Transport in quantitative structure-activity relationships VI: Relationship between transport rate constants and partition coefficients
Abstract
The transport rate constant of a drug partitioned in a two-phase system from an aqueous to an organic phase (k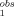 ) and vice versa (k
) and vice versa (k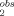 ) is a function of the partition coefficient P and of a solvent system-dependent parameter β. Drug transport is shown to be independent of molecular structure for a number of arbitrary compounds.
) is a function of the partition coefficient P and of a solvent system-dependent parameter β. Drug transport is shown to be independent of molecular structure for a number of arbitrary compounds.




