Antibacterial Diphenyl Ether, Benzophenone and Xanthone Derivatives from Aspergillus flavipes
Abstract
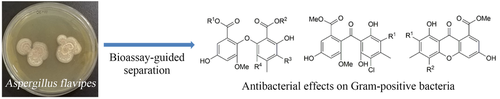
The extract of the strain Aspergillus flavipes DL-11 exerted antibacterial activities against six Gram-positive bacteria. During the following bioassay-guided separation, ten diphenyl ethers (1–10), two benzophenones (11–12), together with two xanthones (13–14) were isolated. Among them, 4′-chloroasterric acid (1) was a new chlorinated diphenyl ether. Their structures were elucidated by extensive spectroscopic data analysis, including IR, HR-ESI-MS, NMR experiments, and by comparison with the literature data. All compounds showed moderate to strong antibacterial effects on different Gram-positive bacteria with MIC values that ranged from 3.13 to 50 μg/mL, but none of the compounds exhibited activity against Gram-negative bacteria Vibrio parahaemolyticus ATCC17802 (MIC>100 μg/mL). In particular, the MICs of some compounds are at the level of positive control.