Manganese-Catalyzed Mono-N-Methylation of Aliphatic Primary Amines without the Requirement of External High-Hydrogen Pressure
Jiale Ji
Shanghai Key Laboratory of Molecular Catalysis and Innovative Materials, Department of Chemistry, Fudan University, 2005 Songhu Road, Shanghai, 200438 China
Search for more papers by this authorYinghao Huo
Shanghai Key Laboratory of Molecular Catalysis and Innovative Materials, Department of Chemistry, Fudan University, 2005 Songhu Road, Shanghai, 200438 China
Search for more papers by this authorZhaowen Dai
Shanghai Key Laboratory of Molecular Catalysis and Innovative Materials, Department of Chemistry, Fudan University, 2005 Songhu Road, Shanghai, 200438 China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Dr. Zhening Chen
State Key Laboratory of Structural Chemistry, Fujian Institute of Research on the Structure of Matter, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 155 Yangqiao West Road, Fuzhou, 350002 China.
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Tao Tu
Shanghai Key Laboratory of Molecular Catalysis and Innovative Materials, Department of Chemistry, Fudan University, 2005 Songhu Road, Shanghai, 200438 China
State Key Laboratory of Organometallic Chemistry, Shanghai Institute of Organic Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 354 Fenglin Road, Shanghai, 200032 China
Search for more papers by this authorJiale Ji
Shanghai Key Laboratory of Molecular Catalysis and Innovative Materials, Department of Chemistry, Fudan University, 2005 Songhu Road, Shanghai, 200438 China
Search for more papers by this authorYinghao Huo
Shanghai Key Laboratory of Molecular Catalysis and Innovative Materials, Department of Chemistry, Fudan University, 2005 Songhu Road, Shanghai, 200438 China
Search for more papers by this authorZhaowen Dai
Shanghai Key Laboratory of Molecular Catalysis and Innovative Materials, Department of Chemistry, Fudan University, 2005 Songhu Road, Shanghai, 200438 China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Dr. Zhening Chen
State Key Laboratory of Structural Chemistry, Fujian Institute of Research on the Structure of Matter, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 155 Yangqiao West Road, Fuzhou, 350002 China.
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Tao Tu
Shanghai Key Laboratory of Molecular Catalysis and Innovative Materials, Department of Chemistry, Fudan University, 2005 Songhu Road, Shanghai, 200438 China
State Key Laboratory of Organometallic Chemistry, Shanghai Institute of Organic Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 354 Fenglin Road, Shanghai, 200032 China
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
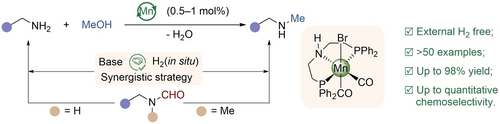
A synergistic strategy enables the selective synthesis of mono-N-methylated aliphatic primary amines, including deuterium-labelled drugs. This innovative approach combines an earth-abundant manganese catalyst with a weak base, resulting in a practical and sustainable protocol for mono-N-methylation. By effectively inhibiting the formation of formamide byproducts, it eliminates the need for external high-pressure hydrogen.
Abstract
The synthesis of mono-N-methylated aliphatic primary amines has traditionally been challenging, requiring noble metal catalysts and high-pressure H2 for achieving satisfactory yields and selectivity. Herein, we developed an approach for the selective coupling of methanol and aliphatic primary amines, without high-pressure hydrogen, using a manganese-based catalyst. Remarkably, up to 98 % yields with broad substrate scope were achieved at low catalyst loadings. Notably, due to the weak base-catalyzed alcoholysis of formamide intermediates, our novel protocol not only obviates the addition of high-pressure H2 but also prevents side secondary N-methylation, supported by control experiments and density functional theory calculations.
Conflict of interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available in the supplementary material of this article.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie202318763-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf6 MB | Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1
- 1aQ. Sun, J. F. Soule, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 10806;
- 1bA. F. B. Rader, F. Reichart, M. Weinmuller, H. Kessler, Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 2766;
- 1cJ. Chatterjee, F. Rechenmacher, H. Kessler, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 254;
- 1dE. J. Barreiro, A. E. Kümmerle, C. A. M. Fraga, Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 5215.
- 2
- 2aY. Chen, Chem. Eur. J. 2019, 25, 3405;
- 2bS. Moulay, Curr. Org. Chem. 2019, 23, 1695;
- 2cG. Yan, A. J. Borah, L. Wang, M. Yang, Adv. Synth. Catal. 2015, 357, 1333.
- 3
- 3aM. He, K. Zhang, Y. Guan, Y. Sun, B. Han, Nat. Sci. Rev. 2023, DOI: 10.1093/nsr/nwad046;
- 3bD. Wen, J. Chen, Q. Zheng, S. Yang, T. Tu, CCS Chem. 2023, 5, 1602;
- 3cP. Gao, L. Zhong, B. Han, M. He, Y. Sun, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202210095;
- 3dA. Kumar, P. Daw, D. Milstein, Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 385;
- 3eC. Wu, D. Cheng, M. Wang, D. Ma, Energy Fuels 2021, 35, 19012;
- 3fS. Kar, A. Goeppert, G. K. S. Prakash, Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 2892;
- 3gR. P. Ye, J. Ding, W. Gong, M. D. Argyle, Q. Zhong, Y. Wang, C. K. Russell, Z. Xu, A. G. Russell, Q. Li, M. Fan, Y. G. Yao, Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5698;
- 3hX. Zhen, Y. Wang, Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev. 2015, 52, 477;
- 3iA. Goeppert, M. Czaun, J. P. Jones, G. K. Surya Prakash, G. A. Olah, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 7995.
- 4
- 4aSheetal, P. Mehara, P. Das, Coord. Chem. Rev. 2023, 475, 214851;
- 4bH. Li, C. Li, W. Liu, Y. Yao, Y. Li, B. Zhang, C. Qiu, ChemSusChem 2023, 16, e202300377;
- 4cV. Goyal, N. Sarki, A. Narani, G. Naik, K. Natte, R. V. Jagadeesh, Coord. Chem. Rev. 2023, 474, 214827;
- 4dM. Jafarzadeh, S. H. Sobhani, K. Gajewski, E. Kianmehr, Org. Biomol. Chem. 2022, 20, 7713;
- 4eE. S. Gulyaeva, E. S. Osipova, R. Buhaibeh, Y. Canac, J.-B. Sortais, D. A. Valyaev, Coord. Chem. Rev. 2022, 458, 214421;
- 4fL. M. Kabadwal, S. Bera, D. Banerjee, Org. Chem. Front. 2021, 8, 7077;
- 4gX. Wang, K. Zhao, H. Wang, F. Shi, Catal. Sci. Technol. 2021, 11, 7239;
- 4hB. Paul, M. Maji, K. Chakrabarti, S. Kundu, Org. Biomol. Chem. 2020, 18, 2193;
- 4iK. Natte, H. Neumann, M. Beller, R. V. Jagadeesh, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 6384.
- 5
- 5aM. A. R. Jamil, A. S. Touchy, M. N. Rashed, K. W. Ting, S. M. A. H. Siddiki, T. Toyao, Z. Maeno, K.-i. Shimizu, J. Catal. 2019, 371, 47;
- 5bG. Choi, S. H. Hong, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 6166;
- 5cG. Choi, S. H. Hong, ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 716;
- 5dA. Lator, S. Gaillard, A. Poater, J.-L. Renaud, Org. Lett. 2018, 20, 5985;
- 5eR. Liang, S. Li, R. Wang, L. Lu, F. Li, Org. Lett. 2017, 19, 5790; T. T. Dang, B. Ramalingam, A. M. Seayad, ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 4082.
- 6
- 6aJ. Wu, C. Darcel, Adv. Synth. Catal. 2023, 365, 948;
- 6bY. Gao, G. Hong, B.-M. Yang, Y. Zhao, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2023, 52, 5541;
- 6cD. Y. Yang, H. Wang, C. R. Chang, Adv. Synth. Catal. 2022, 364, 3100;
- 6dB. G. Reed-Berendt, D. E. Latham, M. B. Dambatta, L. C. Morrill, ACS Cent. Sci. 2021, 7, 570;
- 6eA. Corma, J. Navas, M. J. Sabater, Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 1410;
- 6fF. Huang, Z. Liu, Z. Yu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 862;
- 6gQ. Yang, Q. Wang, Z. Yu, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 2305;
- 6hY. Obora, ACS Catal. 2014, 4, 3972;
- 6iC. Gunanathan, D. Milstein, Science 2013, 341, 249.
- 7T. R. B. M. R. Grigg, S. Sutthivaiyakit, N. Tongpenyai, J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1981, 611.
- 8Z. Shao, Y. Li, C. Liu, W. Ai, S. P. Luo, Q. Liu, Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 591.
- 9N. Sarki, V. Goyal, N. K. Tyagi, Puttaswamy, A. Narani, A. Ray, K. Natte, ChemCatChem 2021, 13, 1722.
- 10L. Jiang, X. Zhang, Y. Wang, F. Guo, Z. Hou, Asian J. Org. Chem. 2021, 10, 2165.
- 11
- 11aI. Borthakur, A. Sau, S. Kundu, Coord. Chem. Rev. 2022, 451, 214257;
- 11bS. Jalwal, V. Atreya, T. Singh, S. Chakraborty, Tetrahedron Lett. 2021, 82, 153362;
- 11cS. Budweg, K. Junge, M. Beller, Catal. Sci. Technol. 2020, 10, 3825;
- 11dM. R. Elsby, R. T. Baker, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 8933;
- 11eL. Alig, M. Fritz, S. Schneider, Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 2681.
- 12
- 12aS. Friães, S. Realista, H. Mourão, B. Royo, Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2022, 2022, e202100884;
- 12bY. Wang, M. Wang, Y. Li, Q. Liu, Chem 2021, 7, 1180;
- 12cN. Sarki, V. Goyal, K. Natte, R. V. Jagadeesh, Adv. Synth. Catal. 2021, 363, 5028;
- 12dB. G. Reed-Berendt, K. Polidano, L. C. Morrill, Org. Biomol. Chem. 2019, 17, 1595;
- 12eT. Irrgang, R. Kempe, Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 2524;
- 12fG. A. Filonenko, R. van Putten, E. J. M. Hensen, E. A. Pidko, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 1459;
- 12gA. Mukherjee, D. Milstein, ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 11435.
- 13
- 13aB. G. Reed-Berendt, N. Mast, L. C. Morrill, Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2020, 2020, 1136;
- 13bJ. Neumann, S. Elangovan, A. Spannenberg, K. Junge, M. Beller, Chem. Eur. J. 2017, 23, 5410;
- 13cA. Bruneau-Voisine, D. Wang, V. Dorcet, T. Roisnel, C. Darcel, J.-B. Sortais, J. Catal. 2017, 347, 57;
- 13dS. Elangovan, J. Neumann, J. B. Sortais, K. Junge, C. Darcel, M. Beller, Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12641.
- 14Z. Lu, Q. Zheng, S. Yang, C. Qian, Y. Shen, T. Tu, ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 10796.
- 15Z. Lu, Q. Zheng, G. Zeng, Y. Kuang, J. H. Clark, T. Tu, Sci. China Chem. 2021, 64, 1361.
- 16
- 16aJ. Wang, J. Wu, Z.-N. Chen, D. Wen, J. Chen, Q. Zheng, X. Xu, T. Tu, J. Catal. 2020, 389, 337;
- 16bJ. Chen, J. Wu, T. Tu, ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 11744.
- 17
- 17aK. Das, S. Waiba, A. Jana, B. Maji, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022, 51, 4386;
- 17bE. Podyacheva, O. I. Afanasyev, D. V. Vasilyev, D. Chusov, ACS Catal. 2022, 12, 7142.
- 18
- 18aC. Huang, J. Li, J. Wang, Q. Zheng, Z. Li, T. Tu, Sci. China Chem. 2020, 64, 66.
- 19
- 19aY. Pan, Z. Luo, X. Xu, H. Zhao, J. Han, L. Xu, Q. Fan, J. Xiao, Adv. Synth. Catal. 2019, 361, 3800;
- 19bY. Pan, Z. Luo, J. Han, X. Xu, C. Chen, H. Zhao, L. Xu, Q. Fan, J. Xiao, Adv. Synth. Catal. 2019, 361, 2301;
- 19cX. Cui, X. Dai, Y. Zhang, Y. Deng, F. Shi, Chem. Sci. 2014, 5, 649;
- 19dX. Cui, Y. Zhang, Y. Deng, F. Shi, Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 13521;
- 19eY. Li, I. Sorribes, T. Yan, K. Junge, M. Beller, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 12156;
- 19fO. Jacquet, X. Frogneux, C. Das Neves Gomes, T. Cantat, Chem. Sci. 2013, 4, 2127.
- 20J. R. Khusnutdinova, Y. Ben-David, D. Milstein, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 6269.
- 21
- 21aP. Liu, X. Chen, X. Xu, L. Yang, G. Zeng, C. Ye, Q. Shi, J. Yang, F. Li, J. Catal. 2022, 410, 333;
- 21bX. Zhang, Q. Chen, R. Song, J. Xu, W. Tian, S. Li, Z. Jin, Y. R. Chi, ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 5475;
- 21cT. Pirali, M. Serafini, S. Cargnin, A. A. Genazzani, J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 5276;
- 21dT. G. Gant, J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 3595;
- 21eA. Katsnelson, Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 656.
- 22
- 22aA. Bruneau-Voisine, L. Pallova, S. Bastin, V. César, J.-B. Sortais, Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 314;
- 22bJ. Sklyaruk, J. C. Borghs, O. El-Sepelgy, M. Rueping, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 58, 775.
- 23
- 23aG. Xu, T. D. Grimes, T. B. Grayson, J. Chen, L. A. Thielen, H. M. Tse, P. Li, M. Kanke, T. T. Lin, A. A. Schepmoes, A. C. Swensen, V. A. Petyuk, F. Ovalle, P. Sethupathy, W. J. Qian, A. Shalev, Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1159;
- 23bF. Ovalle, T. Grimes, G. Xu, A. J. Patel, T. B. Grayson, L. A. Thielen, P. Li, A. Shalev, Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 1108.
- 24
- 24aG. Zeng, J. Wu, L. Shen, Q. Zheng, Z. N. Chen, X. Xu, T. Tu, ACS Catal. 2023, 13, 2061;
- 24bG. Zeng, L. Shen, Q. Zheng, T. Tu, ACS Catal. 2023, 13, 6222;
- 24cD. A. Kuß, M. Hölscher, W. Leitner, ACS Catal. 2022, 12, 15310;
- 24dM.-K. Zhang, W. Chen, Z. Wei, M.-L. Xu, Z. He, J. Cai, Y.-X. Chen, E. Santos, ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 6920;
- 24eL. Shen, Z.-N. Chen, Q. Zheng, J. Wu, X. Xu, T. Tu, ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 12833.
- 25S. Chakraborty, U. Gellrich, Y. Diskin-Posner, G. Leitus, L. Avram, D. Milstein, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 4229.
- 26
- 26aY. Wang, S. Liu, H. Yang, H. Li, Y. Lan, Q. Liu, Nat. Chem. 2022, 14, 1233;
- 26bW. Yang, T. Y. Kalavalapalli, A. M. Krieger, T. A. Khvorost, I. Y. Chernyshov, M. Weber, E. A. Uslamin, E. A. Pidko, G. A. Filonenko, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 8129;
- 26cR. Thenarukandiyil, R. Kamte, S. Garhwal, P. Effnert, N. Fridman, G. de Ruiter, Organometallics 2022, 42, 62;
- 26dT. W. Ng, G. Liao, K. K. Lau, H. J. Pan, Y. Zhao, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 11384;
- 26eR. Fertig, T. Irrgang, F. Freitag, J. Zander, R. Kempe, ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 8525.
- 27
- 27aW. K. Das, A. Kumar, Y. Ben-David, M. A. Iron, D. Milstein, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 12962;
- 27bS. Kar, A. Goeppert, J. Kothandaraman, G. K. S. Prakash, ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 6347.
- 28
- 28aJ. C. Borghs, V. Zubar, L. M. Azofra, J. Sklyaruk, M. Rueping, Org. Lett. 2020, 22, 4222;
- 28bJ. Sklyaruk, V. Zubar, J. C. Borghs, M. Rueping, Org. Lett. 2020, 22, 6067;
- 28cY. Wang, L. Zhu, Z. Shao, G. Li, Y. Lan, Q. Liu, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 17337;
- 28dZ. Shao, Y. Wang, Y. Liu, Q. Wang, X. Fu, Q. Liu, Org. Chem. Front. 2018, 5, 1248.
- 29
- 29aT. W. Ng, R. Tao, W. W. L. See, S. B. Poh, Y. Zhao, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202212528;
- 29bJ. Tang, J. He, S. Y. Zhao, W. Liu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202215882;
- 29cF. Sun, J. Huang, Z. Wei, C. Tang, W. Liu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202303433;
- 29dC. Liu, M. Wang, S. Liu, Y. Wang, Y. Peng, Y. Lan, Q. Liu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 5108;
- 29eP. Liu, J. Yang, Y. Ai, S. Hao, X. Chen, F. Li, J. Catal. 2021, 396, 281;
- 29fZ. Tan, B. Xiong, J. Yang, C. Ci, H. Jiang, M. Zhang, J. Catal. 2020, 392, 135;
- 29gW. Ma, X. Zhang, J. Fan, Y. Liu, W. Tang, D. Xue, C. Li, J. Xiao, C. Wang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 13506.
- 30
- 30aS. Waiba, M. Maiti, B. Maji, ACS Catal. 2022, 12, 3995–4001;
- 30bK. Das, K. Sarkar, B. Maji, ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 7060.
- 31
- 31aJ. Guo, J. Tang, H. Xi, S.-Y. Zhao, W. Liu, Chin. Chem. Lett. 2023, 34, 107731;
- 31bU. K. Das, Y. Ben-David, G. Leitus, Y. Diskin-Posner, D. Milstein, ACS Catal. 2018, 9, 479;
- 31cD. H. Nguyen, X. Trivelli, F. Capet, J.-F. Paul, F. Dumeignil, R. M. Gauvin, ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 2022.
- 32
- 32aY. Liu, H. Diao, G. Hong, J. Edward, T. Zhang, G. Yang, B. M. Yang, Y. Zhao, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 5007;
- 32bH. J. Pan, Y. Lin, T. Gao, K. K. Lau, W. Feng, B. Yang, Y. Zhao, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 18599.
- 33
- 33aW. Li, M. Huang, J. Liu, Y.-L. Huang, X.-B. Lan, Z. Ye, C. Zhao, Y. Liu, Z. Ke, ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 10377;
- 33bK. Murugesan, Z. Wei, V. G. Chandrashekhar, H. Neumann, A. Spannenberg, H. Jiao, M. Beller, R. V. Jagadeesh, Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5443.