Sensing Mechanism of Excited-State Intermolecular Hydrogen Bond for Phthalimide: Indispensable Role of Dimethyl Sulfoxide
Dongdong Wang
Key Laboratory of Separation Science for Analytical Chemistry, Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Dalian, Liaoning, 116023 China
‡ These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorTianxin Bai
Institute of Molecular Sciences and Engineering, Shandong University, Qingdao, Shandong, 266237 China
‡ These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorXue Wang
Key Laboratory of Separation Science for Analytical Chemistry, Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Dalian, Liaoning, 116023 China
Search for more papers by this authorYuting Xiong
Key Laboratory of Separation Science for Analytical Chemistry, Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Dalian, Liaoning, 116023 China
Search for more papers by this authorYahui Zhang
Key Laboratory of Separation Science for Analytical Chemistry, Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Dalian, Liaoning, 116023 China
Search for more papers by this authorZhenqiang Shi
Key Laboratory of Separation Science for Analytical Chemistry, Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Dalian, Liaoning, 116023 China
Search for more papers by this authorFusheng Zhang
Key Laboratory of Separation Science for Analytical Chemistry, Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Dalian, Liaoning, 116023 China
Search for more papers by this authorWenqi Lu
Key Laboratory of Separation Science for Analytical Chemistry, Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Dalian, Liaoning, 116023 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Guangyan Qing
Key Laboratory of Separation Science for Analytical Chemistry, Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Dalian, Liaoning, 116023 China
College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Wuhan Textile University, 1 Sunshine Road, Wuhan, Hubei, 430200 China
E-mail: [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorDongdong Wang
Key Laboratory of Separation Science for Analytical Chemistry, Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Dalian, Liaoning, 116023 China
‡ These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorTianxin Bai
Institute of Molecular Sciences and Engineering, Shandong University, Qingdao, Shandong, 266237 China
‡ These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorXue Wang
Key Laboratory of Separation Science for Analytical Chemistry, Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Dalian, Liaoning, 116023 China
Search for more papers by this authorYuting Xiong
Key Laboratory of Separation Science for Analytical Chemistry, Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Dalian, Liaoning, 116023 China
Search for more papers by this authorYahui Zhang
Key Laboratory of Separation Science for Analytical Chemistry, Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Dalian, Liaoning, 116023 China
Search for more papers by this authorZhenqiang Shi
Key Laboratory of Separation Science for Analytical Chemistry, Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Dalian, Liaoning, 116023 China
Search for more papers by this authorFusheng Zhang
Key Laboratory of Separation Science for Analytical Chemistry, Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Dalian, Liaoning, 116023 China
Search for more papers by this authorWenqi Lu
Key Laboratory of Separation Science for Analytical Chemistry, Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Dalian, Liaoning, 116023 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Guangyan Qing
Key Laboratory of Separation Science for Analytical Chemistry, Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Dalian, Liaoning, 116023 China
College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Wuhan Textile University, 1 Sunshine Road, Wuhan, Hubei, 430200 China
E-mail: [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorMain observation and conclusion
Excited-state hydrogen bond strongly affects the intramolecular charge conversion process, which is very suitable for the design and development of high-performance fluorescent probes. However, as one of the most common solvents or additives used in sensing, the role of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) in the system of the excited-state hydrogen bond is seldom explored. As the goal of this research, we investigated the sensing mechanism of a CORM3-green fluorescent probe system for carbon monoxide releasing molecule (CORM-3) detection and tracking in vivo, through quantum chemistry calculations based on density-functional-theory (DFT)/ time-dependent density-functional-theory (TDDFT) methods. Based on the analysis of the solvent effect of DMSO by the reduced density gradient function and IR spectroscopy, we provided a new strategy to explain the fluorescence mechanism. Subsequently, we verified the result through the potential energy curve of Phthalimide (PTI, the reduced product of CORM3-green). The excited-state hydrogen bond between PTI and DMSO promotes radiation transition and leads to obvious difference in the photophysical properties of PTI and PTI-DMSO.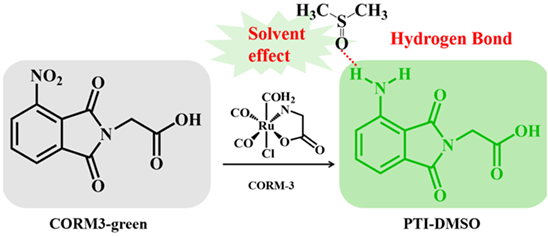
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| cjoc202000604-sup-0001-Supinfo.pdfPDF document, 1 MB |
Appendix S1: Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1 Zhao, G. J.; Han, K. L. Hydrogen bonding in the electronic excited state. Acc. Chem. Res. 2012, 45, 404–413.
- 2 Xu, Y.; Song, X. D.; Hao, C. LCOFs: Role of the excited state hydrogen bonding in the detection for nitro-explosives. J. Lumin. 2019, 215, 116733.
- 3
Kokado, K.; Sada, K. Consideration of Molecular Structure in the Excited State to Design New Luminogens with Aggregation-Induced Emission. Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 8724–8731.
10.1002/ange.201814462 Google Scholar
- 4 Zhao, D.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Gao, J. W.; Liu, S. X.; Zhao, Z. Theoretical insights into the excited-state intermolecular hydrogen bonding dynamics of PRODAN derivative in toluene solution. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2019, 725, 109–113.
- 5 Tran, T.; Prlj, A.; Lin, K. H.; Hollas, D.; Corminboeuf, C. Mechanisms of fluorescence quenching in prototypical aggregation-induced emission systems: excited state dynamics with TD-DFTB. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2019, 21, 9026–9035.
- 6 Omidyan, R.; Omidyan, M.; Mohammadzadeh, A. Electronically excited state of neutral/protonated, indole/5-hydroxyinodole-water clusters: a theoretical study. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 33148–33158.
- 7 Hisham, S.; Tajuddin, H. A.; Chee, C. F.; Hasan, Z. A.; Abdullah, Z. Synthesis and fluorescence studies of selected N-aryl-2-aminoquinolines: effect of hydrogen bonding, substituents and ESIPT on their fluorescence quantum yields. J. Lumin. 2019, 208, 245–252.
- 8 Wang, F. H.; Wang, M. S.; Xin, M. L.; Liu, E. F.; Yang, C. L. Excited-state hydrogen bonding dynamics of methyl isocyanide in methanol solvent: A DFT/TDDFT study. Cent. Eur. J. Phys. 2011, 9, 792–799.
- 9 Zhao, G. J.; Han, K. L.; Lei, Y. B.; Dou, Y. Ultrafast excited-state dynamics oftetraphenylethylene studied by semiclassical simulation. J. Chem. Phys. 2007, 127, 094307.
- 10 Zhao, G. J.; Han, K. L. Ultrafast hydrogen bond strengthening of the photoexcited fluorenone in alcohols for facilitating the fluorescence quenching. J. Phys. Chem. A 2007, 111, 9218–9223.
- 11 Lu, Q.; Zhan, M. M.; Deng, L. J.; Qing, G. Y.; Sun, T. L. Rapid and high-efficiency discrimination of different sialic acid species using dipeptide-based fluorescent sensors. Analyst 2017, 142 3564–3568.
- 12 Chang, Y. X.; Li, B.; Mei, H. H.; Yang, L.; Xu, K. X.; Pang, X. B. Indole-based colori/fluorimetric probe for selective detection of Cu2+ and application in living cell imaging. Spectrochim. Acta, Part A 2020, 226, 117631.
- 13 Gao, L. X.; Tian, M.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, F. L. Syntheses, kinetics and thermodynamics of BODIPY-based fluorescent probes with different kinds of hydrophilic groups for the detection of biothiols. Dyes Pigm. 2020, 180, 108434.
- 14 Wang, R.; Hao, C.; Li, P.; Wei, N. N.; Chen, J. W.; Qiu, J. S. Time-dependent density functional theory study on the electronic excited-state hydrogen-bonding dynamics of 4-aminophthalimide (4AP) in aqueous solution: 4AP and 4AP-(H2O)1,2 clusters. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 2157–2163.
- 15 Schultz, T.; Samoylova, E.; Radloff, W.; Sobolewski, A. L.; Domcke, W. Efficient deactivation of a model base pair via excited-state hydrogen transfer. Science 2004, 306, 1765–1768.
- 16 Zhou, P. W.; Han, K. L. Unraveling the detailed mechanism of excited-state proton transfer. Acc. Chem. Res. 2018, 51, 1681–1690.
- 17 Paul, B. K.; Guchhait, N. 1-Hydroxy-2-naphthaldehyde: A prospective excited-state intramolecular proton transfer (ESIPT) probe with multi-faceted applications. J. Lumin. 2012, 132, 2194–2208.
- 18 Liu, Y. H.; Mehata, M. S.; Liu, J. Y. Excited-state proton transfer via hydrogen-bonded acetic acid (AcOH) wire for 6-hydroxyquinoline. J. Phys. Chem. A 2011, 115, 19–24.
- 19 Wang, Y.; Yin, H.; Shi, Y.; Jin, M. X.; Ding, D. J. Ground-state and excited-state multiple proton transfer via a hydrogen-bonded water wire for 3-hydroxypyridine. New J. Chem. 2014, 38, 4458–4464.
- 20 Yang, D. P.; Zhao, J. F.; Jia, M.; Song, X. Y. A theoretical study about the excited state intermolecular proton transfer mechanisms for 2-phenylimidazo [4,5-b] pyridine in methanol solvent. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 34034–34040.
- 21 Yang, D. P.; Yang, G.; Zhao, J. F.; Song, N. H.; Zheng, R.; Wang, Y. S. Solvent controlling excited state proton transfer reaction in quinoline/isoquinoline-pyrazole isomer QP-I: A theoretical study. J. Phys. Org. Chem. 2018, 31, e3729.
- 22 Chen, M.; Zheng, L. X.; Santra, B.; Ko, H. Y.; DiStasio, R. A.; Klein, M. L.; Car, R.; Wu, X. F. Hydroxide diffuses slower than hydronium in water because its solvated structure inhibits correlated proton transfer. Nat. Chem. 2018, 10, 413–419.
- 23 Jaramillo, P.; Coutinho, K.; Canuto, S. Solvent effects in chemical processes. water-assisted proton transfer reaction of pterin in aqueous environment. J. Phys. Chem. A 2019, 113, 12485–12495.
- 24 Mera-Adase, R.; Rezende, M. C.; Dominguez, M. On the physical- chemical nature of solvent polarizability and dipolarity. Spectrochim. Acta, Part A 2020, 229, 1386–1425.
- 25 Sun, C. F.; Zhao, H. F.; Liu, X. C.; Yin, H.; Shi, Y. Tunable ESIPT reaction and antioxidant activities of 3-hydroxyflavone and its derivatives by altering atomic alectronegativity. Org. Chem. Front. 2018, 5, 3435–3442.
- 26 Smith, G. J.; Dunford, C. L.; Roberts, P. B. The photostability and fluorescence of hydroxycoumarins in aprotic solvents. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 2010, 210, 31–35.
- 27 Liu, Y. F.; Deng, D. P.; Shi, D. H.; Sun, J. F. A TD-DFT study on the hydrogen bonding of three esculetin complexes in electronically excited states: Strengthening and weakening. J. Comput. Chem. 2011, 32, 3475–3484.
- 28 McGarry, P. F.; Jockusch, S.; Fujiwara, Y.; Kaprinidis, N. A.; Turro, N. J. DMSO Solvent Induced Photochemistry in Highly Photostable Compounds. The Role of Intermolecular Hydrogen Bonding. J. Phys. Chem. A 1997, 101, 764–767.
- 29 Clark, J. E.; Naughton, P.; Shurey, S.; Green, C. J.; Johnson, T. R.; Mann, B. E.; Foresti, R.; Motterlini, R. Cardioprotective actions by a water-soluble carbon monoxide-releasing molecule. Circ. Res. 2003, 93, 2−8.
- 30 Feng, W. Y.; Feng, S. M.; Feng, G. Q. A fluorescent ESIPT probe for imaging CO-releasing molecule-3 in living Systems. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 8602–8606.
- 31 Weller, A. Innermolekularer protonenubergang im angereg the zustand. Phys. Chem. 1956, 60, 1144–1147.
- 32 Suzuki, N.; Fukazawa, A.; Nagura, K.; Saito, S.; Kitoh-Nishioka, H.; Yokogawa, D.; Irle, S.; Yamaguchi, S. A strap strategy for construction of an excited-state intramolecular proton transfer (ESIPT) system with dual fluorescence. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 8231–8235.
- 33 Santos, F. S.; Ramasamy, E.; Ramamurthy, V.; Rodembusch, F. S. Excited state behavior of benzoxazole derivatives in a confined environment afforded by a water soluble octaacid capsule. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 2016, 317, 175–185.
- 34 Hsieh, C. C.; Ho, M. L.; Chou, P. T. Organic dyes with excited-state transformations (electron, charge, and proton transfers). In Advanced Fluorescence Reporters in Chemistry and Biology I, Springer Series on Fluorescence (Methods and Applications), Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, 2010, 8, 225–266.
- 35 Tang, Z.; Yang, Y. F.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tian, J.; Fei, X. Theoretical investigation of twisted charge-transfer-promoted intramolecular proton transfer in the excited state of 4’-dimethylaminoflavonol in a highly polar solvent. J. Lumin. 2018, 194, 785–790.
- 36 Zhao, Y.; Yang, Y. F.; Ma, Y. Z.; Li, Q. Y. Stimuli-responsive luminescent coumarin thiazole hybrid dye: Mechanism of excited-state intramolecular double proton transfer. J. Lumin. 2018, 201, 189–195.
- 37 Li, Y.; Zhao, J. F.; Chu, T. S. Glutathione sensing mechanism of a fluorescent probe: Excited state intramolecular proton transfer and photoinduced electron transfer. J. Lumin. 2018, 204, 642–648.
- 38 Bai, T. X.; Chu, T. S. A Theoretical Study on the Fluorescence Signal Sensing of a Colorimetric ClO Chemosensor. J. Phys. Org. Chem. 2020, 33, e4039.
- 39Frisch, M. J.; Trucks, G. W.; Schlegel, H. B.; Scuseria, G. E.; Robb, M. A.; Cheeseman, J. R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Mennucci, B.; Petersson, G. A.; Nakatsuji, H.; Caricato, M.; Li, X.; Hratchian, H. P.; Izmaylov, A. F.; Bloino, J.; Zheng, G.; Sonnenberg, J. L.; Hada, M.; Ehara, M.; Toyota, K.; Fukuda, R.; Hasegawa, J.; Ishida, M.; Nakajima, T.; Honda, Y.; Kitao, O.; Nakai, H.; Vreven, T.; Montgomery, J. A., Jr.; Peralta, J. E.; Ogliaro, F.; Bearpark, M.; Heyd, J. J.; Brothers, E.; Kudin, K. N.; Staroverov, V. N.; Keith, T.; Kobayashi, R.; Normand, J.; Raghavachari, K.; Rendell, A.; Burant, J. C.; Iyengar, S. S.; Tomasi, J.; Cossi, M.; Rega, N.; Millam, J. M.; Klene, M.; Knox, J. E.; Cross, J. B.; Bakken, V.; Adamo, C.; Jaramillo, J.; Gomperts, R.; Stratmann, R. E.; Yazyev, O.; Austin, A. J.; Cammi, R.; Pomelli, C.; Ochterski, J. W.; Martin, R. L.; Morokuma, K.; Zakrzewski, V. G.; Voth, G. A.; Salvador, P.; Dannenberg, J. J.; Dapprich, S.; Daniels, A. D.; Farkas, O.; Foresman, J. B.; Ortiz, J. V.; Cioslowski, J.; Fox, D. J. Gaussian 09, Revision C.01, Gaussian, Inc., Wallingford, CT, 2009.
- 40 Becke, A. D. Density-functional thermochemistry. III. the role of exact exchange. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 5648–5652.
- 41 Lee, C. T.; Yang, W. T.; Parr, R. G. Development of the colle-salvetti correlation-energy formula into a functional of the electron density. Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 1988, 37, 785–789.
- 42 Miehlich, B.; Savin, A.; Stoll, H.; Preuss, H. Results obtained with the correlation energy density functionals of becke and Lee, Yang and Parr. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1989, 157, 200–206.
- 43 Schafer, A.; Huber, C.; Ahlrichs, R. Fully optimized contracted gaussian-basis sets of triple zeta valence quality for atoms Li to Kr. J. Chem. Phys. 1994, 100, 829–5835.
- 44 Feller, D. J. The role of databases in support of computational chemistry calculations. J. Comput. Chem. 1996, 17, 1571−1586.
- 45 Yanai, T.; Tew, D. P.; Handy, N. C. A new hybrid exchange-correlation functional using the coulomb-attenuating method (Cam-B3lyp). Chem. Phys. Lett. 2004, 393, 51–57.
- 46 Cammi, R.; Tomasi, J. Remarks on the use of the apparent surface-charges (ASC) methods in solvation problems-iterative versus matrix-inversion procedures and the renormalization of the apparent charges. J. Comput. Chem. 1995, 16, 1449–1458.
- 47 Mennucci, B.; Cancès, E.; Tomasi, J. Evaluation of solvent effects in isotropic and anisotropic dielectrics and in ionic solutions with a unified integral equation method: theoretical bases, computational implementation, and numerical applications. J. Phys. Chem. B 1997, 101, 10506–10517.
- 48 d'Antuono, P.; Botek, E.; Champagne, B.; Spassova, M.; Denkova, P. Theoretical investigation on 1H and 13C NMR chemical shifts of small alkanes and chloroalkanes. J. Chem. Phys. 2006, 125, 144309.
- 49 Johnson, E. R.; Keinan, S.; Mori-Sanchez, P.; Contreras-Garcia, J.; Cohen, A. J.; Yang, W. Revealing noncovalent interactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 6498–6506.
- 50 Contreras-Garcia, J.; Johnson, E. R.; Keinan, S.; Chaudret, R.; Piquemal, J. P.; Beratan, D. N.; Yang, W. T. Nciplot: A program for plotting noncovalent interaction regions. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2011, 7, 625–632.
- 51 Tang, W.; Sanville, E.; Henkelman, G. A grid-based Bader analysis algorithm without lattice bias. J. Phys. Condes. Matter 2009, 21, 7.
- 52 Lu, T.; Chen, F. W. Multiwfn: A multifunctional wavefunction analyzer. J. Comput. Chem. 2012, 33, 580–592.
- 53 Lu, M. H.; Zhang, X. X.; Zhou, P. W.; Tang, Z.; Qiao, Y.; Yang, Y. Q.; Liu, J. Y. Theoretical insights into the sensing mechanism of a series of terpyridine-based chemosensors for TNP. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2019, 725, 45–51.
- 54 Liu, X. C.; Yin, H.; Li, H.; Shi, Y. Altering intra- to inter-molecular hydrogen bonding by dimethylsulfoxide: A TDDFT study of charge transfer for coumarin 343. Spectrochim. Acta, Part A 2017, 177, 1–5.
- 55 Zhao, J. F.; Chen, J. S.; Cui, Y. L.;Wang, J.; Xia, L. X.; Dai, Y. M.; Song, P.; Ma, F. C. A questionable excited-state double-proton transfer mechanism for 3-hydroxyisoquinoline. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 1142–1150.
- 56 Zhao, J.; Yang, Y. A theoretical study on ESPT mechanism of DALL-AcOH complex. Commun. Comput. Chem. 2016, 4, 1–8.
- 57 Plasser, F.; Barbatti, M.; Aquino, A. J. A.; Lischka, H. Excited-state diproton transfer in [2,2’-Bipyridyl]-3,3’-diol: the mechanism is sequential, not concerted. J. Phys. Chem. A 2009, 113, 8490–8499.
- 58 Markovic, Z. S.; Mentus, S. V.; Markovic, J. M. D. Electrochemical and density functional theory study on the reactivity of fisetin and its radicals: implications on in vitro antioxidant activity. J. Phys. Chem. A 2009, 113, 14170–14179.
- 59 Li, H.; Shi, Y.; Yin, H.; Wang, Y.; Cong, L.; Jin, M. X.; Ding, D. J. New insights into the solvent-assisted excited-state double proton transfer of 2-(1H-pyrazol-5-yl) pyridine with alcoholic partners: A TDDFT investigation. Spectrochim. Acta, Part A 2015, 141, 211–215.
- 60 Serdiuk, I. E.; Roshalb, A. D. Single and double intramolecular proton transfersin the electronically excited state of flavone derivatives. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 102191–102203.
- 61 Zhao, G. J.; Han, K. L. Effects of hydrogen bonding on tuning photochemistry: concerted hydrogen-bond strengthening and weakening. Chem. Phys. Chem. 2008, 9, 1842–1846.
- 62 Zhao, J. F.; Song, P.; Cui, Y. L.; Liu, X. M.; Sun, S. W.; Hou, S. Y.; Ma, F. C. Effects of hydrogen bond on 2-aminopyridine and its derivatives complexes in methanol solvent. Spectrochim. Acta, Part A 2014, 131, 282–287.
- 63 Hisham, S.; Tajuddin, H. A.; Chee,C. F.; Hasan, Z. A.; Abdullah, Z. Synthesis and fluorescence studies of selected N-aryl-2-aminoquinolines: effect of hydrogen bonding, substituents and ESIPT on their fluorescence quantum yields. J. Lumin. 2019, 208, 245–252.
- 64 Yuan, J. Y.; Yuan, Y. H.; Tian, X. H.; Liu, Y. D.; Sun, J. Y. Insights into the photobehavior of fluorescent oxazinone, quinazoline, and difluoroboron derivatives: molecular design based on the structure- property relationships. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 8091–8108.
- 65 Zhao, N. J.; Li, Y.; Jia, Y.; Li, P. Identifying the role of intramolecular charge transfer and excited-state proton transfer in fluorescence mechanism for an azido-based chemosensor. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 26576–26583.
- 66kasha, M. Characterization of electronic transition in complex molecules, Discuss. Faraday Soc. 1950, 9, 14–19.




