Uncovering Photoelectronic and Photothermal Effects in Plasmon-Mediated Electrocatalytic CO2 Reduction
Yan Wei
Shanghai Key Laboratory of Molecular Catalysis and Innovative Materials, Collaborative Innovation Center of Chemistry for Energy Materials (iChEM), Department of Chemistry, Fudan University, Shanghai, 200438 China
Search for more papers by this authorZijie Mao
Shanghai Key Laboratory of Molecular Catalysis and Innovative Materials, Collaborative Innovation Center of Chemistry for Energy Materials (iChEM), Department of Chemistry, Fudan University, Shanghai, 200438 China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Tian-Wen Jiang
Shanghai Key Laboratory of Molecular Catalysis and Innovative Materials, Collaborative Innovation Center of Chemistry for Energy Materials (iChEM), Department of Chemistry, Fudan University, Shanghai, 200438 China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Hong Li
Shanghai Key Laboratory of Molecular Catalysis and Innovative Materials, Collaborative Innovation Center of Chemistry for Energy Materials (iChEM), Department of Chemistry, Fudan University, Shanghai, 200438 China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Xian-Yin Ma
Shanghai Key Laboratory of Molecular Catalysis and Innovative Materials, Collaborative Innovation Center of Chemistry for Energy Materials (iChEM), Department of Chemistry, Fudan University, Shanghai, 200438 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Chao Zhan
State Key Laboratory of Physical Chemistry of Solid Surfaces, Collaborative Innovation Center of Chemistry for Energy Materials (iChEM), College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Xiamen University, Xiamen, 361005 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Wen-Bin Cai
Shanghai Key Laboratory of Molecular Catalysis and Innovative Materials, Collaborative Innovation Center of Chemistry for Energy Materials (iChEM), Department of Chemistry, Fudan University, Shanghai, 200438 China
Search for more papers by this authorYan Wei
Shanghai Key Laboratory of Molecular Catalysis and Innovative Materials, Collaborative Innovation Center of Chemistry for Energy Materials (iChEM), Department of Chemistry, Fudan University, Shanghai, 200438 China
Search for more papers by this authorZijie Mao
Shanghai Key Laboratory of Molecular Catalysis and Innovative Materials, Collaborative Innovation Center of Chemistry for Energy Materials (iChEM), Department of Chemistry, Fudan University, Shanghai, 200438 China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Tian-Wen Jiang
Shanghai Key Laboratory of Molecular Catalysis and Innovative Materials, Collaborative Innovation Center of Chemistry for Energy Materials (iChEM), Department of Chemistry, Fudan University, Shanghai, 200438 China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Hong Li
Shanghai Key Laboratory of Molecular Catalysis and Innovative Materials, Collaborative Innovation Center of Chemistry for Energy Materials (iChEM), Department of Chemistry, Fudan University, Shanghai, 200438 China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Xian-Yin Ma
Shanghai Key Laboratory of Molecular Catalysis and Innovative Materials, Collaborative Innovation Center of Chemistry for Energy Materials (iChEM), Department of Chemistry, Fudan University, Shanghai, 200438 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Chao Zhan
State Key Laboratory of Physical Chemistry of Solid Surfaces, Collaborative Innovation Center of Chemistry for Energy Materials (iChEM), College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Xiamen University, Xiamen, 361005 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Wen-Bin Cai
Shanghai Key Laboratory of Molecular Catalysis and Innovative Materials, Collaborative Innovation Center of Chemistry for Energy Materials (iChEM), Department of Chemistry, Fudan University, Shanghai, 200438 China
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
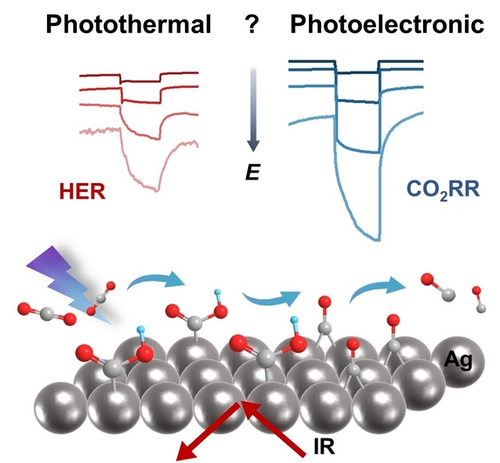
This work quantitatively disentangles the photoelectronic (PE) and photothermal (PT) effects in plasmon-mediated electrocatalysis using CO2RR on Ag NPs electrode as the model system. The PE effect prevails over a wide potential window for the CO2RR to CO, while the PT effect dominates the H2 evolution reaction at high overpotentials. It is revealed spectroscopically that the carbonyl-containing C1 intermediate applies to the plasmon-promoted CO2RR to CO process.
Abstract
Plasmon-mediated electrocatalysis that rests on the ability of coupling localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR) and electrochemical activation, emerges as an intriguing and booming area. However, its development seriously suffers from the entanglement between the photoelectronic and photothermal effects induced by the decay of plasmons, especially under the influence of applied potential. Herein, using LSPR-mediated CO2 reduction on Ag electrocatalyst as a model system, we quantitatively uncover the dominant photoelectronic effect on CO2 reduction reaction over a wide potential window, in contrast to the leading photothermal effect on H2 evolution reaction at relatively negative potentials. The excitation of LSPR selectively enhances the CO faradaic efficiency (17-fold at −0.6 VRHE) and partial current density (100-fold at −0.6 VRHE), suppressing the undesired H2 faradaic efficiency. Furthermore, in situ attenuated total reflection-surface enhanced infrared absorption spectroscopy (ATR-SEIRAS) reveals a plasmon-promoted formation of the bridge-bonded CO on Ag surface via a carbonyl-containing C1 intermediate. The present work demonstrates a deep mechanistic understanding of selective regulation of interfacial reactions by coupling plasmons and electrochemistry.
Conflict of interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie202317740-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf1.5 MB | Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1
- 1aC. Zhan, X.-J. Chen, J. Yi, J.-F. Li, D.-Y. Wu, Z.-Q. Tian, Nat. Chem. Rev. 2018, 2, 216–230;
- 1bC. Zhan, J. Yi, S. Hu, X. G. Zhang, D.-Y. Wu, Z.-Q. Tian, Nat. Rev. Methods Primers 2023, 3, 12;
- 1cJ. Zhao, S. Xue, R. Ji, B. Li, J. Li, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 12070–12097;
- 1dR. Nixon, E. Contreras, P. K. Jain, Trends Chem. 2023, 5, 605–619;
- 1eU. Aslam, V. G. Rao, S. Chavez, S. Linic, Nat. Catal. 2018, 1, 656–665;
- 1fE. Cortes, W. Xie, J. Cambiasso, A. S. Jermyn, R. Sundararaman, P. Narang, S. Schlucker, S. A. Maier, Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14880;
- 1gL. L. Du, G. D. Shi, Y. R. Zhao, X. Chen, H. M. Sun, F. M. Liu, F. Y. Cheng, W. Xie, Chem. Sci. 2019, 10, 9605–9612.
- 2
- 2aH. Yang, L. Q. He, Y. W. Hu, X. Lu, G. R. Li, B. Liu, B. Ren, Y. Tong, P.-P. Fang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 11462–11466;
- 2bL. Huang, J. Zou, J. Y. Ye, Z. Y. Zhou, Z. Lin, X. Kang, P. K. Jain, S. Chen, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 8794–8798;
- 2cX. Xie, J. Feng, X. Cui, J. Liu, L. Jiang, L. Dong, ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 13160–13168;
- 2dH. Yang, Z. H. Wang, Y. Y. Zheng, L. Q. He, C. Zhan, X. Lu, Z.-Q. Tian, P.-P. Fang, Y. Tong, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 16204–16207;
- 2eY. Wei, Z. Mao, X.-Y. Ma, C. Zhan, W.-B. Cai, J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2022, 13, 11288–11294.
- 3R. D. Wan, S. L. Liu, Y. Wang, Y. Yang, Y. Tian, P. K. Jain, X. W. Kang, Nano Lett. 2022, 22, 7819–7825.
- 4S. C. Lin, C. S. Hsu, S. Y. Chiu, T. Y. Liao, H. M. Chen, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 2224–2233.
- 5
- 5aS. Linic, P. Christopher, D. B. Ingram, Nat. Mater. 2011, 10, 911–921;
- 5bL. A. Zhou, D. F. Swearer, C. Zhang, H. Robatjazi, H. Q. Zhao, L. Henderson, L. L. Dong, P. Christopher, E. A. Carter, P. Nordlander, N. J. Halas, Science 2018, 362, 69–72;
- 5cY. Xin, K. Yu, L. Zhang, Y. Yang, H. Yuan, H. Li, L. Wang, J. Zeng, Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, e2008145;
- 5dZ. J. Geng, Y. F. Yu, A. J. Offen, J. Liu, Nat. Catal. 2023, 10.1038/s41929-023-01045-9;
- 5eG. Ghimire, J. Guo, R. Halmagian, J. He, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202302215;
- 5fC. Wang, X. G. Nie, Y. Shi, Y. Zhou, J. J. Xu, X.-H. Xia, H.-Y. Chen, ACS Nano 2017, 11, 5897–5905;
- 5gS. Ganguli, Z. W. Zhao, O. Parlak, Y. Hattori, J. Sa, A. Sekretareva, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202302394;
- 5hS. Ganguli, A. Sekretareva, ACS Catal. 2022, 12, 4110–4118.
- 6
- 6aY. Hori, H. Wakebe, T. Tsukamoto, O. Koga, Electrochim. Acta 1994, 39, 1833–1839;
- 6bS. Nitopi, E. Bertheussen, S. B. Scott, X. Liu, A. K. Engstfeld, S. Horch, B. Seger, I. E. L. Stephens, K. Chan, C. Hahn, J. K. Norskov, T. F. Jaramillo, I. Chorkendorff, Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 7610–7672;
- 6cM. B. Ross, P. De Luna, Y. Li, C.-T. Dinh, D. Kim, P. Yang, E. H. Sargent, Nat. Catal. 2019, 2, 648–658;
- 6dP. De Luna, C. Hahn, D. Higgins, S. A. Jaffer, T. F. Jaramillo, E. H. Sargent, Science 2019, 364, 350;
- 6eJ. W. Li, H. L. Zeng, X. Dong, Y. M. Ding, S. P. Hu, R. H. Zhang, Y. Z. Dai, P. X. Cui, Z. Xiao, D. H. Zhao, L. J. Zhou, T. T. Zheng, J. P. Xiao, J. Zeng, C. Xia, Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 340;
- 6fQ. J. Wu, D. H. Si, P. P. Sun, Y. L. Dong, S. Zheng, Q. Chen, S. H. Ye, D. Sun, R. Cao, Y. B. Huang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 135, e202306822.
- 7
- 7aS. Yu, A. J. Wilson, G. Kumari, X. Zhang, P. K. Jain, ACS Energy Lett. 2017, 2, 2058–2070;
- 7bC. Y. Hu, X. Chen, J. Low, Y. W. Yang, H. Li, D. Wu, S. M. Chen, J. B. Jin, H. Li, H. X. Ju, C. H. Wang, Z. Lu, R. Long, L. Song, Y. J. Xiong, Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 221;
- 7cE. B. Creel, E. R. Corson, J. Eichhorn, R. Kostecki, J. J. Urban, B. D. McCloskey, ACS Energy Lett. 2019, 4, 1098–1105.
- 8
- 8aW. H. Ou, B. B. Zhou, J. D. Shen, T. W. Lo, D. Y. Lei, S. L. Li, J. Zhong, Y. Y. Li, J. Lu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 6790–6793;
- 8bJ. Liu, Z. Y. Cai, W. X. Sun, J. Z. Wang, X. R. Shen, C. Zhan, R. Devasenathipathy, J. Z. Zhou, D.-Y. Wu, B. W. Mao, Z.-Q. Tian, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 17489–17498.
- 9
- 9aA. Thevenon, A. Rosas-Hernandez, A. M. F. Herreros, T. Agapie, J. C. Peters, ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 4530–4537;
- 9bC. Kim, H. S. Jeon, T. Eom, M. S. Jee, H. Kim, C. M. Friend, B. K. Min, Y. J. Hwang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 13844–13850;
- 9cS. Liu, H. Tao, L. Zeng, Q. Liu, Z. Xu, Q. Liu, J. L. Luo, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 2160–2163;
- 9dQ. Chen, K. Liu, Y. J. Zhou, X. Q. Wang, K. Z. Wu, H. M. Li, E. Pensa, J. W. Fu, M. Miyauchi, E. Cortés, M. Liu, Nano Lett. 2022, 22, 6276–6284.
- 10C. Zhan, B. W. Liu, Y. F. Huang, S. Hu, B. Ren, M. Moskovits, Z.-Q. Tian, Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2671.
- 11
- 11aM. Osawa, B. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1997, 70, 2861–2880;
- 11bW. Y. Deng, L. Zhang, H. Dong, X. X. Chang, T. Wang, J. L. Gong, Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 6599–6604;
- 11cH. Li, T.-W. Jiang, X. X. Qin, J. Chen, X.-Y. Ma, K. Jiang, X. G. Zhang, W.-B. Cai, ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 6846–6856;
- 11dT.-W. Jiang, X. X. Qin, K. Ye, W. Y. Zhang, H. Li, W. H. Liu, S. J. Huo, X. G. Zhang, K. Jiang, W.-B. Cai, Appl. Catal. B 2023, 334, 122815;
- 11eE. R. Corson, R. Kas, R. Kostecki, J. J. Urban, W. A. Smith, B. D. McCloskey, R. Kortlever, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 11750–11762.
- 12H. Jing, N. Large, Q. Zhang, H. Wang, J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 19948–19963.
- 13M. Li, Y. Hu, G. Dong, T. C. Wu, D. S. Geng, Small 2023, 19, 2207242.
- 14W. M. Zhang, J. Li, X.-H. Xia, Y. G. Zhou, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202115819.
- 15M. Azuma, K. Hashimoto, M. Hiramoto, M. Watanabe, T. Sakata, J. Electrochem. Soc. 1990, 137, 1772–1778.
- 16
- 16aM. Moradzaman, G. Mul, ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 8049–8057;
- 16bS. Q. Zhu, B. Jiang, W.-B. Cai, M. H. Shao, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 15664–15667.
- 17K. L. Yang, R. Kas, W. A. Smith, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 15891–15900.
- 18
- 18aD. H. Nam, O. Shekhah, G. Lee, A. Mallick, H. Jiang, F. Li, B. Chen, J. Wicks, M. Eddaoudi, E. H. Sargent, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 21513–21521;
- 18bD. Ohl, Y. U. Kayran, J. R. C. Junqueira, V. Essmann, T. Bobrowski, W. Schuhmann, Langmuir 2018, 34, 12293–12301.
- 19M. Dunwell, Q. Lu, J. M. Heyes, J. Rosen, J. G. G. Chen, Y. S. Yan, F. Jiao, B. J. Xu, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 3774–3783.
- 20S. Mubeen, J. Lee, N. Singh, S. Kramer, G. D. Stucky, M. Moskovits, Nat. Nanotechnol. 2013, 8, 247–251.
- 21B. Kim, S. Ma, H. R. M. Jhong, P. J. A. Kenis, Electrochim. Acta 2015, 166, 271–276.
- 22N. C. Nelson, M. T. Nguyen, V. A. Glezakou, R. Rousseau, J. Szanyi, Nat. Catal. 2019, 2, 916–924.
- 23N. J. Firet, W. A. Smith, ACS Catal. 2016, 7, 606–612.
- 24X. G. Zhang, Y. X. Liu, C. Zhan, X. Jin, Q. J. Chi, D. Y. Wu, Y. Zhao, Z. Q. Tian, J. Phys. Chem. C 2019, 123, 11101–11108.
- 25J. Gargiulo, R. Berté, Y. Li, S. A. Maier, E. Cortés, Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 2525–2535.