Development of Mannosylated Lipid Nanoparticles for mRNA Cancer Vaccine with High Antigen Presentation Efficiency and Immunomodulatory Capability
Jiaqi Lei
Key Laboratory of Bioorganic Phosphorus Chemistry & Chemical Biology, Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University, 100084 Beijing, P. R. China
These authors contributed equally to the work.
Contribution: Data curation (lead), Investigation (lead), Writing - original draft (lead)
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Shaolong Qi
Key Laboratory of Bioorganic Phosphorus Chemistry & Chemical Biology, Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University, 100084 Beijing, P. R. China
These authors contributed equally to the work.
Contribution: Data curation (equal), Investigation (equal)
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Xinyang Yu
Key Laboratory of Bioorganic Phosphorus Chemistry & Chemical Biology, Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University, 100084 Beijing, P. R. China
Contribution: Investigation (supporting), Writing - original draft (supporting)
Search for more papers by this authorXiaomin Gao
Key Laboratory of Bioorganic Phosphorus Chemistry & Chemical Biology, Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University, 100084 Beijing, P. R. China
Contribution: Investigation (supporting)
Search for more papers by this authorKai Yang
Key Laboratory of Bioorganic Phosphorus Chemistry & Chemical Biology, Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University, 100084 Beijing, P. R. China
Contribution: Investigation (supporting)
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Xueyan Zhang
Key Laboratory of Bioorganic Phosphorus Chemistry & Chemical Biology, Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University, 100084 Beijing, P. R. China
Contribution: Investigation (supporting)
Search for more papers by this authorMeiqi Cheng
Key Laboratory of Bioorganic Phosphorus Chemistry & Chemical Biology, Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University, 100084 Beijing, P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Bing Bai
Key Laboratory of Bioorganic Phosphorus Chemistry & Chemical Biology, Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University, 100084 Beijing, P. R. China
Contribution: Investigation (supporting)
Search for more papers by this authorYunxuan Feng
Key Laboratory of Bioorganic Phosphorus Chemistry & Chemical Biology, Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University, 100084 Beijing, P. R. China
Contribution: Investigation (supporting)
Search for more papers by this authorMeixin Lu
Key Laboratory of Bioorganic Phosphorus Chemistry & Chemical Biology, Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University, 100084 Beijing, P. R. China
Contribution: Investigation (supporting)
Search for more papers by this authorYangfan Wang
Key Laboratory of Bioorganic Phosphorus Chemistry & Chemical Biology, Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University, 100084 Beijing, P. R. China
Contribution: Writing - original draft (supporting)
Search for more papers by this authorHongjian Li
School of Medicine, Tsinghua University, 100084 Beijing, P. R. China
Contribution: Investigation (supporting)
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Guocan Yu
Key Laboratory of Bioorganic Phosphorus Chemistry & Chemical Biology, Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University, 100084 Beijing, P. R. China
School of Medicine, Tsinghua University, 100084 Beijing, P. R. China
Contribution: Conceptualization (lead), Funding acquisition (lead), Supervision (lead), Writing - review & editing (lead)
Search for more papers by this authorJiaqi Lei
Key Laboratory of Bioorganic Phosphorus Chemistry & Chemical Biology, Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University, 100084 Beijing, P. R. China
These authors contributed equally to the work.
Contribution: Data curation (lead), Investigation (lead), Writing - original draft (lead)
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Shaolong Qi
Key Laboratory of Bioorganic Phosphorus Chemistry & Chemical Biology, Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University, 100084 Beijing, P. R. China
These authors contributed equally to the work.
Contribution: Data curation (equal), Investigation (equal)
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Xinyang Yu
Key Laboratory of Bioorganic Phosphorus Chemistry & Chemical Biology, Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University, 100084 Beijing, P. R. China
Contribution: Investigation (supporting), Writing - original draft (supporting)
Search for more papers by this authorXiaomin Gao
Key Laboratory of Bioorganic Phosphorus Chemistry & Chemical Biology, Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University, 100084 Beijing, P. R. China
Contribution: Investigation (supporting)
Search for more papers by this authorKai Yang
Key Laboratory of Bioorganic Phosphorus Chemistry & Chemical Biology, Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University, 100084 Beijing, P. R. China
Contribution: Investigation (supporting)
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Xueyan Zhang
Key Laboratory of Bioorganic Phosphorus Chemistry & Chemical Biology, Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University, 100084 Beijing, P. R. China
Contribution: Investigation (supporting)
Search for more papers by this authorMeiqi Cheng
Key Laboratory of Bioorganic Phosphorus Chemistry & Chemical Biology, Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University, 100084 Beijing, P. R. China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Bing Bai
Key Laboratory of Bioorganic Phosphorus Chemistry & Chemical Biology, Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University, 100084 Beijing, P. R. China
Contribution: Investigation (supporting)
Search for more papers by this authorYunxuan Feng
Key Laboratory of Bioorganic Phosphorus Chemistry & Chemical Biology, Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University, 100084 Beijing, P. R. China
Contribution: Investigation (supporting)
Search for more papers by this authorMeixin Lu
Key Laboratory of Bioorganic Phosphorus Chemistry & Chemical Biology, Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University, 100084 Beijing, P. R. China
Contribution: Investigation (supporting)
Search for more papers by this authorYangfan Wang
Key Laboratory of Bioorganic Phosphorus Chemistry & Chemical Biology, Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University, 100084 Beijing, P. R. China
Contribution: Writing - original draft (supporting)
Search for more papers by this authorHongjian Li
School of Medicine, Tsinghua University, 100084 Beijing, P. R. China
Contribution: Investigation (supporting)
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Guocan Yu
Key Laboratory of Bioorganic Phosphorus Chemistry & Chemical Biology, Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University, 100084 Beijing, P. R. China
School of Medicine, Tsinghua University, 100084 Beijing, P. R. China
Contribution: Conceptualization (lead), Funding acquisition (lead), Supervision (lead), Writing - review & editing (lead)
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
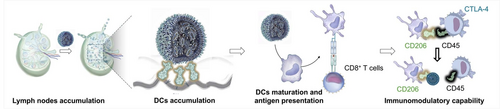
In order to promote the antitumor efficacy of mRNA vaccines, sweet lipid nanoparticles (STLNPs-Man) are developed by incorporating a mannosylated ionizable lipid to enhance the uptake by DCs through the mannose receptor-mediated endocytosis. Interestingly, STLNPs-Man exhibits the ability to downregulate the expression of cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4 on T cells through the blockade of CD206/CD45 axis to further potentiate the antitumor immunity.
Abstract
Insufficient accumulation of lipid nanoparticles (LNPs)-based mRNA vaccines in antigen presenting cells remains a key barrier to eliciting potent antitumor immune responses. Herein, we develop dendritic cells (DCs) targeting LNPs by taking advantage of mannose receptor-mediated endocytosis. Efficient delivery of mRNA to DCs is achieved in vitro and in vivo utilizing the sweet LNPs (STLNPs-Man). Intramuscular injection of mRNA vaccine (STLNPs-Man@mRNAOVA) results in a four-fold higher uptake by DCs in comparison with commercially used LNPs. Benefiting from its DCs targeting ability, STLNPs-Man@mRNAOVA significantly promotes the antitumor performances, showing a comparable therapeutic efficacy by using one-fifth of the injection dosage as the vaccine prepared from normal LNPs, thus remarkably avoiding the side effects brought by conventional mRNA vaccines. More intriguingly, STLNPs-Man@mRNAOVA exhibits the ability to downregulate the expression of cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4 on T cells due to the blockade of CD206/CD45 axis, showing brilliant potentials in promoting antitumor efficacy combined with immune checkpoint blockade therapy.
Conflict of interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie202318515-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf3.9 MB | Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1O. J. Watson, G. Barnsley, J. Toor, A. B. Hogan, P. Winskill, A. C. Ghani, Lancet Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, 1293–1302.
- 2F. P. Polack, S. J. Thomas, N. Kitchin, J. Absalon, A. Gurtman, S. Lockhart, J. L. Perez, G. Perez Marc, E. D. Moreira, C. Zerbini, R. Bailey, K. A. Swanson, S. Roychoudhury, K. Koury, P. Li, W. V. Kalina, D. Cooper, R. W. Frenck, Jr., L. L. Hammitt, O. Tureci, H. Nell, A. Schaefer, S. Unal, D. B. Tresnan, S. Mather, P. R. Dormitzer, U. Sahin, K. U. Jansen, W. C. Gruber, C. C. T. Group, N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2603–2615.
- 3C. L. Lorentzen, J. B. Haanen, O. Met, I. M. Svane, Lancet Oncol. 2022, 23, e450–e458.
- 4O. P. Joffre, E. Segura, A. Savina, S. Amigorena, Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 12, 557–569.
- 5J. A. Katakowski, G. Mukherjee, S. E. Wilner, K. E. Maier, M. T. Harrison, T. P. DiLorenzo, M. Levy, D. Palliser, Mol. Ther. 2016, 24, 146–155.
- 6P. J. Tacken, I. J. de Vries, R. Torensma, C. G. Figdor, Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 7, 790–802.
- 7H. Wang, M. C. Sobral, D. K. Y. Zhang, A. N. Cartwright, A. W. Li, M. O. Dellacherie, C. M. Tringides, S. T. Koshy, K. W. Wucherpfennig, D. J. Mooney, Nat. Mater. 2020, 19, 1244–1252.
- 8J. M. Jaynes, R. Sable, M. Ronzetti, W. Bautista, Z. Knotts, A. Abisoye-Ogunniyan, D. Li, R. Calvo, M. Dashnyam, A. Singh, T. Guerin, J. White, S. Ravichandran, P. Kumar, K. Talsania, V. Chen, A. Ghebremedhin, B. Karanam, A. Bin Salam, R. Amin, T. Odzorig, T. Aiken, V. Nguyen, Y. Bian, J. C. Zarif, A. E. de Groot, M. Mehta, L. Fan, X. Hu, A. Simeonov, N. Pate, M. Abu-Asab, M. Ferrer, N. Southall, C.-Y. Ock, Y. Zhao, H. Lopez, S. Kozlov, N. de Val, C. C. Yates, B. Baljinnyam, J. Marugan, U. Rudloff, Sci. Transl. Med. 2020, 12, eaax6337.
- 9L. Martinez-Pomares, J. Leukocyte Biol. 2012, 92, 1177–1186.
- 10H. Feinberg, S. A. F. Jegouzo, Y. Lasanajak, D. F. Smith, K. Drickamer, W. I. Weis, M. E. Taylor, J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 296, 100368.
- 11H. Feinberg, S. Park-Snyder, A. R. Kolatkar, C. T. Heise, M. E. Taylor, W. I. Weis, J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 21539–21548.
- 12M. E. Taylor, K. Bezouska, K. Drickamer, J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 1719–1726.
- 13P. Paracuellos, D. C. Briggs, F. Carafoli, T. Loncar, E. Hohenester, Structure 2015, 23, 2133–2142.
- 14R. Goswami, D. Chatzikleanthous, G. Lou, F. Giusti, A. Bonci, M. Taccone, M. Brazzoli, S. Gallorini, I. Ferlenghi, F. Berti, D. T. O′Hagan, C. Pergola, B. C. Baudner, R. Adamo, ACS Infect. Dis. 2019, 5, 1546–1558.
- 15R. Yang, J. Xu, L. Xu, X. Sun, Q. Chen, Y. Zhao, R. Peng, Z. Liu, ACS Nano 2018, 12, 5121–5129.
- 16S. Burgdorf, A. Kautz, V. Böhnert, P. A. Knolle, C. Kurts, Science 2007, 316, 612–616.
- 17S. Qi, Y. Wang, Y. Zhu, X. Zhang, X. Wang, X. Yu, K. Yang, B. Bai, Y. Feng, J. Lei, K. Zhang, Z. Lu, S. Zhu, J. Du, G. Yu, Nano Today 2023, 49, 101795.
- 18B. J. Read, L. Won, J. C. Kraft, I. Sappington, A. Aung, S. Wu, J. Bals, C. Chen, K. K. Lee, D. Lingwood, N. P. King, D. J. Irvine, Cell Rep. 2022, 38, 110217.
- 19T. Tokatlian, B. J. Read, C. A. Jones, D. W. Kulp, S. Menis, J. Y. H. Chang, J. M. Steichen, S. Kumari, J. D. Allen, E. L. Dane, A. Liguori, M. Sangesland, D. Lingwood, M. Crispin, W. R. Schief, D. J. Irvine, Science 2019, 363, 649–654.
- 20F. Zhang, N. N. Parayath, C. I. Ene, S. B. Stephan, A. L. Koehne, M. E. Coon, E. C. Holland, M. T. Stephan, Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3974.
- 21T. Boettler, B. Csernalabics, H. Salie, H. Luxenburger, L. Wischer, E. Salimi Alizei, K. Zoldan, L. Krimmel, P. Bronsert, M. Schwabenland, M. Prinz, C. Mogler, C. Neumann-Haefelin, R. Thimme, M. Hofmann, B. Bengsch, J. Hepatol. 2022, 77, 653–659.
- 22Ö. Türeci, U. Sahin, Nature 2016, 534, 396–401.
- 23J. Chen, Z. Ye, C. Huang, M. Qiu, D. Song, Y. Li, Q. Xu, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2207841119.
- 24U. Sahin, P. Oehm, E. Derhovanessian, R. A. Jabulowsky, M. Vormehr, M. Gold, D. Maurus, D. Schwarck-Kokarakis, A. N. Kuhn, T. Omokoko, L. M. Kranz, M. Diken, S. Kreiter, H. Haas, S. Attig, R. Rae, K. Cuk, A. Kemmer-Bruck, A. Breitkreuz, C. Tolliver, J. Caspar, J. Quinkhardt, L. Hebich, M. Stein, A. Hohberger, I. Vogler, I. Liebig, S. Renken, J. Sikorski, M. Leierer, V. Muller, H. Mitzel-Rink, M. Miederer, C. Huber, S. Grabbe, J. Utikal, A. Pinter, R. Kaufmann, J. C. Hassel, C. Loquai, O. Tureci, Nature 2020, 585, 107–112.
- 25Q. Cheng, T. Wei, L. Farbiak, L. T. Johnson, S. A. Dilliard, D. J. Siegwart, Nat. Nanotechnol. 2020, 15, 313–320.
- 26S. Luozhong, Z. Yuan, T. Sarmiento, Y. Chen, W. Gu, C. McCurdy, W. Gao, R. Li, S. Wilkens, S. Jiang, Nano Lett. 2022, 22, 8304–8311.
- 27S. Du, W. Li, Y. Zhang, Y. Xue, X. Hou, J. Yan, J. Cheng, B. Deng, D. W. McComb, J. Lin, H. Zeng, X. Cheng, D. J. Irvine, R. Weiss, Y. Dong, Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, 2300188.
- 28J. Yan, Y. Zhang, S. Du, X. Hou, W. Li, C. Zeng, C. Zhang, J. Cheng, B. Deng, D. W. McComb, W. Zhao, Y. Xue, D. D. Kang, X. Cheng, Y. Dong, Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, e2207486.
- 29N. Kong, R. Zhang, G. Wu, X. Sui, J. Wang, N. Y. Kim, S. Blake, D. De, T. Xie, Y. Cao, W. Tao, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2112696119.
- 30P. Huang, L. Jiang, H. Pan, L. Ding, B. Zhou, M. Zhao, J. Zou, B. Li, M. Qi, H. Deng, Y. Zhou, X. Chen, Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, e2207471.
- 31X. Han, M. G. Alameh, K. Butowska, J. J. Knox, K. Lundgreen, M. Ghattas, N. Gong, L. Xue, Y. Xu, M. Lavertu, P. Bates, J. Xu, G. Nie, Y. Zhong, D. Weissman, M. J. Mitchell, Nat. Nanotechnol. 2023, 10.1038/s41565-023-01404-4.
- 32P. Jangili, N. Kong, J. H. Kim, J. Zhou, H. Liu, X. Zhang, W. Tao, J. S. Kim, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202117075; Angew. Chem. 2022, 134, e202117075.
- 33K. L. Swingle, H. C. Safford, H. C. Geisler, A. G. Hamilton, A. S. Thatte, M. M. Billingsley, R. A. Joseph, K. Mrksich, M. S. Padilla, A. A. Ghalsasi, M. G. Alameh, D. Weissman, M. J. Mitchell, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 4691–4706.
- 34Y. Liu, X. Ji, W. W. L. Tong, D. Askhatova, T. Yang, H. Cheng, Y. Wang, J. Shi, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2018, 57, 1510–1513; Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 1526–1529.
- 35J. Liu, S. S. Liew, J. Wang, K. Pu, Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, e2103790.
- 36P. Cheng, R. Wang, S. He, P. Yan, H. Huang, J. Chen, J. Shen, K. Pu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202306539; Angew. Chem. 2023, 135, e202306539.
- 37D. Ni, E. B. Ehlerding, W. Cai, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 2570–2579; Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 2592–2602.
- 38C. A. Ferreira, D. Ni, Z. T. Rosenkrans, W. Cai, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 13232–13252; Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 13366–13387.
- 39K. Yang, S. Qi, X. Yu, B. Bai, X. Zhang, Z. Mao, F. Huang, G. Yu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202203786; Angew. Chem. 2022, 134, e202203786.
- 40S. Fecteau, G. P. Basadonna, A. Freitas, C. Ariyan, M. H. Sayegh, D. M. Rothstein, Nat. Immunol. 2001, 2, 58–63.
- 41V. Schuette, M. Embgenbroich, T. Ulas, M. Welz, J. Schulte-Schrepping, A. M. Draffehn, T. Quast, K. Koch, M. Nehring, J. Konig, A. Zweynert, F. L. Harms, N. Steiner, A. Limmer, I. Forster, F. Berberich-Siebelt, P. A. Knolle, D. Wohlleber, W. Kolanus, M. Beyer, J. L. Schultze, S. Burgdorf, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 10649–10654.