Efficient Photothermal CO Hydrogenation into C2+ Hydrocarbons on in situ Generated Fe0 in Fe5C2 Active Sites via Cu-Promoted Hydrogen Dissociation and Spillover†
Renjie Zhou
College of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Collaborative Innovation Center of Advanced Microstructure, National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures, the Frontiers Science Center for Critical Earth Material Cyclings, Nanjing University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, 210023 China
Search for more papers by this authorHaoyang Jiang
College of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Collaborative Innovation Center of Advanced Microstructure, National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures, the Frontiers Science Center for Critical Earth Material Cyclings, Nanjing University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, 210023 China
Search for more papers by this authorYongcheng Xiao
College of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Collaborative Innovation Center of Advanced Microstructure, National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures, the Frontiers Science Center for Critical Earth Material Cyclings, Nanjing University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, 210023 China
Search for more papers by this authorYueren Liu
College of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Collaborative Innovation Center of Advanced Microstructure, National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures, the Frontiers Science Center for Critical Earth Material Cyclings, Nanjing University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, 210023 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Miao Zhong
College of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Collaborative Innovation Center of Advanced Microstructure, National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures, the Frontiers Science Center for Critical Earth Material Cyclings, Nanjing University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, 210023 China
E-mail: [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorRenjie Zhou
College of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Collaborative Innovation Center of Advanced Microstructure, National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures, the Frontiers Science Center for Critical Earth Material Cyclings, Nanjing University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, 210023 China
Search for more papers by this authorHaoyang Jiang
College of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Collaborative Innovation Center of Advanced Microstructure, National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures, the Frontiers Science Center for Critical Earth Material Cyclings, Nanjing University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, 210023 China
Search for more papers by this authorYongcheng Xiao
College of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Collaborative Innovation Center of Advanced Microstructure, National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures, the Frontiers Science Center for Critical Earth Material Cyclings, Nanjing University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, 210023 China
Search for more papers by this authorYueren Liu
College of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Collaborative Innovation Center of Advanced Microstructure, National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures, the Frontiers Science Center for Critical Earth Material Cyclings, Nanjing University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, 210023 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Miao Zhong
College of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Collaborative Innovation Center of Advanced Microstructure, National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures, the Frontiers Science Center for Critical Earth Material Cyclings, Nanjing University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, 210023 China
E-mail: [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorDedicated to the Special Issue of Emerging Investigators in 2024.
Comprehensive Summary
Photothermal hydrogenation of carbon monoxide (CO) holds the potential to generate valuable C2+ chemicals using renewable solar energy. However, its activity and selectivity towards C2—C3 alkanes are limited compared to conventional thermal catalysis. In this study, we developed a robust catalyst consisting of Cu/Fe3O4 nanoparticles on Mo2CTx MXene, showing enhanced photothermal C2—C3 production. The Cu component plays a crucial role in H2 dissociation and subsequent H spillover, facilitating the in situ generation of Fe0 in Fe5C2 active sites and thus efficiently promoting photothermal CO hydrogenation. As a result, we achieved a 51.3% C2+ selectivity and 78.5% CO conversion at a high gas hourly space velocity (GHSV) of 12000 mL·gcat−1·h−1 and 2.5 MPa in a flow reactor at 320 °C. The overall C2—C3 yield reached 23.6% with Cu/Fe3O4/Mo2CTx catalysts, marking a 2.8-fold increase compared to the performance of the bare Fe3O4/Mo2CTx catalyst.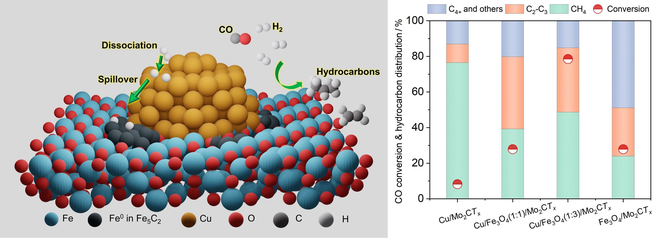
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| cjoc202400905-sup-0001-Supinfo.pdfPDF document, 1.6 MB |
Appendix S1: Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1 Chen, G.; Syzgantseva, O. A.; Syzgantseva, M. A.; Yang, S.; Yan, G.; Peng, L.; Cao, C.; Chen, W.; Wang, Z.; Qin, F.; et al. Construction of Synergistic Co and Cu Diatomic Sites for Enhanced Higher Alcohol Synthesis. CCS Chem. 2023, 5, 851–864.
- 2 Jiang, H.; Zhu, F.; Zhou, R.; Wang, L.; Xiao, Y.; Zhong, M. Promoted Photothermal Catalytic CO Hydrogenation by Using TiC-Supported Co−Fe5C2 Catalysts. Chem. Eur. J. 2023, 29, e202202891.
- 3 Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, Z.; Waterhouse, G. I. N.; Shi, R.; Wen, X.; Zhang, T. Manganese Oxide Modified Nickel Catalysts for Photothermal CO Hydrogenation to Light Olefins. Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 10, 1902860.
- 4 Guo, X.-N.; Jiao, Z.-F.; Jin, G.-Q.; Guo, X.-Y. Photocatalytic Fischer–Tropsch Synthesis on Graphene-Supported Worm-Like Ruthenium Nanostructures. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 3836–3840.
- 5 Li, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Waterhouse, G. I. N.; Chen, G.; Shi, R.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Wei, Y.; Wen, X.-D.; et al. Co-Based Catalysts Derived from Layered-Double-Hydroxide Nanosheets for the Photothermal Production of Light Olefins. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1800527.
- 6 Jiang, H.; Wang, L.; Kaneko, H.; Gu, R.; Su, G.; Li, L.; Zhang, J.; Song, H.; Zhu, F.; Yamaguchi, A.; et al. Light-driven CO2 methanation over Au-grafted Ce0.95Ru0.05O2 solid-solution catalysts with activities approaching the thermodynamic limit. Nat. Catal. 2023, 6, 519–530.
- 7 Gao, W.; Gao, R.; Zhao, Y.; Peng, M.; Song, C.; Li, M.; Li, S.; Liu, J.; Li, W.; Deng, Y.; et al. Photo-Driven Syngas Conversion to Lower Olefins over Oxygen-Decorated Fe5C2 Catalyst. Chem 2018, 4, 2917–2928.
- 8 Li, Y.; Gao, W.; Peng, M.; Zhang, J.; Sun, J.; Xu, Y.; Hong, S.; Liu, X.; Liu, X.; Wei, M.; et al. Interfacial Fe5C2-Cu catalysts toward low-pressure syngas conversion to long-chain alcohols. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 61.
- 9 Zhai, P.; Xu, C.; Gao, R.; Liu, X.; Li, M.; Li, W.; Fu, X.; Jia, C.; Xie, J.; Zhao, M.; et al. Highly Tunable Selectivity for Syngas-Derived Alkenes over Zinc and Sodium-Modulated Fe5C2 Catalyst. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 9902–9907.
- 10 Yu, X.; Xu, Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, M.; Qin, W.; Che, F.; Zhong, M. Coverage enhancement accelerates acidic CO2 electrolysis at ampere-level current with high energy and carbon efficiencies. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 1711.
- 11 Shi, Y.; Li, Z.; Hao, Q.; Li, R.; Li, Y.; Guo, L.; Ouyang, S.; Yuan, H.; Zhang, T. Hydrophobic Fe-Based Catalyst Derived from Prussian Blue for Enhanced Photothermal Conversion of Syngas to Light Olefins. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2308670.
- 12 Song, R.; Li, Z.; Guo, J.; Duchesne, P. N.; Qiu, C.; Mao. Guo, C.; Jing, D.; Ozin, G. A. Solar Hydrocarbons: Single-Step, Atmospheric-Pressure Synthesis of C2−C4 Alkanes and Alkenes from CO2. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202304470.
- 13 Xie, B.; Wong, R. J.; Tan, T. H.; Higham, M.; Gibson, E. K.; Decarolis, D.; Callison, J.; Aguey-Zinsou, K.-F.; Bowker, M.; Catlow, C. R. A.; et al. Synergistic ultraviolet and visible light photo-activation enables intensified low-temperature methanol synthesis over copper/zinc oxide/alumina. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1615.
- 14 Yang, H.; Dang, Y.; Cui, X.; Bu, X.; Li, J.; Li, S.; Sun, Y.; Gao, P. Selective synthesis of olefins via CO2 hydrogenation over transition-metal- doped iron-based catalysts. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 2023, 321, 122050.
- 15 Fang, C.; Wei, J.; Wang, R.; Ge, Q.; Xu, H. Catalytic Conversion of Syngas to Light Olefins over Cu-Fe based Catalyst. J. Mol. Catal. 2015, 29, 27–34.
- 16 Liu, J.; Zhang, A.; Jiang, X.; Liu, M.; Sun, Y.; Song, C.; Guo, X. Selective CO2 Hydrogenation to Hydrocarbons on Cu-Promoted Fe-Based Catalysts: Dependence on Cu–Fe Interaction. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 10182–10190.
- 17 Peña, D.; Jensen, L.; Cognigni, A.; Myrstad, R.; Neumayer, T.; van Beek, W.; Rønning, M. The Effect of Copper Loading on Iron Carbide Formation and Surface Species in Iron-Based Fischer–Tropsch Synthesis Catalysts. ChemCatChem 2018, 10, 1300–1312.
- 18 Li, W.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, X.; Lei, B.; Li, L.; Zhou, H.; Zhong, M. Sustainable Electrosynthesis of N,N-Dimethylformamide via Relay Catalysis on Synergistic Active Sites. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 21968–21976.
- 19 Zhao, J.; Bai, Y.; Liang, X.; Wang, T.; Wang, C. Photothermal catalytic CO2 hydrogenation over molybdenum carbides: Crystal structure and photothermocatalytic synergistic effects. J. CO2 Util. 2021, 49, 101562.
- 20 Deeva, E. B.; Kurlov, A.; Abdala, P. M.; Lebedev, D.; Kim, S. M.; Gordon, C. P.; Tsoukalou, A.; Fedorov, A.; Müller, C. R. In Situ XANES/XRD Study of the Structural Stability of Two-Dimensional Molybdenum Carbide Mo2CTx: Implications for the Catalytic Activity in the Water–Gas Shift Reaction. Chem. Mater. 2019, 31, 4505–4513.
- 21 Peng, W.; Luo, M.; Xu, X.; Jiang, K.; Peng, M.; Chen, D.; Chan, T.-S.; Tan, Y. Spontaneous Atomic Ruthenium Doping in Mo2CTX MXene Defects Enhances Electrocatalytic Activity for the Nitrogen Reduction Reaction. Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 10, 2001364.
- 22 Zhou, H.; Chen, Z.; Kountoupi, E.; Tsoukalou, A.; Abdala, P. M.; Florian, P.; Fedorov, A.; Müller, C. R. Two-dimensional molybdenum carbide 2D-Mo2C as a superior catalyst for CO2 hydrogenation. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5510.
- 23 Morales-García, Á.; Fernández-Fernández, A.; Viñes, F.; Illas, F. CO abatement using two-dimensional MXene carbides. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 3381–3385.
- 24 Zhou, H.; Chen, Z.; López, A. V.; López, E. D.; Lam, E.; Tsoukalou, A.; Willinger, E.; Kuznetsov, D. A.; Mance, D.; Kierzkowska, A.; et al. Engineering the Cu/Mo2CTx (MXene) interface to drive CO2 hydrogenation to methanol. Nat. Catal. 2021, 4, 860–871.
- 25 Yamashita, T.; Hayes, P. Analysis of XPS spectra of Fe2+ and Fe3+ ions in oxide materials. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2008, 254, 2441–2449.
- 26 Yue, Y.; Liu, B.; Qin, P.; Lv, N.; Wang, T.; Bi, X.; Zhu, H.; Yuan, P.; Bai, Z.; Cui, Q.; et al. One-pot synthesis of FeCu-SSZ-13 zeolite with superior performance in selective catalytic reduction of NO by NH3 from natural aluminosilicates. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 398, 125515.
- 27 Xu, D.; Li, Z.; Li, L.; Wang, J. Insights into the Photothermal Conversion of 2D MXene Nanomaterials: Synthesis, Mechanism, and Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2000712.
- 28 Pastor-Pérez, L.; Baibars, F.; Le Sache, E.; Arellano-García, H.; Gu, S.; Reina, T. R. CO2 valorisation via Reverse Water-Gas Shift reaction using advanced Cs doped Fe-Cu/Al2O3 catalysts. J. CO2 Util. 2017, 21, 423–428.
- 29 Krishnamoorthy, S.; Li, A.; Iglesia, E. Pathways for CO2 Formation and Conversion During Fischer–Tropsch Synthesis on Iron-Based Catalysts. Catal. Lett. 2002, 80, 77–86.
- 30 Liu, B.; Li, W.; Zheng, J.; Lin, Q.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, F.; Xu, Y.; Liu, X. CO2 formation mechanism in Fischer–Tropsch synthesis over iron-based catalysts: a combined experimental and theoretical study. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2018, 8, 5288–5301.
- 31 Wang, P.; Chen, W.; Chiang, F.-K.; Dugulan, A. I.; Song, Y.; Pestman, R.; Zhang, K.; Yao, J.; Feng, B.; Miao, P.; et al. Synthesis of stable and low-CO2 selective iron-carbide Fischer-Tropsch catalysts. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaau2947.
- 32 Liu, L.; Puga, A. V.; Cored, J.; Concepción, P.; Pérez-Dieste, V.; García, H.; Corma, A. Sunlight-assisted hydrogenation of CO2 into ethanol and C2+ hydrocarbons by sodium-promoted Co@C nanocomposites. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 2018, 235, 186–196.
- 33 Zhang, H.; Dong, A.; Liu, B.; Chen, J.; Xu, Y.; Liu, X. Hydrogen spillover effects in the Fischer–Tropsch reaction over carbon nanotube supported cobalt catalysts. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2023, 13, 1888–1904.
- 34 Li, L.; Liu, Z.; Yu, X.; Zhong, M. Achieving High Single-Pass Carbon Conversion Efficiencies in Durable CO2 Electroreduction in Strong Acids via Electrode Structure Engineering. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202300226.
- 35 Li, Z.; Wu, W.; Wang, M.; Wang, Y.; Ma, X.; Luo, L.; Chen, Y.; Fan, K.; Pan, Y.; Li, H.; et al. Ambient-pressure hydrogenation of CO2 into long-chain olefins. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2396.
- 36 Xiao, K.; Bao, Z.; Qi, X.; Wang, X.; Zhong, L.; Fang, K.; Lin, M.; Sun, Y. Structural evolution of CuFe bimetallic nanoparticles for higher alcohol synthesis. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2013, 378, 319–325.
- 37 Li, S.; Meitzner, G. D.; Iglesia, E. Structure and Site Evolution of Iron Oxide Catalyst Precursors during the Fischer−Tropsch Synthesis. J. Phys. Chem. B 2001, 105, 5743–5750.
- 38 Puga, A. V. On the nature of active phases and sites in CO and CO2 hydrogenation catalysts. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2018, 8, 5681–5707.
- 39 Li, R.; Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Wei, W.; Hao, Q.; Shi, Y.; Ouyang, S.; Yuan, H.; Zhang, T. Electronically Activated Fe5C2 via N-Doped Carbon to Enhance Photothermal Syngas Conversion to Light Olefins. ACS Catal. 2022, 12, 5316–5326.




