Storage Failure Mechanisms and Modifications of Ni-Rich Cathode Materials: From Polycrystalline to Single-Crystal Forms†
Ran An
Beijing Key Laboratory of Environmental Science and Engineering, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, 100081 China
College of Materials Science and Technology, Beijing University of Technology, Beijing, 100124 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Yuefeng Su
Beijing Key Laboratory of Environmental Science and Engineering, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, 100081 China
Chongqing Innovation Center, Beijing Institute of Technology, Chongqing, 401120 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorChenxing Yang
Beijing Key Laboratory of Environmental Science and Engineering, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, 100081 China
Chongqing Innovation Center, Beijing Institute of Technology, Chongqing, 401120 China
Search for more papers by this authorXinyu Zhu
Beijing Key Laboratory of Environmental Science and Engineering, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, 100081 China
Chongqing Innovation Center, Beijing Institute of Technology, Chongqing, 401120 China
Search for more papers by this authorYihong Wang
Beijing Key Laboratory of Environmental Science and Engineering, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, 100081 China
Chongqing Innovation Center, Beijing Institute of Technology, Chongqing, 401120 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Yongjian Li
Beijing Key Laboratory of Environmental Science and Engineering, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, 100081 China
Chongqing Innovation Center, Beijing Institute of Technology, Chongqing, 401120 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorLai Chen
Beijing Key Laboratory of Environmental Science and Engineering, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, 100081 China
Chongqing Innovation Center, Beijing Institute of Technology, Chongqing, 401120 China
Search for more papers by this authorYun Lu
Beijing Key Laboratory of Environmental Science and Engineering, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, 100081 China
Chongqing Innovation Center, Beijing Institute of Technology, Chongqing, 401120 China
Search for more papers by this authorQing Huang
Beijing Key Laboratory of Environmental Science and Engineering, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, 100081 China
Chongqing Innovation Center, Beijing Institute of Technology, Chongqing, 401120 China
Search for more papers by this authorMeng Wang
Chongqing Innovation Center, Beijing Institute of Technology, Chongqing, 401120 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Ning Li
Beijing Key Laboratory of Environmental Science and Engineering, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, 100081 China
Chongqing Innovation Center, Beijing Institute of Technology, Chongqing, 401120 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorFeng Wu
Beijing Key Laboratory of Environmental Science and Engineering, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, 100081 China
Chongqing Innovation Center, Beijing Institute of Technology, Chongqing, 401120 China
Search for more papers by this authorRan An
Beijing Key Laboratory of Environmental Science and Engineering, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, 100081 China
College of Materials Science and Technology, Beijing University of Technology, Beijing, 100124 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Yuefeng Su
Beijing Key Laboratory of Environmental Science and Engineering, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, 100081 China
Chongqing Innovation Center, Beijing Institute of Technology, Chongqing, 401120 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorChenxing Yang
Beijing Key Laboratory of Environmental Science and Engineering, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, 100081 China
Chongqing Innovation Center, Beijing Institute of Technology, Chongqing, 401120 China
Search for more papers by this authorXinyu Zhu
Beijing Key Laboratory of Environmental Science and Engineering, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, 100081 China
Chongqing Innovation Center, Beijing Institute of Technology, Chongqing, 401120 China
Search for more papers by this authorYihong Wang
Beijing Key Laboratory of Environmental Science and Engineering, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, 100081 China
Chongqing Innovation Center, Beijing Institute of Technology, Chongqing, 401120 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Yongjian Li
Beijing Key Laboratory of Environmental Science and Engineering, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, 100081 China
Chongqing Innovation Center, Beijing Institute of Technology, Chongqing, 401120 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorLai Chen
Beijing Key Laboratory of Environmental Science and Engineering, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, 100081 China
Chongqing Innovation Center, Beijing Institute of Technology, Chongqing, 401120 China
Search for more papers by this authorYun Lu
Beijing Key Laboratory of Environmental Science and Engineering, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, 100081 China
Chongqing Innovation Center, Beijing Institute of Technology, Chongqing, 401120 China
Search for more papers by this authorQing Huang
Beijing Key Laboratory of Environmental Science and Engineering, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, 100081 China
Chongqing Innovation Center, Beijing Institute of Technology, Chongqing, 401120 China
Search for more papers by this authorMeng Wang
Chongqing Innovation Center, Beijing Institute of Technology, Chongqing, 401120 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Ning Li
Beijing Key Laboratory of Environmental Science and Engineering, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, 100081 China
Chongqing Innovation Center, Beijing Institute of Technology, Chongqing, 401120 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorFeng Wu
Beijing Key Laboratory of Environmental Science and Engineering, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing, 100081 China
Chongqing Innovation Center, Beijing Institute of Technology, Chongqing, 401120 China
Search for more papers by this author† Dedicated to the Special Issue of Batteries.
Comprehensive Summary
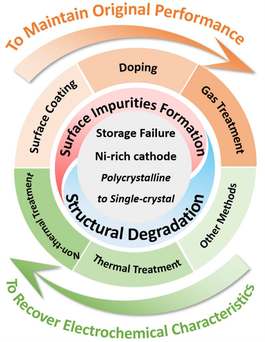
Ni-rich cathode materials, exemplified by LiNi1–x–yCoxMnyO2 (NCM), have significantly propelled Li-ion battery (LIB) technology forward owing to their high energy density. However, the long-term storage stability of these materials remains a critical challenge that must be addressed. This review provides a comprehensive analysis of the storage failure mechanisms in both polycrystalline (PC-NCM) and single crystal (SC-NCM) forms, a topic that has been seldom reviewed. It delves into the microstructural changes and performance degradation that occur during storage, emphasizing the effects of environmental factors on NCM materials, including the formation of surface impurities and structural deterioration. Additionally, the review discusses various enhancement strategies, such as surface coatings, doping, and gas treatments, which are designed to improve storage stability. Furthermore, the review projects insights from current polycrystalline studies to suggest future research directions aimed at enhancing the air stability of SC-NCM, which is vital for improving the safety and durability of LIBs.
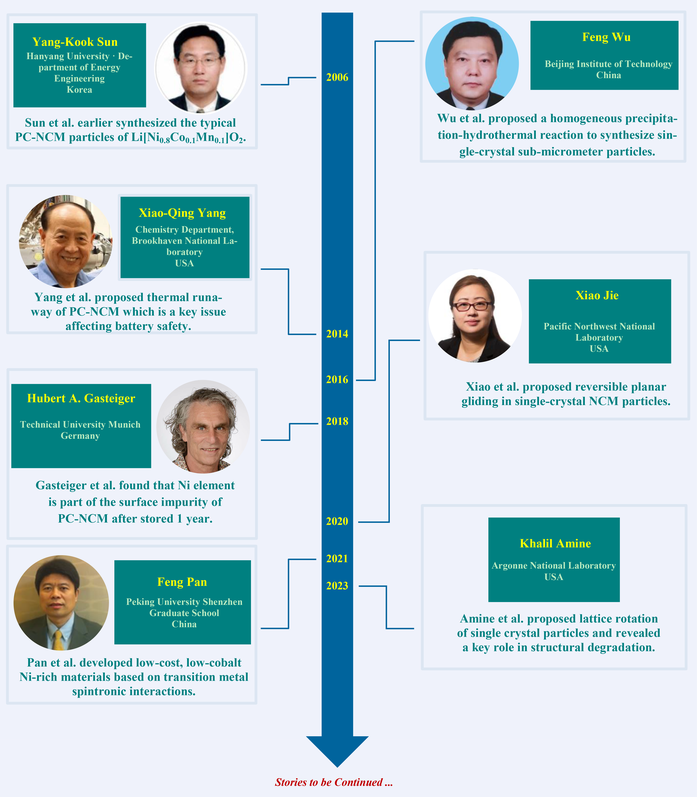
Key Scientists
References
- 1 Qiu, L.; Zhang, M.; Song, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Wu, Z.; Xiang, W.; Liu, Y.; Wang, G.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, B.; Guo, X. Recent Advance in Structure Regulation of High-Capacity Ni-rich Layered Oxide Cathodes. EcoMat 2021, 3, e12141.
- 2 Yang, J.; Liang, X.; Ryu, H.-H.; Yoon, C. S.; Sun, Y.-K. Ni-rich Layered Cathodes for Lithium-ion Batteries: From Challenges to the Future. Energy Storage Mater. 2023, 63, 102969.
- 3 Hu, J.; Wang, H.; Xiao, B.; Liu, P.; Huang, T.; Li, Y.; Ren, X.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, J.; Ouyang, X. J. N. S. R. Challenges and Approaches of Single-Crystal Ni-rich Layered Cathodes in Lithium Batteries. Mater. Sci. 2023, 10, nwad252.
- 4 Langdon, J.; Manthiram, A. A Perspective on Single-crystal Layered Oxide Cathodes for Lithium-ion Batteries. Energy Storage Mater. 2021, 37, 143–160.
- 5 Faenza, N. V.; Bruce, L.; Lebens-Higgins, Z. W.; Plitz, I.; Pereira, N.; Piper, L. F. J.; Amatucci, G. G. Growth of Ambient Induced Surface Impurity Species on Layered Positive Electrode Materials and Impact on Electrochemical Performance. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2017, 164, A3727–A3741.
- 6 Jung, R.; Morasch, R.; Karayaylali, P.; Phillips, K.; Maglia, F.; Stinner, C.; Shao-Horn, Y.; Gasteiger, H. A. Effect of Ambient Storage on the Degradation of Ni-rich Positive Electrode Materials (NMC811) for Li-Ion Batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2018, 165, A132–A141.
- 7 Sicklinger, J.; Metzger, M.; Beyer, H.; Pritzl, D.; Gasteiger, H. A. Ambient Storage Derived Surface Contamination of Ncm811 and Ncm111: Performance Implications and Mitigation Strategies. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2019, 166, A2322–A2335.
- 8 Zhang, H.; He, X.; Chen, Z.; Yang, Y.; Xu, H.; Wang, L.; He, X. Single-Crystalline Ni-Rich LiNixMnyCo1−X−YO2 Cathode Materials: A Perspective. Adv. Energy Mater. 2022, 12, 2202022.
- 9 Liao, P. Y.; Duh, J. G.; Sheen, S. R. Microstructure and Electrochemical Performance of Lini0. 6co0. 4-Xmnxo2 Cathode Materials. J. Power Sources 2005, 143, 212–218.
- 10 Kim, M.-H.; Shin, H.-S.; Shin, D.; Sun, Y.-K. Synthesis and Electrochemical Properties of Li [Ni0.8Co0.1Mn0.1]O2 and Li [Ni0.8Co0.2]O2 via Co-Precipitation. J. Power Sources 2006, 159, 1328–1333.
- 11 Bak, S.-M.; Hu, E.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, X.; Senanayake, S. D.; Cho, S.-J.; Kim, K.-B.; Chung, K. Y.; Yang, X.-Q.; Nam, K.-W. Structural Changes and Thermal Stability of Charged LiNixMnyCozO2 Cathode Materials Studied by Combined in situ Time-Resolved Xrd and Mass Spectroscopy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 22594–22601.
- 12 Kim, H.; Kim, M. G.; Jeong, H. Y.; Nam, H.; Cho, J. A New Coating Method for Alleviating Surface Degradation of LiNi0.6Co0.2Mn0.2O2 Cathode Material: Nanoscale Surface Treatment of Primary Particles. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 2111–2119.
- 13 Lv, C.; Li, Z.; Ren, X.; Li, K.; Ma, J.; Duan, X. Revealing the Degradation Mechanism of Ni-rich Cathode Materials after Ambient Storage and Related Regeneration Method. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 3995–4006.
- 14 Su, M.; Chen, Y.; Liu, H.; Li, J.; Fu, K.; Zhou, Y.; Dou, A.; Liu, Y. Storage Degradation Mechanism of Layered Ni-rich Oxide Cathode Material LiNi0.8Co0.1Mn0.1O2. Electrochim. Acta 2022, 422, 140559.
- 15 Wang, L.; Wu, B.; Mu, D.; Liu, X.; Peng, Y.; Xu, H.; Liu, Q.; Gai, L.; Wu, F. Single-crystal LiNi0.6Co0.2Mn0.2O2 as High Performance Cathode Materials for Li-Ion Batteries. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 674, 360–367.
- 16 Liu, G.; Li, M.; Wu, N.; Cui, L.; Huang, X.; Liu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, H.; Yuan, W.; Bai, Y. Single-crystalline Particles: An Effective Way to Ameliorate the Intragranular Cracking, Thermal Stability, and Capacity Fading of the LiNi0.6Co0.2Mn0.2O2 Electrodes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2018, 165, A3040–A3047.
- 17 Bi, Y.; Tao, J.; Wu, Y.; Li, L.; Xu, Y.; Hu, E.; Wu, B.; Hu, J.; Wang, C.; Zhang, J.-G. Reversible Planar Gliding and Microcracking in a Single- crystalline Ni-rich Cathode. Science 2020, 370, 1313–1317.
- 18 Fan, X.; Ou, X.; Zhao, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, J.; Zou, L.; Seidl, L.; Li, Y.; Hu, G.; Battaglia, C.; Yang, Y. In Situ Inorganic Conductive Network Formation in High-Voltage Single-crystal Ni-rich Cathodes. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5320.
- 19 Shi, H.; Zhang, H.; Wen, Z.; Song, Y.; Su, M.; Dou, A.; Zhou, Y.; Hou, X.; Naveed, A.; Zhang, P. Storage Performance and Structure Degradation Mechanism of Single-crystal Ni-rich Material. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2023, 7, 353–362.
- 20 Manthiram, A.; Song, B.; Li, W. A Perspective on Nickel-Rich Layered Oxide Cathodes for Lithium-ion Batteries. Energy Storage Mater. 2017, 6, 125–139.
- 21 Dahn, J.; Von Sacken, U.; Juzkow, M.; AlJanaby, H. Rechargeable LiNiO2/Carbon Cells. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1991, 138, 2207–2211.
- 22 Kim, D.; Lim, J.-M.; Lim, Y.-G.; Yu, J.-S.; Park, M.-S.; Cho, M.; Cho, K. Design of Nickel-Rich Layered Oxides Using D Electronic Donor for Redox Reactions. Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 6450–6456.
- 23 Mao, Y.; Wang, X.; Xia, S.; Zhang, K.; Wei, C.; Bak, S.; Shadike, Z.; Liu, X.; Yang, Y.; Xu, R. High-Voltage Charging-Induced Strain, Heterogeneity, and Micro-Cracks in Secondary Particles of a Nickel-Rich Layered Cathode Material. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1900247.
- 24 Besli, M. n. M.; Xia, S.; Kuppan, S.; Huang, Y.; Metzger, M.; Shukla, A. K.; Schneider, G.; Hellstrom, S.; Christensen, J.; Doeff, M. M. Mesoscale Chemomechanical Interplay of the LiNi0.8Co0.15Al0.05O2 Cathode in Solid-State Polymer Batteries. Chem. Mater. 2018, 31, 491–501.
- 25 Trevisanello, E.; Ruess, R.; Conforto, G.; Richter, F. H.; Janek, J. Polycrystalline and Single Crystalline Ncm Cathode Materials–Quantifying Particle Cracking, Active Surface Area, and Lithium Diffusion. Adv. Energy Mater. 2021, 11, 2003400.
- 26 Lu, S.-j.; Tang, L.-b.; Wei, H.-x.; Huang, Y.-d.; Yan, C.; He, Z.-j.; Li, Y.-j.; Mao, J.; Dai, K.; Zheng, J.-c. Single-crystal Nickel-Based Cathodes: Fundamentals and Recent Advances. Electrochem. Energy Rev. 2022, 5, 15.
- 27 Deng, X.; Zhang, R.; Zhou, K.; Gao, Z.; He, W.; Zhang, L.; Han, C.; Kang, F.; Li, B. A Comparative Investigation of Single Crystal and Polycrystalline Ni-rich NCMs as Cathodes for Lithium-ion Batteries. Energy Environ. Mater. 2023, 6, e12331.
- 28 Sun, J.; Cao, X.; Yang, H.; He, P.; Dato, M. A.; Cabana, J.; Zhou, H. The Origin of High-Voltage Stability in Single-crystal Layered Ni-rich Cathode Materials. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202207225.
- 29 Qian, G.; Zhang, Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, R.; Xu, J.; Cheng, Z.; Xie, S.; Wang, H.; Rao, Q.; He, Y. Single-crystal Nickel-Rich Layered-Oxide Battery Cathode Materials: Synthesis, Electrochemistry, and Intra-Granular Fracture. Energy Storage Mater. 2020, 27, 140–149.
- 30 Wang, C.; Yu, R.; Hwang, S.; Liang, J.; Li, X.; Zhao, C.; Sun, Y.; Wang, J.; Holmes, N.; Li, R. Single Crystal Cathodes Enabling High-Performance All-Solid-State Lithium-ion Batteries. Energy Storage Mater. 2020, 30, 98–103.
- 31 Ran, A.; Chen, S.; Cheng, M.; Liang, Z.; Li, B.; Zhou, G.; Kang, F.; Zhang, X.; Wei, G. A Single-crystal Nickel-Rich Material as a Highly Stable Cathode for Lithium-ion Batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 2022, 10, 19680–19689.
- 32 Xu, X.; Huo, H.; Jian, J.; Wang, L.; Zhu, H.; Xu, S.; He, X.; Yin, G.; Du, C.; Sun, X. Radially Oriented Single-crystal Primary Nanosheets Enable Ultrahigh Rate and Cycling Properties of LiNi0.8Co0.1Mn0.1O2 Cathode Material for Lithium-ion Batteries. Adv. Energy Mater. 2019, 9, 1803963.
- 33 Zhong, Z.; Chen, L.; Huang, S.; Shang, W.; Kong, L.; Sun, M.; Chen, L.; Ren, W. Single-crystal LiNi0.5Co0.2Mn0.3O2: A High Thermal and Cycling Stable Cathodes for Lithium-ion Batteries. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 55, 2913–2922.
- 34 Shen, J.; Zhang, B.; Huang, W.; Li, X.; Xiao, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhou, T.; Wen, J.; Liu, T.; Amine, K. Achieving Thermodynamic Stability of Single- crystal Co-Free Ni-rich Cathode Material for High Voltage Lithium-ion Batteries. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2300081.
- 35 Kong, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, H.; Dai, P.; Zeng, J.; Zhao, J. Single- crystal Structure Helps Enhance the Thermal Performance of Ni-rich Layered Cathode Materials for Lithium-ion Batteries. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 434, 134638.
- 36 Shi, C. G.; Peng, X.; Dai, P.; Xiao, P.; Zheng, W. C.; Li, H. Y.; Li, H.; Indris, S.; Mangold, S.; Hong, Y. H. Investigation and Suppression of Oxygen Release by LiNi0.8Co0.1Mn0.1O2 Cathode under Overcharge Conditions. Adv. Energy Mater. 2022, 12, 2200569.
- 37 Wang, S.; Hua, W.; Missyul, A.; Darma, M. S. D.; Tayal, A.; Indris, S.; Ehrenberg, H.; Liu, L.; Knapp, M. Kinetic Control of Long-range Cationic Ordering in the Synthesis of Layered Ni-rich Oxides. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2009949.
- 38 Li, L.; Fu, L.; Li, M.; Wang, C.; Zhao, Z.; Xie, S.; Lin, H.; Wu, X.; Liu, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Tan, L. B-doped and La4NiLiO8-coated Ni-rich Cathode with Enhanced Structural and Interfacial Stability for Lithium-ion Batteries. J. Energy Chem. 2022, 71, 588–594.
- 39 Giordano, L.; Karayaylali, P.; Yu, Y.; Katayama, Y.; Maglia, F.; Lux, S.; Shao-Horn, Y. Chemical Reactivity Descriptor for the Oxide-Electrolyte Interface in Li-ion Batteries. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2017, 8, 3881–3887.
- 40 Noh, H.-J.; Youn, S.; Yoon, C. S.; Sun, Y.-K. Comparison of the Structural and Electrochemical Properties of Layered Li[NixoyMnz]O2 (x = 1/3, 0.5, 0.6, 0.7, 0.8 and 0.85) Cathode Material for Lithium-ion Batteries. J. Power Sources 2013, 233, 121–130.
- 41 Yang, J.; Xia, Y. Suppressing the Phase Transition of the Layered Ni-rich Oxide Cathode During High-Voltage Cycling by Introducing Low-Content Li2MnO3. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 1297–1308.
- 42 Zhang, R.; Yang, S.; Li, H.; Zhai, T.; Li, H. Air Sensitivity of Electrode Materials in Li/Na Ion Batteries: Issues and Strategies. InfoMat 2022, 4, e12305.
- 43 Cho, D.-H.; Jo, C.-H.; Cho, W.; Kim, Y.-J.; Yashiro, H.; Sun, Y.-K.; Myung, S.-T. Effect of Residual Lithium Compounds on Layer Ni-rich Li[Ni0.7Mn0.3]O2. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2014, 161, A920–A926.
- 44 Chen, Z.; Wang, J.; Huang, J.; Fu, T.; Sun, G.; Lai, S.; Zhou, R.; Li, K.; Zhao, J. The High-Temperature and High-Humidity Storage Behaviors and Electrochemical Degradation Mechanism of LiNi0.6Co0.2Mn0.2O2 Cathode Material for Lithium Ion Batteries. J. Power Sources 2017, 363, 168–176.
- 45 Hartmann, L.; Pritzl, D.; Beyer, H.; Gasteiger, H. A. Evidence for Li+/H+ Exchange During Ambient Storage of Ni-rich Cathode Active Materials. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2021, 168, 070507.
- 46
Van der Ven, A.; Morgan, D.; Meng, Y. S.; Ceder, G. Phase Stability of Nickel Hydroxides and Oxyhydroxides. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2005, 153, A210–A215.
10.1149/1.2138572 Google Scholar
- 47 Liu, H. S.; Zhang, Z. R.; Gong, Z. L.; Yang, Y. Origin of Deterioration for LiNiO2 Cathode Material During Storage in Air. Electrochem. Solid-State Lett. 2004, 7, A190–A193.
- 48 Su, Y.; Li, L.; Chen, G.; Chen, L.; Li, N.; Lu, Y.; Bao, L.; Chen, S.; Wu, F. Strategies of Removing Residual Lithium Compounds on the Surface of Ni-rich Cathode Materials. Chin. J. Chem. 2021, 39, 189–198.
- 49 Liu, A.; Phattharasupakun, N.; Ronald, V.; Ouyang, D.; Dahn, J. R. Tracking the Fate of Excess Li in the Synthesis of Various Liy[Ni1-xMnx]O2 Positive Electrode Materials under Different Atmospheres. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2022, 169, 030538.
- 50 Kim, J.; Lee, H.; Cha, H.; Yoon, M.; Park, M.; Cho, J. Prospect and Reality of Ni-rich Cathode for Commercialization. Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1702028.
- 51 Wu, N.; Wu, H.; Kim, J. K.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y. Restoration of Degraded Nickel-rich Cathode Materials for Long-Life Lithium-ion Batteries. ChemElectroChem 2018, 5, 78–83.
- 52 Williams, D. D.; Miller, R. R. Effect of Water Vapor on the LiOH-CO2 Reaction. Dynamic Isothermal System. Ind. Eng. Chem. Fundamen. 1970, 9, 454–457.
- 53 Martinez, A. C.; Grugeon, S.; Cailleu, D.; Courty, M.; Tran-Van, P.; Delobel, B.; Laruelle, S. High Reactivity of the Nickel-rich LiNi1-x-yMnxCoyO2 Layered Materials Surface Towards H2O/CO2 Atmosphere and LiPF6-Based Electrolyte. J. Power Sources 2020, 468, 228204.
- 54 Qian, K.; Huang, B.; Liu, Y.; Wagemaker, M.; Liu, M.; Duan, H.; Liu, D.; He, Y.-B.; Li, B.; Kang, F. Increase and Discretization of the Energy Barrier for Individual LiNixCoyMnyO2 (x+2y=1) Particles with the Growth of a Li2CO3 Surface Film. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 12723–12731.
- 55 Shizuka, K.; Kiyohara, C.; Shima, K.; Takeda, Y. Effect of CO2 on Layered Li1+zNi1−x−yCoxMyO2 (M = Al, Mn) Cathode Materials for Lithium ion Batteries. J. Power Sources 2007, 166, 233–238.
- 56 Liu, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, J. Investigation and Improvement on the Storage Property of LiNi0.8Co0.2O2 as a Cathode Material for Lithium- ion Batteries. J. Power Sources 2006, 162, 644–650.
- 57 Watanabe, S.; Kinoshita, M.; Hosokawa, T.; Morigaki, K.; Nakura, K. Capacity Fade of LiAlyNi1-X-YCoxO2 Cathode for Lithium-ion Batteries During Accelerated Calendar and Cycle Life Tests (Surface Analysis of LiAlyNi1-x-yCoxO2 Cathode after Cycle Tests in Restricted Depth of Discharge Ranges). J. Power Sources 2014, 258, 210–217.
- 58
Kim, J.; Hong, Y.; Ryu, K. S.; Kim, M. G.; Cho, J. Washing Effect of a LiNi0.83Co0.15Al0.02O2 Cathode in Water. Electrochem. Solid-State Lett. 2005, 9, A19–A23.
10.1149/1.1833687 Google Scholar
- 59 You, Y.; Celio, H.; Li, J.; Dolocan, A.; Manthiram, A. Modified High- Nickel Cathodes with Stable Surface Chemistry against Ambient Air for Lithium-ion Batteries. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 6480–6485.
- 60 Huang, B.; Liu, D.; Qian, K.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, K.; Liu, Y.; Kang, F.; Li, B. A Simple Method for the Complete Performance Recovery of Degraded Ni-rich LiNi0.70Co0.15Mn0.15O2 Cathode via Surface Reconstruction. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 14076–14084.
- 61 Zhang, F.; Liang, Y.; Ye, Z.; Deng, L.; Guo, Y.; Qiu, P.; Jia, P.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, L. Enhanced Electrochemical Performance of Nanoscale Single Crystal NMC811 Modification by Coating LiNbO3. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2024, 35, 108655.
- 62 Ge, M.; Wi, S.; Liu, X.; Bai, J.; Ehrlich, S.; Lu, D.; Lee, W. K.; Chen, Z.; Wang, F. Kinetic Limitations in Single-crystal High-Nickel Cathodes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 17350–17355.
- 63 Meng, X.-H.; Lin, T.; Mao, H.; Shi, J.-L.; Sheng, H.; Zou, Y.-G.; Fan, M.; Jiang, K.; Xiao, R.-J.; Xiao, D.; Gu, L.; Wan, L.-J.; Guo, Y.-G. Kinetic Origin of Planar Gliding in Single-crystalline Ni-rich Cathodes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 11338–11347.
- 64 Huang, W.; Liu, T.; Yu, L.; Wang, J.; Zhou, T.; Liu, J.; Li, T.; Amine, R.; Xiao, X.; Ge, M. Unrecoverable Lattice Rotation Governs Structural Degradation of Single-crystalline Cathodes. Science 2024, 384, 912–919.
- 65 Liang, L.; Su, M.; Sun, Z.; Wang, L.; Hou, L.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Q.; Yuan, C. High-Entropy Doping Promising Ultrahigh-Ni Co-Free Single-crystalline Cathode toward Commercializable High-Energy Lithium-ion Batteries. Sci. Adv. 2024, 10, eado4472.
- 66 Ryu, H.-H.; Namkoong, B.; Kim, J.-H.; Belharouak, I.; Yoon, C. S.; Sun, Y.-K. Capacity Fading Mechanisms in Ni-rich Single-crystal NCM Cathodes. ACS Energy Lett. 2021, 6, 2726–2734.
- 67 Wu, H.; Zhou, X.; Yang, C.; Xu, D.; Zhu, Y.-H.; Zhou, T.; Xin, S.; You, Y. Concentration-Gradient Nb-Doping in a Single-crystal Lini0.83Co0.12Mn0.05O2 Cathode for High-Rate and Long-Cycle Lithium- ion Batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 18828–18835.
- 68 Zhang, F.; Lou, S.; Li, S.; Yu, Z.; Liu, Q.; Dai, A.; Cao, C.; Toney, M. F.; Ge, M.; Xiao, X. Surface Regulation Enables High Stability of Single- crystal Lithium-ion Cathodes at High Voltage. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3050.
- 69 Mu, Y.; Ming, H.; Chen, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, W.; Cao, G.; Qiu, J. Molecular-Scale Polysiloxane-Crosslinking Hydrophobic Coating Boosting High-Performance Ni-rich Cathode in Damp-Heat Environment. Electrochim. Acta 2023, 460, 142554.
- 70 Kang, H.; Choi, M.; Kim, M.; Park, D.; Park, J.-H.; Choi, W. Tailored Coating Method for the Spontaneous Formation of Li2MoO4 Nanolayer from Residual Lithium on Single Crystal Ni-rich Cathode in Lithium-ion Batteries. Surf. Interfaces 2023, 41, 103304.
- 71 Chen, H.; Ericson, T.; Temperton, R. H.; Ida Källquist, I.; Liu, H.; Eads, C. N.; Mikheenkova, A.; Andersson, M.; Kokkonen, E.; Brant, W. R. Investigating Surface Reactivity of a Ni-rich Cathode Material toward CO2, H2O, and O2 Using Ambient Pressure X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2023, 6, 11458–11467.
- 72 Kong, X.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, S.; Zeng, J.; Zhao, J. Superiority of Single-crystal to Polycrystalline LiNixCoyMn1-x-yO2 Cathode Materials in Storage Behaviors for Lithium-ion Batteries. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 14938–14948.
- 73 Hamam, I.; Zhang, N.; Liu, A.; Johnson, M. B.; Dahn, J. R. Study of the Reactions between Ni-rich Positive Electrode Materials and Aqueous Solutions and Their Relation to the Failure of Li-ion Cells. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 130521.
- 74 Renfrew, S. E.; McCloskey, B. D. Residual Lithium Carbonate Predominantly Accounts for First Cycle CO2 and Co Outgassing of Li-Stoichiometric and Li-rich Layered Transition-Metal Oxides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 17853–17860.
- 75 Jung, R.; Strobl, P.; Maglia, F.; Stinner, C.; Gasteiger, H. A. Temperature Dependence of Oxygen Release from LiNi0.6Mn0.2Co0.2O2 (NMC622) Cathode Materials for Li-ion Batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2018, 165, A2869–A2879.
- 76 Ross, G. J.; Watts, J. F.; Hill, M. P.; Morrissey, P. Surface Modification of Poly (Vinylidene Fluoride) by Alkaline Treatment1. The Degradation Mechanism. Polymer 2000, 41, 1685–1696.
- 77 Zhang, S. S. Problems and Their Origins of Ni-rich Layered Oxide Cathode Materials. Energy Storage Mater. 2020, 24, 247–254.
- 78 Seong, W. M.; Kim, Y.; Manthiram, A. Impact of Residual Lithium on the Adoption of High-nickel Layered Oxide Cathodes for Lithium-ion Batteries. Chem. Mater. 2020, 32, 9479–9489.
- 79 Lin, F.; Markus, I. M.; Nordlund, D.; Weng, T.-C.; Asta, M. D.; Xin, H. L.; Doeff, M. M. Surface Reconstruction and Chemical Evolution of Stoichiometric Layered Cathode Materials for Lithium-ion Batteries. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3529.
- 80
Zhang, Q.; Cui, C.; Chen, H.; Pan, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Lu, B. Surface Cobaltization for Boosted Kinetics and Excellent Stability of Nickel-Rich Layered Cathodes. Natl. Sci. Open. 2024, 3, 20240010.
10.1360/nso/20240010 Google Scholar
- 81 Zhuang, G. V.; Chen, G.; Shim, J.; Song, X.; Ross, P. N.; Richardson, T. J. Li2Co3 in LiNi0.8Co0.15Al0.05O2 Cathodes and Its Effects on Capacity and Power. J. Power Sources 2004, 134, 293–297.
- 82 Ryu, H.-H.; Park, K.-J.; Yoon, C. S.; Sun, Y.-K. Capacity Fading of Ni-rich Li[NixCoyMn1-x-y]O2 (0.6≤X≤0.95) Cathodes for High-Energy-Density Lithium-ion Batteries: Bulk or Surface Degradation? Chem. Mater. 2018, 30, 1155–1163.
- 83 Wang, Y.; Jiang, J.; Dahn, J. R. The Reactivity of Delithiated Li (Ni1/3Co1/3Mn1/3)O2, Li(Ni0.8Co0.15Al0.05)O2 or LiCoO2 with Non-Aqueous Electrolyte. Electrochem. Commun. 2007, 9, 2534–2540.
- 84 Bi, Y.; Wang, T.; Liu, M.; Du, R.; Yang, W.; Liu, Z.; Peng, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, D.; Sun, X. Stability of Li2CO3 in Cathode of Lithium Ion Battery and Its Influence on Electrochemical Performance. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 19233–19237.
- 85 Zhao, J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Guo, H.; Li, X.; Yan, G.; Gui, W.; Chen, N. The Role of a MnO2 Functional Layer on the Surface of Ni-rich Cathode Materials: Towards Enhanced Chemical Stability on Exposure to Air. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 13341–13348.
- 86 Kim, Y.; Park, H.; Warner, J. H.; Manthiram, A. Unraveling the Intricacies of Residual Lithium in High-Ni Cathodes for Lithium-ion Batteries. ACS Energy Lett. 2021, 6, 941–948.
- 87 Kim, Y.; Park, H.; Shin, K.; Henkelman, G.; Warner, J. H.; Manthiram, A. Rational Design of Coating Ions Via Advantageous Surface Reconstruction in High-Nickel Layered Oxide Cathodes for Lithium-ion Batteries. Adv. Energy Mater. 2021, 11, 2101112.
- 88 Oh, P.; Song, B.; Li, W.; Manthiram, A. Overcoming the Chemical Instability on Exposure to Air of Ni-rich Layered Oxide Cathodes by Coating with Spinel LiMn1.9Al0.1O4. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 5839–5841.
- 89 Gu, W.; Dong, Q.; Zheng, L.; Liu, Y.; Mao, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Duan, W.; Lin, H.; Shen, Y.; Chen, L. Ambient Air Stable Ni-rich Layered Oxides Enabled by Hydrophobic Self-Assembled Monolayer. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 12, 1937–1943.
- 90 Luu, N. S.; Meza, P. E.; Tayamen, A. M.; Kahvecioglu, O.; Rangnekar, S. V.; Hui, J.; Downing, J. R.; Hersam, M. C. Enabling Ambient Stability of LiNiO2 Lithium-ion Battery Cathode Materials via Graphene-Cellulose Composite Coatings. Chem. Mater. 2023, 35, 5150–5159.
- 91 Doo, S. W.; Lee, S.; Kim, H.; Choi, J. H.; Lee, K. T. Hydrophobic Ni-rich Layered Oxides as Cathode Materials for Lithium-ion Batteries. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2019, 2, 6246–6253.
- 92 Sicklinger, J.; Beyer, H.; Hartmann, L.; Riewald, F.; Sedlmeier, C.; Gasteiger, H. A. SO3 Treatment of Lithium-and Manganese-Rich Ncms for Li-ion Batteries: Enhanced Robustness Towards Humid Ambient Air and Improved Full-Cell Performance. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 130507.
- 93 Seong, W. M.; Cho, K. H.; Park, J. W.; Park, H.; Eum, D.; Lee, M. H.; Kim, I. s. S.; Lim, J.; Kang, K. Controlling Residual Lithium in High- Nickel (> 90%) Lithium Layered Oxides for Cathodes in Lithium-ion Batteries. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 18662–18669.
- 94 Mu, Y.; Ming, H.; Chen, X.; Zhang, W.; Cao, G.; Xiang, Y.; Qiu, J. Molecular-Scale Hydrophobic Modification of Ni-rich Cathode Materials toward Superior Critical Endurability and Environmental Stability. Adv. Sustainable Syst. 2022, 6, 2200002.
- 95 Huang, Y.; Li, P.-Y.; Wei, H.-X.; Luo, Y.-H.; Tang, L.-B.; Chen, H.-Z.; Zhang, X.-h.; Zheng, J.-c. Suppress Moisture Sensitivity of Ni-rich Cathode Materials by Bioinspired Self-Assembly Hydrophobic Layer. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 477, 146850.
- 96 Guan, P.; Zhu, Y.; Li, M.; Zeng, T.; Li, X.; Tian, R.; Sharma, N.; Xu, Z.; Wan, T.; Hu, L. Enhancing Cyclic and in-Air Stability of Ni-rich Cathodes through Perovskite Oxide Surface Coating. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 628, 407–418.
- 97 Xie, Q.; Manthiram, A. Long-Life, Ultrahigh-Nickel Cathodes with Excellent Air Storage Stability for High-Energy Density Lithium-Based Batteries. Chem. Mater. 2020, 32, 7413–7424.
- 98 Li, Y.-C.; Xiang, W.; Wu, Z.-G.; Xu, C.-L.; Xu, Y.-D.; Xiao, Y.; Yang, Z.-G.; Wu, C.-J.; Lv, G.-P.; Guo, X.-D. Construction of Homogeneously Al3+ Doped Ni Rich Ni-Co-Mn Cathode with High Stable Cycling Performance and Storage Stability Via Scalable Continuous Precipitation. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 291, 84–94.
- 99 Lin, W.; Bao, W.; Cai, J.; Cai, X.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, Y.; Yang, S.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, Z. Degradation of Nickel-Rich Layered Oxides in Ambient Air and Its Inhibition by Surface Coating and Doping. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 615, 156278.
- 100 Lai, Y.; Wu, J.; Tang, Y.; Shang, G.; Yang, X.; Fan, H.; Peng, C.; Zhang, Z. Alleviating the Air Sensitivity of Nickel-Rich LiNi0.815Co0.15Al0.035O2 Cathode by Zr4+-Modification for Li-Ion Batteries. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 14270–14277.
- 101 Mu, L.; Yang, Z.; Tao, L.; Waters, C. K.; Xu, Z.; Li, L.; Sainio, S.; Du, Y.; Xin, H. L.; Nordlund, D. The Sensitive Surface Chemistry of Co-Free, Ni-rich Layered Oxides: Identifying Experimental Conditions That Influence Characterization Results. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 17487–17497.
- 102 Xie, Q.; Li, W.; Dolocan, A.; Manthiram, A. Insights into Boron-Based Polyanion-Tuned High-Nickel Cathodes for High-Energy-Density Lithium-ion Batteries. Chem. Mater. 2019, 31, 8886–8897.
- 103 Qu, J.; Sadighi, Z.; Yuan, H.; Zuin, L.; Goward, G. R.; Botton, G. A. Effective Recovery of the Air-Exposed Ni-rich Lithium Transition Metal Oxide Cathodes with a Coating-Stabilized Surface. J. Power Sources 2024, 614, 234983.
- 104 Yuan, K.; Ning, R.-Q.; Zhou, L.-J.; Shen, C.; Zhou, S.-S.; Li, J.; Jin, T.; Zhang, X.-G.; Xie, K.-Y. A Low-Carbon Strategy for Revival of Degraded Single Crystal LiNi0.6Co0.2Mn0.2O2. Rare Met. 2023, 42, 459–470.
- 105 Pritzl, D.; Teufl, T.; Freiberg, A. T. S.; Strehle, B.; Sicklinger, J.; Sommer, H.; Hartmann, P.; Gasteiger, H. A. Washing of Nickel-rich Cathode Materials for Lithium-ion Batteries: Towards a Mechanistic Understanding. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2019, 166, A4056–A4066.
- 106 Xia, Y.; Chen, A.; Wang, K.; Mao, Q.; Huang, H.; Zhang, J.; He, X.; Gan, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Zhang, W. Industrial Modification Comparison of Ni-rich Cathode Materials Towards Enhanced Surface Chemical Stability against Ambient Air for Advanced Lithium-ion Batteries. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 450, 138382.
- 107 Su, Y.; Chen, G.; Chen, L.; Li, L.; Li, C.; Ding, R.; Liu, J.; Lv, Z.; Lu, Y.; Bao, L. Clean the Ni-rich Cathode Material Surface with Boric Acid to Improve Its Storage Performance. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 573.
- 108 Hu, B.-R.; Yuan, Y.-Y.; Wang, Y.-C.; Xiong, X.-H. Simultaneously Enhanced Electrochemical Performance and Air Stability of Ni-rich Cathode with a Modified Washing Process. Rare Met. 2024, 43, 87–97.
- 109 Ryu, H.-H.; Lim, H.-W.; Lee, S. G.; Sun, Y.-K. Near-Surface Reconstruction in Ni-rich Layered Cathodes for High-Performance Lithium- ion Batteries. Nat. Energy 2024, 9, 47–56.
- 110 Li, L.; Chen, J.; Huang, H.; Tan, L.; Song, L.; Wu, H.-H.; Wang, C.; Zhao, Z.; Yi, H.; Duan, J. Role of Residual Li and Oxygen Vacancies in Ni-rich Cathode Materials. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 42554–42563.
- 111 Huang, B.; Liu, D.; Qian, K.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, K.; Liu, Y.; Kang, F.; Li, B. A Simple Method for the Complete Performance Recovery of Degraded Ni-rich LiNi0.70Co0.15Mn0.15O2 Cathode via Surface Reconstruction. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 14076–14084.
- 112 Chi, Z.; Li, J.; Wang, L.; Li, T.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Tao, S.; Zhang, M.; Xiao, Y.; Chen, Y. Direct Regeneration Method of Spent LiNi1/3Co1/3Mn1/3O2 Cathode Materials via Surface Lithium Residues. Green Chem. 2021, 23, 9099–9108.
- 113 Wang, C.; Shao, L.; Guo, X.; Xi, X.; Yang, L.; Huang, C.; Zhou, C.; Zhao, H.; Yin, D.; Wang, Z. Air-Induced Degradation and Electrochemical Regeneration for the Performance of Layered Ni-rich Cathodes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 44036–44045.
- 114 Li, G.; Mo, C.; Cai, Q.; Li, Z.; Li, W.; Liao, Y. Degradation Mechanism of LiNi0.8Co0.1Mn0.1O2 Cathode after Ambient Storage and Self-Repairing Strategy by Electrolyte Additive. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 471, 144382.
- 115 Sun, Z.; Pan, J.; Chen, W.; Chen, H.; Zhou, S.; Wu, X.; Wang, Y.; Kim, K.; Li, J.; Liu, H. Electrochemical Processes and Reactions in Rechargeable Battery Materials Revealed Via in Situ Transmission Electron Microscopy. Adv. Energy Mater. 2024, 14, 2303165.
- 116 Meng, X. H.; Zhang, X. D.; Sheng, H.; Fan, M.; Lin, T.; Xiao, D.; Tian, J.; Wen, R.; Liu, W. Z.; Shi, J. L. Chemical-Mechanical Robustness of Single-crystalline Ni-rich Cathode Enabled by Surface Atomic Arrangement Control. Angew. Chem. 2023, 135, e202302170.
- 117
Vinayak, A. K.; Li, M.; Huang, X.; Dong, P.; Amine, K.; Lu, J.; Wang, X. Circular Economies for Lithium-ion Batteries and Challenges to Their Implementation. Next Mater. 2024, 5, 100231.
10.1016/j.nxmate.2024.100231 Google Scholar
- 118 Ramasubramanian, B.; Ling, J.; Jose, R.; Ramakrishna, S. Ten Major Challenges for Sustainable Lithium-ion Batteries. Cell Rep. Phys. Sci. 2024, 5, 102032.




