Recent Advances in PROTAC Technology Toward New Therapeutic Modalities
Corresponding Author
Dr. Hidetomo Yokoo
Medical Chemistry, Graduate School of Medical Science, Kyoto Prefectural University of Medicine, 1-5 Shimogamo Hangicho, Sakyo-ku, Kyoto, 606-0823 Japan
Division of Organic Chemistry, National Institute of Health Sciences, 3-25-26 Tonomachi, Kawasaki, Kanagawa, 210-9501 Japan
Search for more papers by this authorMiyako Naganuma
Division of Organic Chemistry, National Institute of Health Sciences, 3-25-26 Tonomachi, Kawasaki, Kanagawa, 210-9501 Japan
Graduate School of Medical Life Science, Yokohama City University, 1-7-29 Suehiro-cho, Tsurumi-ku, Yokohama, 230-0045 Japan
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Makoto Oba
Medical Chemistry, Graduate School of Medical Science, Kyoto Prefectural University of Medicine, 1-5 Shimogamo Hangicho, Sakyo-ku, Kyoto, 606-0823 Japan
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dr. Yosuke Demizu
Division of Organic Chemistry, National Institute of Health Sciences, 3-25-26 Tonomachi, Kawasaki, Kanagawa, 210-9501 Japan
Graduate School of Medical Life Science, Yokohama City University, 1-7-29 Suehiro-cho, Tsurumi-ku, Yokohama, 230-0045 Japan
Graduate School of Medicine, Dentistry and Pharmaceutical Sciences, Okayama University, 1-1-1 Tsushimanaka, Kita-ku, Okayama, 700-8530 Japan
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dr. Hidetomo Yokoo
Medical Chemistry, Graduate School of Medical Science, Kyoto Prefectural University of Medicine, 1-5 Shimogamo Hangicho, Sakyo-ku, Kyoto, 606-0823 Japan
Division of Organic Chemistry, National Institute of Health Sciences, 3-25-26 Tonomachi, Kawasaki, Kanagawa, 210-9501 Japan
Search for more papers by this authorMiyako Naganuma
Division of Organic Chemistry, National Institute of Health Sciences, 3-25-26 Tonomachi, Kawasaki, Kanagawa, 210-9501 Japan
Graduate School of Medical Life Science, Yokohama City University, 1-7-29 Suehiro-cho, Tsurumi-ku, Yokohama, 230-0045 Japan
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Makoto Oba
Medical Chemistry, Graduate School of Medical Science, Kyoto Prefectural University of Medicine, 1-5 Shimogamo Hangicho, Sakyo-ku, Kyoto, 606-0823 Japan
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dr. Yosuke Demizu
Division of Organic Chemistry, National Institute of Health Sciences, 3-25-26 Tonomachi, Kawasaki, Kanagawa, 210-9501 Japan
Graduate School of Medical Life Science, Yokohama City University, 1-7-29 Suehiro-cho, Tsurumi-ku, Yokohama, 230-0045 Japan
Graduate School of Medicine, Dentistry and Pharmaceutical Sciences, Okayama University, 1-1-1 Tsushimanaka, Kita-ku, Okayama, 700-8530 Japan
Search for more papers by this authorAbstract
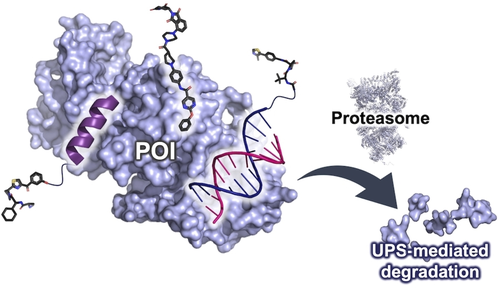
Proteolysis targeting chimeras (PROTACs) have emerged as a powerful technology for the degradation of disease-related proteins by the hijacking of the endogenous ubiquitin-proteasome system. A multitude of bifunctional PROTACs have been developed using small-molecule ligands; one ligand binds to the target protein of interest and one ligand binds to an E3 ligase. The characteristics of those PROTACs vary, including their reversible or irreversible covalent binding to the target protein, their binding to orthosteric and allosteric sites, their agonist or antagonist activity, and their use of multiple ligands. In addition, oligopeptides and nucleotides have recently been used as alternative targeting ligands. The properties of PROTACs, such as selectivity, delivery and sensitivity to drug resistance, can be improved through the use of a variety of targeting ligand modalities. This minireview introduces the mechanisms and behavior of small-molecule based PROTACs as well as targeted proteolysis techniques using peptides and nucleic acids as targeting ligands.
Graphical Abstract
References
- 1M. Bekes, D. R. Langley, C. M. Crews, ‘PROTAC targeted protein degraders: the past is prologue’, Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery 2022, 21, 181–200.
- 2S. Tomoshige, M. Ishikawa, ‘PROTACs and other chemical protein degradation technologies for the treatment of neurodegenerative disorders’, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2021, 60, 3346–3354.
- 3K. M. Sakamoto, K. B. Kim, A. Kumagai, F. Mercurio, C. M. Crews, R. J. Deshaies, ‘Protacs: chimeric molecules that target proteins to the Skp1-Cullin-F box complex for ubiquitination and degradation’, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 8554–8559.
- 4Y. Itoh, M. Ishikawa, M. Naito, Y. Hashimoto, ‘Protein knockdown using methyl bestatin-ligand hybrid molecules: design and synthesis of inducers of ubiquitination-mediated degradation of cellular retinoic acid-binding proteins’, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 5820–5826.
- 5H. Kiely-Collins, G. E. Winter, G. J.L. Bernardes, ‘The role of reversible and irreversible covalent chemistry in targeted protein degradation’, Cell Chem. Biol. 2021, 28, 952–968.
- 6B. E. Smith, S. L. Wang, S. Jaime-Figueroa, A. Harbin, J. Wang, B. D. Hamman, ‘Differential PROTAC substrate specificity dictated by orientation of recruited E3 ligase’, Nat. Commun. 2019. 10, 131.
- 7R. Verma, D. Mohl, R. J. Deshaies, ‘Harnessing the power of proteolysis for targeted protein inactivation’, Moll. Cell. 2020, 77, 446–460.
- 8J. Yan, T. Li, Z. Miao, P. Wang, C. Sheng, C. Zhuang, ‘Homobivalent, trivalent, and covalent PROTACs: Emerging strategies for protein degradation’, J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 8798–8827.
- 9R. G. Guenette, S. W. Yang, J. Min, B. Pei, P. R. Potts, ‘Target and tissue selectivity of PROTAC degraders’, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022, 51, 5740–5756.
- 10J. Chotitumnavee, Y. Yamashita, Y. Takahashi, Y. Takada, T. Iida, M. Oba, Y. Itoh, T. Suzuki, ‘Selective degradation of histone deacetylase 8 mediated by a proteolysis targeting chimera (PROTAC)’, Chem. Commun. (Camb.) 2022, 58, 4635–4638.
- 11C. M. Crews, ‘Targeting the undruggable proteome: the small molecules of my dreams’, Chem. Biol. 2010, 17, 551–555.
- 12D. P. Bondeson, B. E. Smith, G. M. Burslem, A. D. Buhimschi, J. Hines, S. Jaime-Figueroa, J. Wang, B. D. Hamman, A. Ishchenko, C. M. Crews, ‘Lessons in PROTAC design from selective degradation with a promiscuous warhead’, Cell Chem. Biol. 2018, 25, 78–87.e75.
- 13H. Yokoo, N. Shibata, A. Endo, T. Ito, Y. Yanase, Y. Murakami, K. Fujii, K. Hamamura, Y. Saeki, M. Naito, K. Aritake, Y. Demizu, ‘Discovery of a highly potent and selective degrader targeting hematopoietic prostaglandin D synthase via in silico design’, J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 15868–15882.
- 14N. Ohoka, K. Okuhira, M. Ito, K. Nagai, N. Shibata, T. Hattori, O. Ujikawa, K. Shimokawa, O. Sano, R. Koyama, H. Fujita, M. Teratani, H. Matsumoto, Y. Imaeda, H. Nara, N. Cho, M. Naito, ‘In vivo knockdown of pathogenic proteins via specific and nongenetic inhibitor of apoptosis protein (IAP)-dependent protein erasers (SNIPERs)’, J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 4556–4570.
- 15J. Chen, M. Qiu, F. Ma, L. Yang, Z. Glass, Q. Xu, ‘Enhanced protein degradation by intracellular delivery of pre-fused PROTACs using lipid-like nanoparticles’, J. Controlled Release 2021, 330, 1244–1249.
- 16A. Saraswat, M. Patki, Y. Fu, S. Barot, V. V. Dukhande, K. Patel, ‘Nanoformulation of PROteolysis TArgeting Chimera targeting ′undruggable′ c-Myc for the treatment of pancreatic cancer’, Nanomedicine (Lond) 2020, 15, 1761–1777.
- 17F. J. Cimas, E. Niza, A. Juan, M. D. M. Noblejas-López, I. Bravo, A. Lara-Sanchez, C. Alonso-Moreno, A. Ocaña, ‘Controlled delivery of BET-PROTACs: In vitro evaluation of MZ1-loaded polymeric antibody conjugated nanoparticles in breast cancer’, Pharmaceutica 2020, 12, 986.
- 18J. Lu, Y. Qian, M. Altieri, H. Dong, J. Wang, K. Raina, J. Hines, J. D. Winkler, A. P. Crew, K. Coleman, C. M. Crews, ‘Hijacking the E3 ubiquitin ligase cereblon to efficiently target BRD4’, Chem. Biol. 2015, 22, 755–763.
- 19M. Yuan, Y. Chu, Y. Duan, ‘Reversible covalent PROTACs: Novel and efficient targeted degradation strategy’, Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 691093.
- 20E. DeVita, ‘10 years into the resurgence of covalent drugs’, Future Med. Chem. 2021, 13, 193–210.
- 21I. D. Kuntz, K. Chen, K. A. Sharp, P. A. Kollman, ‘The maximal affinity of ligands’, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 9997–10002.
- 22A. J. Smith, X. Zhang, A. G. Leach, K. N. Houk, ‘Beyond picomolar affinities: Quantitative aspects of noncovalent and covalent binding of drugs to proteins’, J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 225–233.
- 23P. A. Borea, A. Dalpiaz, K. Varani, P. Gilli, G. Gilli, ‘Can thermodynamic measurements of receptor binding yield information on drug affinity and efficacy?’, Biochem. Pharmacol. 2000, 60, 1549–1556.
- 24P. Gilli, V. Ferretti, G. Gilli, P. A. Borea, ‘Enthalpy-entropy compensation in drug-receptor binding’, J. Phys. Chem. 1994, 98, 1515–1518.
- 25J. Singh, R. C. Petter, T. A. Baillie, A. Whitty, ‘The resurgence of covalent drugs’, Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery 2011, 10, 307–317.
- 26H. Lebraud, D. J. Wright, C. N. Johnson, T. D. Heightman, ‘Protein degradation by in-cell self-assembly of proteolysis targeting chimeras’, ACS Cent. Sci. 2016, 2, 927–934.
- 27G. M. Burslem, B. E. Smith, A. C. Lai, S. Jaime-Figueroa, D. C. McQuaid, D. P. Bondeson, M. Toure, H. Dong, Y. Qian, J. Wang, A. P. Crew, J. Hines, C. M. Crews, ‘The advantages of targeted protein degradation over inhibition: An RTK case study’, Cell Chem. Biol. 2018, 25, 67–77.e63.
- 28D. L. Buckley, K. Raina, N. Darricarrere, J. Hines, J. L. Gustafson, I. E. Smith, A. H. Miah, J. D. Harling, C. M. Crews, ‘HaloPROTACS: Use of small molecule PROTACs to induce degradation of HaloTag fusion proteins’, ACS Chem. Biol. 2015, 10, 1831–1837.
- 29S. Tomoshige, M. Naito, Y. Hashimoto, M. Ishikawa, ‘Degradation of HaloTag-fused nuclear proteins using bestatin-HaloTag ligand hybrid molecules’, Org. Biomol. Chem. 2015, 13, 9746–9750.
- 30G. Xue, J. Chen, L. Liu, D. Zhou, Y. Zuo, T. Fu, Z. Pan, ‘Protein degradation through covalent inhibitor-based PROTACs’, Chem. Commun. (Camb.) 2020, 56, 1521–1524.
- 31C. P. Tinworth, H. Lithgow, L. Dittus, Z. I. Bassi, S. E. Hughes, M. Muelbaier, H. Dai, I. E. D. Smith, W. J. Kerr, G. A. Burley, M. Bantscheff, J. D. Harling, ‘PROTAC-mediated degradation of Bruton's tyrosine kinase is inhibited by covalent binding’, ACS Chem. Biol. 2019, 14, 342–347.
- 32R. Gabizon, N. London, ‘The rise of covalent proteolysis targeting chimeras’, Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2021, 62, 24–33.
- 33X. Zhang, V. M. Crowley, T. G. Wucherpfennig, M. M. Dix, B. F. Cravatt, Nat. Chem. Biol. 2019, 15, 737–746.
- 34C. C. Ward, J. I. Kleinman, S. M. Brittain, P. S. Lee, C. Y. S. Chung, K. Kim, Y. Petri, J. R. Thomas, J. A. Tallarico, J. M. McKenna, M. Schirle, D. K. Nomura, ‘Electrophilic PROTACs that degrade nuclear proteins by engaging DCAF16’, ACS Chem. Biol. 2019, 14, 2430–2440.
- 35J. N. Spradlin, X. Hu, C. C. Ward, S. M. Brittain, M. D. Jones, L. Ou, M. To, A. Proudfoot, E. Ornelas, M. Woldegiorgis, J. A. Olzmann, D. E. Bussiere, J. R. Thomas, J. A. Tallarico, J. M. McKenna, M. Schirle, T. J. Maimone, D. K. Nomura, ‘Harnessing the anti-cancer natural product nimbolide for targeted protein degradation’, Nat. Chem. Biol. 2019, 15, 747–755.
- 36W. H. Guo, X. Qi, X. Yu, Y. Liu, C. I. Chung, F. Bai, X. Lin, D. Lu, L. Wang, J. Chen, L. H. Su, K. J. Nomie, F. Li, M. C. Wang, X. Shu, J. N. Onuchic, J. A. Woyach, M. L. Wang, J. Wang, ‘Enhancing intracellular accumulation and target engagement of PROTACs with reversible covalent chemistry’, Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4268.
- 37R. Gabizon, A. Shraga, P. Gehrtz, E. Livnah, Y. Shorer, N. Gurwicz, L. Avram, T. Unger, H. Aharoni, S. Albeck, A. Brandis, Z. Shulman, B. Z. Katz, Y. Herishanu, N. London, ‘Efficient targeted degradation via reversible and irreversible covalent PROTACs’, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 11734–11742.
- 38D. Abegg, G. Gasparini, D. G. Hoch, A. Shuster, E. Bartolami, S. Matile, A. Adibekian, ‘Strained cyclic disulfides enable cellular uptake by reacting with the transferrin receptor’, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 231–238.
- 39G. Gasparini, G. Sargsyan, E. K. Bang, N. Sakai, S. Matile, ‘Ring tension applied to thiol-mediated cellular uptake’, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2015, 54, 7328–7331.
- 40A. Chandrasekaran, L. Shen, S. Lockhead, A. Oganesian, J. Wang, J. Scatina, ‘Reversible covalent binding of neratinib to human serum albumin in vitro’, Drug Metab. Lett. 2010, 4, 220–227.
- 41D. Lin, S. Saleh, D. C. Liebler, ‘Reversibility of covalent electrophile-protein adducts and chemical toxicity’, Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2008, 21, 2361–2369.
- 42L. Peng, Z. Zhang, C. Lei, S. Li, Z. Zhang, X. Ren, Y. Chang, Y. Zhang, Y. Xu, K. Ding, ‘Identification of new small-molecule inducers of estrogen-related receptor α (ERRα) degradation’, ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 10, 767–772.
- 43B. Tong, M. Luo, Y. Xie, J. N. Spradlin, J. A. Tallarico, J. M. McKenna, M. Schirle, T. J. Maimone, D. K. Nomura, ‘Bardoxolone conjugation enables targeted protein degradation of BRD’, Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15543.
- 44S. Lu, X. He, D. Ni, J. Zhang, ‘Allosteric modulator discovery: From serendipity to structure-based design’, J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 6405–6421.
- 45X. Lu, J. B. Smaill, K. Ding, ‘New promise and opportunities for allosteric kinase inhibitors’, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2020, 59, 13764–13776.
- 46K. Shimokawa, N. Shibata, T. Sameshima, N. Miyamoto, O. Ujikawa, H. Nara, N. Ohoka, T. Hattori, N. Cho, M. Naito, ‘Targeting the allosteric site of oncoprotein BCR-ABL as an alternative strategy for effective target protein degradation’, ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 8, 1042–1047.
- 47G. M. Burslem, A. R. Schultz, D. P. Bondeson, C. A. Eide, S. L. SavageStevens, B. J. Druker, C. M. Crews, ‘Targeting BCR-ABL1 in chronic myeloid leukemia by PROTAC-mediated targeted protein degradation’, Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 4744–4753.
- 48M. Wang, J. Lu, M. Wang, C. Y. Yang, S. Wang, ‘Discovery of SHP2-D26 as a first, potent, and effective PROTAC degrader of SHP2 protein’, J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 7510–7528.
- 49S. Vollmer, D. Cunoosamy, H. Lv, H. Feng, X. Li, Z. Nan, W. Yang, M. W. D. Perry, ‘Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of MEK PROTACs’, J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 157–162.
- 50C. Zhou, Z. Fan, Z. Zhou, Y. Li, R. Cui, C. Liu, G. Zhou, X. Diao, H. Jiang, M. Zheng, S. Zhang, T. Xu, ‘Discovery of the first-in-class agonist-based SOS1 PROTACs effective in human cancer cells harboring various KRAS mutations’, J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 3923–3942.
- 51H. Xu, N. Ohoka, H. Yokoo, K. Nemoto, T. Ohtsuki, H. Matsufuji, M. Naito, T. Inoue, G. Tsuji, Y. Demizu, ‘Development of agonist-based PROTACs targeting liver × receptor’, Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 674967.
- 52M. X. Li, Y. Q. Yang, Q. Y. Zhao, Y. Wu, L. Song, H. Y. Yang, M. He, H. Y. Gao, B. L. Song, J. Luo, Y. Rao, ‘Degradation versus inhibition: Development of proteolysis-targeting chimeras for overcoming statin-induced compensatory upregulation of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase’, J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 4908–4928.
- 53M. S. Brown, J. L. Goldstein, ‘Multivalent feedback regulation of HMG CoA reductase, a control mechanism coordinating isoprenoid synthesis and cell growth’, J. Lipid Res. 1980, 21, 505–517.
- 54J. L. Goldstein, M. S. Brown, ‘Regulation of the mevalonate pathway’, Nature 1990, 343, 425–430.
- 55Y. Itoh, R. Kitaguchi, M. Ishikawa, M. Naito, Y. Hashimoto, ‘Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of nuclear receptor-degradation inducers’, Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 6768–6778.
- 56F. Morgillo, H. Y. Lee, ‘Resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor-targeted therapy’, Drug Resist. Updat. 2005, 8, 298–310.
- 57J. Schmitt, S. Huang, E. Goodfellow, C. Williams, B. J. Jean-Claude, ‘Design and synthesis of a trifunctional molecular system ‘programmed’ to block epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase, induce high levels of DNA damage, and inhibit the DNA repair enzyme (poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase) in prostate cancer cells’, J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 5752–5762.
- 58T. DiDesidero, A. Fioravanti, P. Orlandi, B. Canu, R. Giannini, N. Borrelli, S. Man, P. Xu, G. Fontanini, F. Basolo, R. S. Kerbel, G. Francia, R. Danesi, G. Bocci, ‘Antiproliferative and proapoptotic activity of sunitinib on endothelial and anaplastic thyroid cancer cells via inhibition of Akt and ERK1/2 phosphorylation and by down-regulation of cyclin-D’, J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, E1465–1473.
- 59J. Lötsch, G. Geisslinger, ‘Low-dose drug combinations along molecular pathways could maximize therapeutic effectiveness while minimizing collateral adverse effects’, Drug. Discov. Today 2011, 16, 1001–1006.
- 60J. Woodcock, J. P. Griffin, R. E. Behrman, ‘Development of novel combination therapies’, N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 985–987.
- 61M. Zheng, J. Huo, X. Gu, Y. Wang, C. Wu, Q. Zhang, W. Wang, Y. Liu, Y. Liu, X. Zhou, L. Chen, Y. Zhou, H. Li, ‘Rational design and synthesis of novel dual PROTACs for simultaneous degradation of EGFR and PARP’, J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 7839–7852.
- 62A. Anighoro, J. Bajorath, G. Rastelli, ‘Polypharmacology: challenges and opportunities in drug discovery’, J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 7874–7887.
- 63S. Imaide, K. M. Riching, N. Makukhin, V. Vetma, C. Whitworth, S. J. Hughes, N. Trainor, S. D. Mahan, N. Murphy, A. D. Cowan, K. H. Chan, C. Craigon, A. Testa, C. Maniaci, M. Urh, D. L. Daniels, A. Ciulli, ‘Trivalent PROTACs enhance protein degradation via combined avidity and cooperativity’, Nat. Chem. Biol. 2021, 17, 1157–1167.
- 64J. Jin, Y. Wu, J. Chen, Y. Shen, L. Zhang, H. Zhang, L. Chen, H. Yuan, H. Chen, W. Zhang, X. Luan, ‘The peptide PROTAC modality: a novel strategy for targeted protein ubiquitination’, Theranostics 2020, 10, 10141–10153.
- 65J. Hines, J. D. Gough, T. W. Corson, C. M. Crews, ‘Posttranslational protein knockdown coupled to receptor tyrosine kinase activation with phosphoPROTACs’, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 8942–8947.
- 66R. E. Moellering, M. Cornejo, T. N. Davis, C. DelBianco, J. C. Aster, S. C. Blacklow, A. L. Kung, D. G. Gilliland, G. L. Verdine, J. E. Bradner, ‘Direct inhibition of the NOTCH transcription factor complex’, Nature 2009, 462, 182–188.
- 67N. Ohoka, T. Misawa, M. Kurihara, Y. Demizu, M. Naito, ‘Development of a peptide-based inducer of protein degradation targeting NOTCH1’, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 4985–4988.
- 68K. Montrose, G. W. Krissansen, ‘Design of a PROTAC that antagonizes and destroys the cancer-forming X-protein of the hepatitis B virus’, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 453, 735–740.
- 69R. K. Henning, J. O. Varghese, S. Das, A. Nag, G. Tang, K. Tang, A. M. Sutherland, J. R. Heath, ‘Degradation of Akt using protein-catalyzed capture agents’, J. Pept. Sci. 2016, 22, 196–200.
- 70D. Ma, Y. Zou, Y. Chu, Z. Liu, G. Liu, J. Chu, M. Li, J. Wang, S. Y. Sun, Z. Chang, ‘A cell-permeable peptide-based PROTAC against the oncoprotein CREPT proficiently inhibits pancreatic cancer’, Theranostics 2020, 10, 3708–3721.
- 71Y. Demizu, N. Ohoka, T. Nagakubo, H. Yamashita, T. Misawa, K. Okuhira, M. Naito, M. Kurihara, ‘Development of a peptide-based inducer of nuclear receptors degradation’, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 2655–2658.
- 72H. Yokoo, N. Ohoka, M. Naito, Y. Demizu, ‘Design and synthesis of peptide-based chimeric molecules to induce degradation of the estrogen and androgen receptors’, Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2020, 28, 115595.
- 73H. Yokoo, N. Ohoka, M. Takyo, T. Ito, K. Tsuchiya, T. Kurohara, K. Fukuhara, T. Inoue, M. Naito, Y. Demizu, ‘Peptide stapling improves the sustainability of a peptide-based chimeric molecule that induces targeted protein degradation’, Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8772.
- 74Y. Jiang, Q. Deng, H. Zhao, M. Xie, L. Chen, F. Yin, X. Qin, W. Zheng, Y. Zhao, Z. Li, ‘Development of stabilized peptide-based PROTACs against estrogen receptor α’, ACS Chem. Biol. 2018, 13, 628–635.
- 75Y. Dai, N. Yue, J. Gong, C. Liu, Q. Li, J. Zhou, W. Huang, H. Qian, ‘Development of cell-permeable peptide-based PROTACs targeting estrogen receptor α’, Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 187, 111967.
- 76Y. Lee, J. Heo, H. Jeong, K. T. Hong, D. H. Kwon, M. H. Shin, M. Oh, G. A. Sable, G. O. Ahn, J. S. Lee, H. K. Song, H. S. Lim, ‘Targeted degradation of transcription coactivator SRC-1 through the N-degron pathway’, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2020, 59, 17548–17555.
- 77C. Zhang, S. He, Z. Zeng, P. Cheng, K. Pu, ‘Smart nano-PROTACs reprogram tumor microenvironment for activatable photo-metabolic cancer immunotherapy’, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2022, 61, e202114957.
- 78C. Zhang, Z. Zeng, D. Cui, S. He, Y. Jiang, J. Li, J. Huang, K. Pu, ‘Semiconducting polymer nano-PROTACs for activatable photo-immunometabolic cancer therapy’, Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2934.
- 79M. Roos, U. Pradère, R. P. Ngondo, A. Behera, S. Allegrini, G. Civenni, J. A. Zagalak, J. R. Marchand, M. Menzi, H. Towbin, J. Scheuermann, D. Neri, A. Caflisch, C. V. Catapano, C. Ciaudo, J. Hall, ‘A small-molecule inhibitor of Lin28’, ACS Chem. Biol. 2016, 11, 2773–2781.
- 80A. Ghidini, A. Clery, F. Halloy, F. H. T. Allain, J. Hall, ‘RNA-PROTACs: Degraders of RNA-binding proteins’, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2021, 60, 3163–3169.
- 81T. W. Corson, N. Aberle, C. M. Crews, ‘Design and applications of bifunctional small molecules: Why two heads are better than one’, ACS Chem. Biol. 2008, 3, 677–692.
- 82F. E. Loughlin, L. F. Gebert, H. Towbin, A. Brunschweiger, J. Hall, F. H. Allain, ‘Structural basis of pre-let-7 miRNA recognition by the zinc knuckles of pluripotency factor Lin28’, Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2011, 19, 84–89.
- 83K. T. G. Samarasinghe, S. Jaime-Figueroa, M. Burgess, D. A. Nalawansha, K. Dai, Z. Hu, A. Bebenek, S. A. Holley, C. M. Crews, ‘Targeted degradation of transcription factors by TRAFTACs: TRAnscription Factor TArgeting Chimeras’, Cell Chem. Biol. 2021, 28, 648–661.
- 84G. E. Winter, D. L. Buckley, J. Paulk, J. M. Roberts, A. Souza, S. Dhe-Paganon, J. E. Bradner, ‘Phthalimide conjugation as a strategy for in vivo target protein degradation’, Science 2015, 348, 1376–1381.
- 85J. Liu, H. Chen, H. Kaniskan, L. Xie, X. Chen, J. Jin, W. Wei, ‘TF-PROTACs enable targeted degradation of transcription factors’, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 8902–8910.
- 86J. Shao, Y. Yan, D. Ding, D. Wang, Y. He, Y. Pan, W. Yan, A. Kharbanda, H. Y. Li, H. Huang, ‘Destruction of DNA-binding proteins by programmable oligonucleotide PROTAC (O′PROTAC): Effective targeting of LEF1 and ERG’, Adv. Sci. (Weinh) 2021, e2102555.
- 87Y. Yan, J. Shao, D. Ding, Y. Pan, P. Tran, W. Yan, Z. Wang, H. Y. Li, H. Huang, ‘3-Aminophthalic acid, a new cereblon ligand for targeted protein degradation by O'PROTAC’, Chem. Commun. (Camb.) 2022, 58, 2383–2386.
- 88M. Naganuma, N. Ohoka, G. Tsuji, H. Tsujimura, K. Matsuno, T. Inoue, M. Naito, Y. Demizu, ‘Development of chimeric molecules that degrade the estrogen receptor using decoy oligonucleotide ligands’, ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2022, 13, 134–139.
- 89D. Varshney, J. Spiegel, K. Zyner, D. Tannahill, S. Balasubramanian, ‘The regulation and functions of DNA and RNA G-quadruplexes’, Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 459–474.
- 90H. Liu, Y. N. Lu, T. Paul, G. Periz, M. T. Banco, A. R. Ferré-D′Amaré, J. D. Rothstein, L. R. Hayes, S. Myong, J. Wang, ‘A helicase unwinds hexanucleotide repeat RNA G-quadruplexes and facilitates repeat-associated non-AUG translation’, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 7368–7379.
- 91K. M. Patil, D. Chin, H. L. Seah, Q. Shi, K. W. Lim, A. T. Phan, ‘G4-PROTAC: targeted degradation of a G-quadruplex binding protein’, Chem. Commun. (Camb.) 2021, 57, 12816–12819.