Uncommon Bis-quinolizidine Alkaloids from the Hainan Sponge Neopetrosia chaliniformis
Bao Chen
Key Laboratory of Marine Drugs, The Ministry of Education of China, School of Medicine and Pharmacy, Ocean University of China, Qingdao, Shandong, 266003 China
State Key Laboratory of Drug Research, Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 555 Zu Chong Zhi Road, Zhangjiang Hi-Tech Park, Shanghai, 201203 China
Search for more papers by this authorXia-Juan Huan
State Key Laboratory of Drug Research, Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 555 Zu Chong Zhi Road, Zhangjiang Hi-Tech Park, Shanghai, 201203 China
Search for more papers by this authorZe-Hong Miao
State Key Laboratory of Drug Research, Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 555 Zu Chong Zhi Road, Zhangjiang Hi-Tech Park, Shanghai, 201203 China
Search for more papers by this authorNicole J. de Voogd
Naturalis Biodiversity Center, P.O. Box 9517, 2300 RA, Leiden, the Netherlands
Leiden University, Institute of Environmental Sciences, P.O. Box 9518, 2300 RA, Leiden, the Netherlands
Search for more papers by this authorYu-Cheng Gu
Syngenta, Jealott's Hill International Research Centre, Bracknell, Berkshire, RG42 6EY United Kingdom
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Chang-Yun Wang
Key Laboratory of Marine Drugs, The Ministry of Education of China, School of Medicine and Pharmacy, Ocean University of China, Qingdao, Shandong, 266003 China
Open Studio for Druggability Research of Marine Natural Products, Pilot National Laboratory for Marine Science and Technology (Qingdao), 1 Wenhai Road, Aoshanwei, Jimo, Qingdao, Shandong, 266237 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Yue-Wei Guo
State Key Laboratory of Drug Research, Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 555 Zu Chong Zhi Road, Zhangjiang Hi-Tech Park, Shanghai, 201203 China
Open Studio for Druggability Research of Marine Natural Products, Pilot National Laboratory for Marine Science and Technology (Qingdao), 1 Wenhai Road, Aoshanwei, Jimo, Qingdao, Shandong, 266237 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Xu-Wen Li
State Key Laboratory of Drug Research, Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 555 Zu Chong Zhi Road, Zhangjiang Hi-Tech Park, Shanghai, 201203 China
Open Studio for Druggability Research of Marine Natural Products, Pilot National Laboratory for Marine Science and Technology (Qingdao), 1 Wenhai Road, Aoshanwei, Jimo, Qingdao, Shandong, 266237 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorBao Chen
Key Laboratory of Marine Drugs, The Ministry of Education of China, School of Medicine and Pharmacy, Ocean University of China, Qingdao, Shandong, 266003 China
State Key Laboratory of Drug Research, Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 555 Zu Chong Zhi Road, Zhangjiang Hi-Tech Park, Shanghai, 201203 China
Search for more papers by this authorXia-Juan Huan
State Key Laboratory of Drug Research, Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 555 Zu Chong Zhi Road, Zhangjiang Hi-Tech Park, Shanghai, 201203 China
Search for more papers by this authorZe-Hong Miao
State Key Laboratory of Drug Research, Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 555 Zu Chong Zhi Road, Zhangjiang Hi-Tech Park, Shanghai, 201203 China
Search for more papers by this authorNicole J. de Voogd
Naturalis Biodiversity Center, P.O. Box 9517, 2300 RA, Leiden, the Netherlands
Leiden University, Institute of Environmental Sciences, P.O. Box 9518, 2300 RA, Leiden, the Netherlands
Search for more papers by this authorYu-Cheng Gu
Syngenta, Jealott's Hill International Research Centre, Bracknell, Berkshire, RG42 6EY United Kingdom
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Chang-Yun Wang
Key Laboratory of Marine Drugs, The Ministry of Education of China, School of Medicine and Pharmacy, Ocean University of China, Qingdao, Shandong, 266003 China
Open Studio for Druggability Research of Marine Natural Products, Pilot National Laboratory for Marine Science and Technology (Qingdao), 1 Wenhai Road, Aoshanwei, Jimo, Qingdao, Shandong, 266237 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Yue-Wei Guo
State Key Laboratory of Drug Research, Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 555 Zu Chong Zhi Road, Zhangjiang Hi-Tech Park, Shanghai, 201203 China
Open Studio for Druggability Research of Marine Natural Products, Pilot National Laboratory for Marine Science and Technology (Qingdao), 1 Wenhai Road, Aoshanwei, Jimo, Qingdao, Shandong, 266237 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Xu-Wen Li
State Key Laboratory of Drug Research, Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 555 Zu Chong Zhi Road, Zhangjiang Hi-Tech Park, Shanghai, 201203 China
Open Studio for Druggability Research of Marine Natural Products, Pilot National Laboratory for Marine Science and Technology (Qingdao), 1 Wenhai Road, Aoshanwei, Jimo, Qingdao, Shandong, 266237 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorMain observation and conclusion
Two new bis-quinolizidine alkaloids, neopetrosiasins A (1) and B (2), possessing cis- and trans-quinolizidine nuclei, one known related analogue petrosin (3) and three known xestospongins (4—6), were isolated from the South China Sea sponge Neopetrosia chaliniformis. The structures of new compounds were unambiguously determined by extensive spectroscopic and single-crystal X-ray analyses. In bioassay, compounds 4—6 exhibited moderate cytotoxicity against several human cancer cells.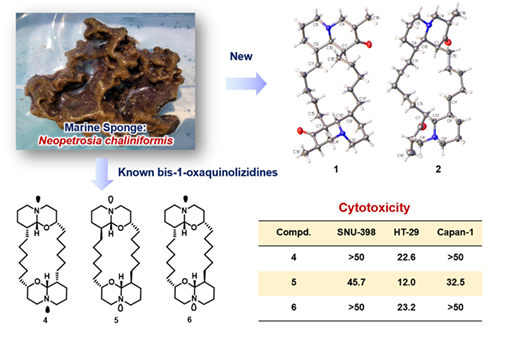
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| cjoc202100091-sup-0001-Supinfo.pdfPDF document, 2.3 MB |
Appendix S1: Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1 Sorek, H.; Rudi, A.; Benayahu, Y.; Kashman, Y. Njaoamines G and H, two new cytotoxic polycyclic alkaloids and a tetrahydroquinolone from the marine sponge Neopetrosia sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 2007, 48, 7691–7694.
- 2 Li, Y.; Qin, S.; Guo, Y.-W.; Gu, Y.-C.; van Soest, R. W. M. 9'-epi-3β,3'β- dimethylxestospongin C, a new macrocyclic diamine alkaloid from the Hainan sponge Neopetrosia exigua. Planta Med. 2011, 77, 179–181.
- 3 Shubina, L. K.; Makarieva, T. N.; Yashunsky, D. V.; Nifantiev, N. E.; Stonik, V. A. Pyridine nucleosides neopetrosides A and B from a marine Neopetrosia sp. sponge. Synthesis of neopetroside A and Its β-riboside analogue. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 1383–1389.
- 4 Winder, P. L.; Baker, H. L.; Linley, P.; Guzmán, E. A.; Pomponi, S. A.; Diaz, M. C.; Reed, J. K.; Wright, A. E. J. B.; Chemistry, M. Neopetrosiquinones A and B, sesquiterpene benzoquinones isolated from the deep-water sponge Neopetrosia cf. proxima. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 6599–6603.
- 5 Oku, N.; Matsunaga, S.; van, S. R. W. M.; Fusetani, N. Renieramycin J, a highly cytotoxic tetrahydroisoquinoline alkaloid, from a marine sponge Neopetrosia sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2003, 66, 1136–1139.
- 6 Priscila, D. A. L.; Carroll, A. R.; Towerzey, L.; King, G.; Mcardle, B. M.; Kern, G.; Fisher, S.; Hooper, J. N. A.; Quinn, R. J. J. O. L. Exiguaquinol: a novel pentacyclic hydroquinone from Neopetrosia exigua that inhibits Helicobacter pylori MurI. Org. Lett. 2008, 10, 2585–2588.
- 7 Wei, X.; Nieves, K.; Rodríguez, A. D. J. B.; Letters, M. C. Neopetrosiamine A, biologically active bis-piperidine alkaloid from the Caribbean sea sponge Neopetrosia proxima. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 5905–5908.
- 8
Liu, H.; Mishima, Y.; Fujiwara, T.; Nagai, H.; Kitazawa, A.; Mine, Y.; Kobayashi, H.; Yao, X.; Yamada, J.; Oda, T.; Namikoshi, M. Isolation of araguspongine M, a new stereoisomer of an araguspongine/xestospongin alkaloid, and dopamine from the marine sponge Neopetrosia exigua collected in Palau. Mar. Drugs 2004, 2, 154–163.
10.3390/md204154 Google Scholar
- 9 Baldwin, J. E.; Whitehead, R. C. J. T. L. On the biosynthesis of manzamines. Tetrahedron Lett. 1992, 33, 2059–2062.
- 10 Nakagawa, M.; Endo, M.; Tanaka, N.; Gen-Pei, L. Structures of xestospongin A, B, C and D, novel vasodilativecompounds from marine sponge, xestospongia exigua. Tetrahedron Lett. 1984, 25, 3227–3230.
- 11 Moon, S. S.; MacMillan, J. B.; Olmstead, M. M.; Ta, T. A.; Molinski, T. F. (+)-7S-hydroxyxestospongin A from the marine sponge Xestospongia sp. and absolute configuration of (+)-xestospongin D. J. Nat. Prod. 2002, 249–254.
- 12 Braekman, J. C.; Daloze, D.; Cimino, G.; Trivellone, E. 2D-NMR study of petrosins: revised structure for petrosin-A. Bull. Soc. Chim. Belg. 1988, 97, 519–524.
- 13 Kobayashi, M.; Miyamoto, Y.; Aoki, S.; Murakami, N.; Kitagawa, I.; In, Y.; Ishida, T. Isomerization of dimeric 2,9-disubstituted 1-oxa-quinolizidine alkaloids and structural revision of araguspongines B and E, isolated from a marine sponge of xestospongia sp. Heteroycles 1998, 47, 195–203.
- 14 Iwagawa, T.; Kaneko, M.; Okamura, H.; Nakatani, M.; Van Soest, R. W. M.; Shiro, M. J. J. o. N. P. A new quinolizidine alkaloid from the Papua New Guinean sponge Xestospongia exigua. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 1310–1311.
- 15 Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 55–63.
- 16 Hansen, M. B.; Nielsen, S. E.; Berg, K. Re-examination and further development of a precise and rapid dye method for measuring cell growth/cell kill. J. Immunol. Methods 1989, 203–210.




