan, A. C. Poulose, M. S. Mohamed, S. H. Varghese, Y. Nagaoka, Y. Yoshida, T. Maekawa, D. S. Kumar, Small 2012, 8, 3476.
- 28 R. Wang, R. Xiao, Z. Zeng, L. Xu, J. Wang, Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 4185.
- 29 S. P. Alom-Ruiz, N. Anilkumar, A. M. Shah, Antioxid. Redox Signal 2008, 10, 1089.
- 30 O. Harush-Frenkel, Y. Altschuler, S. Benita, Crit. Rev. Ther. Drug Carrier Syst. 2008, 25, 485.
- 31 J. W. Perry, C. E. Wobus, J. Virol. 2010, 84, 6163.
- 32 T. dos Santos, J. Varela, I. Lynch, A. Salvati, K. A. Dawson, PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24438.
- 33 I. Mager, K. Langel, T. Lehto, E. Eiriksdottir, U. Langel, Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1818, 502.
- 34 J.-Z. Tang, Z.-H. Zuo, X.-J. Kong, M. Steiner, Z. Yin, J. K. Perry, T. Zhu, D.-X. Liu, P. E. Lobie, Endocrinology 2010, 151, 43.
- 35 D. C. Aliteri, Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 46.
- 36 W. Xu, H. Baribault, E. D. Adamson, Development 1998, 125, 327.
- 37 R. M. Ezzell, W. H. Goldmann, N. Wang, N. Parasharama, D. E. Ingber, Exp. Cell Res. 1997, 231, 14.
- 38 C. Godugu, A. R. Patel, U. Desai, T. Andey, A. Sams, M. Singh, PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53708.
- 39 B. Kim, Semin. Cancer Biol. 2005, 15, 365.
- 40 C. Fischbach, H. J. Kong, S. X. Hsiong, M. B. Evangelista, W. Yuen, D. J. Mooney, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 399.
- 41 M. Yamada, E. Cukierman, Cell 2007, 130, 601.
- 42 R. K. Jain, T. Stylianopoulos, Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 7, 653.
- 43 Q. Huang, Q.-B. Zhang, J. Dong, Y.-Y. Wu, Y.-T. Shen, Y.-D. Zhao, Y.-D. Zhu, A.-D. Wang, Q. Lan, BMC Cancer 2008, 8, 304.
- 44 N. Hashemi-Sadraei, D. M. Peereboom, Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2010, 2, 273.
- 45 H. K. Dhiman, A. R. Ray, A. K. Panda, Biomaterials 2005, 26, 979.
- 46 H. Kyle, L. A. Huxham, D. M. Yeoman, A. I. Minchinton, Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 2804.
- 47 S. Mohamed, S. Veeranarayanan, A. C. Poulose, Y. Nagaoka, H. Minegishi, Y. Yoshida, T. Maekawa, D. S. Kumar, Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1840, 1657.




