Proton-Coupled Electron Transfer Aided Thermoelectric Energy Conversion and Storage
Graphical Abstract
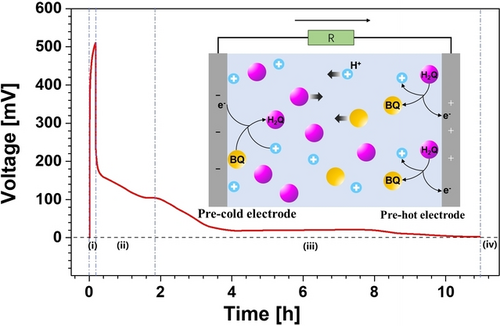
The combination of the Soret effect of protons and the classical proton-coupled electron transfer of benzoquinone (BQ) and hydroquinone (H2Q) in hydrogels results in overall and giant thermoelectric performance in terms of the thermopower, ionic conductivity, power factor, ionic Figure of merit. Above all, an energy-storage function is achieved by the BQ and H2Q redox couple after the removal of temperature difference.
Abstract
Low-grade heat is ubiquitous in the environment and its thermoelectric conversion by the ionic conductors remains a challenge because of the low efficiency and poor sustainability. Here we demonstrate that the thermoelectric performances can be boosted by combining the Soret effect of protons and proton-coupled electron transfer (PCET) reaction of benzoquinone and hydroquinone in hydrogels. An overall enhancement of thermopower (25.9 mV K−1), power factor (5 mW m−1 K−2), figure of merit (>2.4) and continuity of power output is achieved. Moreover, an energy-storage function can be achieved by the redox couple, and a retained power output of 27.7 %, or 14 mW m−2 for more than 3 hours is obtained by the re-balance of PCET reactants in the hydrogel after the removal of the temperature gradient.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.