Bottom-Up Preparation of Twisted Graphene Nanoribbons by Cu-Catalyzed Deoxygenative Coupling
Dr. Yuan Gao
State Key Laboratory of Applied Organic Chemistry, Lanzhou University, Tianshui Southern Road 222, Lanzhou, 730000 Gansu, Province, China
Contribution: Data curation (lead), Formal analysis (lead), Investigation (lead), Writing - review & editing (supporting)
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Xinqiang Hua
State Key Laboratory of Applied Organic Chemistry, Lanzhou University, Tianshui Southern Road 222, Lanzhou, 730000 Gansu, Province, China
Contribution: Investigation (supporting), Software (lead)
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Wei Jiang
State Key Laboratory of Applied Organic Chemistry, Lanzhou University, Tianshui Southern Road 222, Lanzhou, 730000 Gansu, Province, China
Contribution: Investigation (supporting), Methodology (supporting)
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Dr. Chun-Lin Sun
State Key Laboratory of Applied Organic Chemistry, Lanzhou University, Tianshui Southern Road 222, Lanzhou, 730000 Gansu, Province, China
Contribution: Data curation (supporting), Formal analysis (supporting)
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Dr. Chengshan Yuan
State Key Laboratory of Applied Organic Chemistry, Lanzhou University, Tianshui Southern Road 222, Lanzhou, 730000 Gansu, Province, China
Contribution: Data curation (supporting), Formal analysis (supporting), Investigation (supporting)
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Dr. Zitong Liu
State Key Laboratory of Applied Organic Chemistry, Lanzhou University, Tianshui Southern Road 222, Lanzhou, 730000 Gansu, Province, China
Contribution: Conceptualization (supporting), Data curation (supporting), Formal analysis (supporting)
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Dr. Hao-Li Zhang
State Key Laboratory of Applied Organic Chemistry, Lanzhou University, Tianshui Southern Road 222, Lanzhou, 730000 Gansu, Province, China
Contribution: Conceptualization (supporting), Funding acquisition (supporting), Investigation (supporting)
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Xiangfeng Shao
State Key Laboratory of Applied Organic Chemistry, Lanzhou University, Tianshui Southern Road 222, Lanzhou, 730000 Gansu, Province, China
Contribution: Conceptualization (lead), Formal analysis (equal), Funding acquisition (lead), Investigation (equal), Project administration (lead), Supervision (lead), Writing - original draft (lead), Writing - review & editing (lead)
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Yuan Gao
State Key Laboratory of Applied Organic Chemistry, Lanzhou University, Tianshui Southern Road 222, Lanzhou, 730000 Gansu, Province, China
Contribution: Data curation (lead), Formal analysis (lead), Investigation (lead), Writing - review & editing (supporting)
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Xinqiang Hua
State Key Laboratory of Applied Organic Chemistry, Lanzhou University, Tianshui Southern Road 222, Lanzhou, 730000 Gansu, Province, China
Contribution: Investigation (supporting), Software (lead)
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Wei Jiang
State Key Laboratory of Applied Organic Chemistry, Lanzhou University, Tianshui Southern Road 222, Lanzhou, 730000 Gansu, Province, China
Contribution: Investigation (supporting), Methodology (supporting)
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Dr. Chun-Lin Sun
State Key Laboratory of Applied Organic Chemistry, Lanzhou University, Tianshui Southern Road 222, Lanzhou, 730000 Gansu, Province, China
Contribution: Data curation (supporting), Formal analysis (supporting)
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Dr. Chengshan Yuan
State Key Laboratory of Applied Organic Chemistry, Lanzhou University, Tianshui Southern Road 222, Lanzhou, 730000 Gansu, Province, China
Contribution: Data curation (supporting), Formal analysis (supporting), Investigation (supporting)
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Dr. Zitong Liu
State Key Laboratory of Applied Organic Chemistry, Lanzhou University, Tianshui Southern Road 222, Lanzhou, 730000 Gansu, Province, China
Contribution: Conceptualization (supporting), Data curation (supporting), Formal analysis (supporting)
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Dr. Hao-Li Zhang
State Key Laboratory of Applied Organic Chemistry, Lanzhou University, Tianshui Southern Road 222, Lanzhou, 730000 Gansu, Province, China
Contribution: Conceptualization (supporting), Funding acquisition (supporting), Investigation (supporting)
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Xiangfeng Shao
State Key Laboratory of Applied Organic Chemistry, Lanzhou University, Tianshui Southern Road 222, Lanzhou, 730000 Gansu, Province, China
Contribution: Conceptualization (lead), Formal analysis (equal), Funding acquisition (lead), Investigation (equal), Project administration (lead), Supervision (lead), Writing - original draft (lead), Writing - review & editing (lead)
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
Abstract
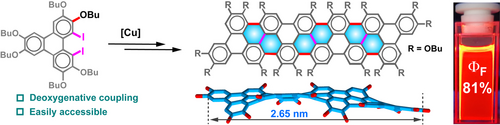
Graphene nanoribbons (GNRs) are promising in organic optoelectronic materials, and their properties largely depend on the size, edge, and conformation. Herein, the fully armchair-edged GNRs (AGNRs) with lengths up to 2.65 nm by using a Cu-catalyzed deoxygenative coupling as a key step. The resulting AGNRs (2HBT, 3HBT, and 4HBT) possess highly twisted π-scaffolds, and the torsion angles between the adjacent triphenylene moieties are larger than 32°, as proved by crystallographic analyses. Theoretical and spectroscopic studies show that the butoxy groups endow AGNRs with electron-rich features, the extension of the π-system from 2HBT to 4HBT reinforces S0→S1 excitation, and the distortion of the π-scaffold enhances the fluorescence quantum yield (ΦF). In particular, 4HBT has the lowest oxidation potential (Eox1=0.55 V vs. SCE) and displays red fluorescence with a ΦF value of 81 %.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available in the supplementary material of this article.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie202210924-sup-0001-2HBT.cif1.2 MB | Supporting Information |
| anie202210924-sup-0001-3HBT.cif2.3 MB | Supporting Information |
| anie202210924-sup-0001-4HBT.cif5.1 MB | Supporting Information |
| anie202210924-sup-0001-Compound_2.cif1.6 MB | Supporting Information |
| anie202210924-sup-0001-Compound_3.cif4.2 MB | Supporting Information |
| anie202210924-sup-0001-Compound_6.cif1.5 MB | Supporting Information |
| anie202210924-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf11.6 MB | Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1
- 1aY.-W. Son, M. L. Cohen, S. G. Louie, Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 97, 216803;
- 1bZ. Chen, Y.-M. Lin, M. J. Rooks, P. Avouris, Phys. E 2007, 40, 228;
- 1cO. V. Yazyev, Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 2319;
- 1dY. Segawa, H. Ito, K. Itami, Nat. Rev. Mater. 2016, 1, 15002;
- 1eY. Huang, W.-T. Dou, F. Xu, H.-B. Ru, Q. Gong, D. Wu, D. Yan, H. Tian, X.-P. He, Y. Mai, X. Feng, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 3366; Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 3424;
- 1fS. Zhao, J. Lavie, L. Rondin, L. Orcin-Chaix, C. Diederichs, P. Roussignol, Y. Chassagneux, C. Voisin, K. Müllen, A. Narita, S. Campidelli, J.-S. Lauret, Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3470;
- 1gY. Yano, N. Mitoma, H. Ito, K. Itami, J. Org. Chem. 2020, 85, 4.
- 2
- 2aN. Mohanty, D. Moore, Z. Xu, T. S. Sreeprasad, A. Nagaraja, A. A. Rodriguez, V. Berry, Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 844;
- 2bL. Tapasztó, G. Dobrik, P. Lambin, L. P. Biro, Nat. Nanotechnol. 2008, 3, 397;
- 2cM. Y. Han, B. Ozyilmaz, Y. Zhang, P. Kim, Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 98, 206805;
- 2dX. Li, X. Wang, L. Zhang, S. W. Lee, H. J. Dai, Science 2008, 319, 1229;
- 2eD. V. Kosynkin, A. L. Higginbotham, A. Sinitskii, J. R. Lomeda, A. Dimiev, B. K. Price, J. M. Tour, Nature 2009, 458, 872;
- 2fL. Jiao, L. Zhang, X. Wang, G. Diankov, H. J. Dai, Nature 2009, 458, 877.
- 3
- 3aL. Chen, Y. Hernandez, X. Feng, K. Müllen, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 7640; Angew. Chem. 2012, 124, 7758;
- 3bA. Narita, X. Wang, X. Feng, K. Müllen, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 6616;
- 3cA. Narita, Z. Chen, Q. Chen, K. Müllen, Chem. Sci. 2019, 10, 964;
- 3dJ. Liu, X. Feng, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 23386; Angew. Chem. 2020, 132, 23591;
- 3eZ. Liu, S. Fu, X. Liu, A. Narita, P. Samorì, M. Bonn, H. I. Wang, Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2106055.
- 4
- 4aR. A. Pascal Jr., Chem. Rev. 2006, 106, 4809;
- 4bM. Ball, Y. Zhong, Y. Wu, C. Schenck, F. Ng, M. Steigerwald, S. Xiao, C. Nuckolls, Acc. Chem. Res. 2015, 48, 267;
- 4cM. Rickhaus, M. Mayor, M. Juríček, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 1542;
- 4dM. Rickhaus, M. Mayor, M. Juríček, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 1643;
- 4eS. H. Pun, Q. Miao, Acc. Chem. Res. 2018, 51, 1630;
- 4fJ. M. Fernández-García, P. J. Evans, S. Filippone, M. A. Herranz, N. Martin, Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 1565;
- 4gI. G. Stará, I. Stary, Acc. Chem. Res. 2020, 53, 144.
- 5
- 5aD. Cortizo-Lacalle, J. P. Mora-Fuentes, K. Strutyński, A. Saeki, M. Melle-Franco, A. Mateo-Alonso, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 703; Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 711;
- 5bJ. P. Mora-Fuentes, A. Riaño, D. Cortizo-Lacalle, A. Saeki, M. Melle-Franco, A. Mateo-Alonso, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 552; Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 562;
- 5cS. Ma, J. Gu, C. Lin, Z. Luo, Y. Zhu, J. Wang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 16887;
- 5dF. Chen, W. Gu, A. Saeki, M. Melle-Franco, A. Mateo-Alonso, Org. Lett. 2020, 22, 3706;
- 5eY. Gu, V. Vega-Mayoral, S. Garcia-Orrit, D. Schollmeyer, A. Narita, J. Cabanillas-González, Z. Qiu, K. Müllen, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202201088; Angew. Chem. 2022, 134, e202201088.
- 6
- 6aS. Xiao, S. J. Kang, Y. Wu, S. Ahn, J. B. Kim, Y.-L. Loo, T. Siegrist, M. L. Steigerwald, H. Li, C. Nuckolls, Chem. Sci. 2013, 4, 2018;
- 6bY. Zhong, B. Kuma, S. Oh, M. T. Trinh, Y. Wu, K. Elbert, P. Li, X. Zhu, S. Xiao, F. Ng, M. L. Steigerwald, C. Nuckolls, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 8122;
- 6cJ. Liu, B.-W. Li, Y.-Z. Tan, A. Giannakopoulos, C. Sanchez-Sanchez, D. Beljonne, P. Ruffieux, R. Fasel, X. Feng, K. Müllen, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 6097;
- 6dT. J. Sisto, Y. Zhong, B. Zhang, M. T. Trinh, Ki. Miyata, X. Zhong, X.-Y. Zhu, M. L. Steigerwald, F. Ng, C. Nuckolls, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 5648;
- 6eW. Niu, J. Ma, P. Soltani, W. Zheng, F. Liu, A. A. Popov, J. J. Weigand, H. Komber, E. Poliani, C. Casiraghi, J. Droste, M. R. Hansen, S. Osella, D. Beljonne, M. Bonn, H. I. Wang, X. Feng, J. Liu, Y. Mai, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 18293;
- 6fY. Gu, R. Muñoz-Mármol, S. Wu, Y. Han, Y. Ni, M. A. Díaz-García, J. Casado, J. Wu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 8113; Angew. Chem. 2020, 132, 8190;
- 6gH. Wu, Y. Wang, B. Song, H.-J. Wang, J. Zhou, Y. Sun, L. O. Jones, W. Liu, L. Zhang, X. Zhang, K. Cai, X.-Y. Chen, C. L. Stern, J. Wei, O. K. Farha, J. M. Anna, G. C. Schatz, Y. Liu, J. F. Stoddart, Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5191;
- 6hR. K. Dubey, M. Melle-Franco, A. Mateo-Alonso, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 6593;
- 6iR. K. Dubey, M. Melle-Franco, A. Mateo-Alonso, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 2765;
- 6jL. Yang, J. Ma, W. Zheng, S. Osella, J. Droste, H. Komber, K. Liu, S. Böckmann, D. Beljonne, M. R. Hansen, M. Bonn, H. I. Wang, J. Liu, X. Feng, Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2200708.
- 7
- 7aM. Daigle, D. Miao, A. Lucotti, M. Tommasini, J.-F. Morin, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 6213; Angew. Chem. 2017, 129, 6309;
- 7bJ. Ma, Y. Fu, E. Dmitrieva, F. Liu, H. Komber, F. Hennersdorf, A. A. Popov, J. J. Weigand, J. Liu, X. Feng, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 5637; Angew. Chem. 2020, 132, 5686;
- 7cM. Roy, V. Berezhnaia, M. Villa, N. Vanthuyne, M. Giorgi, J.-V. Naubron, S. Poyer, V. Monnier, L. Charles, Y. Carissan, D. Hagebaum-Reignier, J. Rodriguez, M. Gingras, Y. Coquerel, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 3264; Angew. Chem. 2020, 132, 3290;
- 7dX. Yao, W. Zheng, S. Osella, Z. Qiu, S. Fu, D. Schollmeyer, B. Müller, D. Beljonne, M. Bonn, H. I. Wang, K. Müllen, A. Narita, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 5654;
- 7eW. Niu, Y. Fu, H. Komber, J. Ma, X. Feng, Y. Mai, J. Liu, Org. Lett. 2021, 23, 2069.
- 8D. Lungerich, O. Papaianina, M. Feofanov, J. Liu, M. Devarajulu, S. I. Troyanov, S. Maier, K. Amsharov, Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4756.
- 9
- 9aX. Qiao, M. A. Padula, D. M. Ho, N. J. Vogelaar, C. E. Schutt, R. A. Pascal Jr., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 741;
- 9bJ. Lu, D. M. Ho, N. J. Vogelaar, C. M. Kraml, R. A. Pascal Jr., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 11168;
- 9cJ. Xiao, H. M. Duong, Y. Liu, W. Shi, L. Ji, G. Li, S. Li, X.-W. Liu, J. Ma, F. Wudl, Q. Zhang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 6094; Angew. Chem. 2012, 124, 6198;
- 9dK. Baumgärtner, A. L. Meza Chincha, A. Dreuw, F. Rominger, M. Mastalerz, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 15594; Angew. Chem. 2016, 128, 15823;
- 9eW. Fan, T. Winands, N. L. Doltsinis, Y. Li, Z. Wang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 15373; Angew. Chem. 2017, 129, 15575;
- 9fW. Chen, X. Li, G. Long, Y. Li, R. Ganguly, M. Zhang, N. Aratani, H. Yamada, M. Liu, Q. Zhang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 13555; Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 13743;
- 9gR. G. Clevenger, B. Kumar, E. M. Menuey, K. V. Kilway, Chem. Eur. J. 2018, 24, 3113;
- 9hY.-M. Liu, H. Hou, Y.-Z. Zhou, X.-J. Zhao, C. Tang, Y.-Z. Tan, K. Müllen, Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1901;
- 9iY. Xiao, J. T. Mague, R. H. Schmehl, F. M. Haque, F. R. A. Pascal Jr., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 2831; Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 2857;
- 9jS. Nishitani, R. Sekiya, T. Haino, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 669; Angew. Chem. 2020, 132, 679;
- 9kG. Liu, C. Xiao, F. Negri, Y. Li, Z. Wang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 2008; Angew. Chem. 2020, 132, 2024;
- 9lY. Wang, Y. Huang, T. Huang, J. Zhang, T. Luo, Y. Ni, B. Li, S. Xie, Z. Zeng, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202200855; Angew. Chem. 2022, 134, e202200855.
- 10X. Wang, A. Narita, K. Müllen, Nat. Chem. Rev. 2018, 2, 0100.
- 11
- 11aJ. Cai, P. Ruffieux, R. Jaafar, M. Bieri, T. Braun, S. Blankenburg, M. Muoth, A. P. Seitsonen, M. Saleh, X. Feng, K. Müllen, R. Fasel, Nature 2010, 466, 470;
- 11bP. Ruffieux, S. Wang, B. Yang, C. Sánchez-Sánchez, J. Liu, T. Dienel, L. Talirz, P. Shinde, C. A. Pignedoli, D. Passerone, T. Dumslaff, X. Feng, K. Müllen, R. Fasel, Nature 2016, 531, 489;
- 11cL. Talirz, P. Ruffieux, R. Fasel, Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 6222;
- 11dZ. Chen, A. Narita, K. Müllen, Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2001893;
- 11eX. Zhou, G. Yu, Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1905957.
- 12
- 12aW. Niu, J. Liu, Y. Mai, K. Müllen, X. Feng, Trends Chem. 2019, 1, 549;
- 12bA. Jolly, D. Miao, M. Daigle, J.-F. Morin, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 4624; Angew. Chem. 2020, 132, 4652;
- 12cM. Grzybowski, B. Sadowski, H. Butenschön, D. T. Gryko, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 2998; Angew. Chem. 2020, 132, 3020;
- 12dK.-Y. Yoon, G. Dong, Mater. Chem. Front. 2020, 4, 29.
- 13
- 13aA. Mateo-Alonso, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 6311;
- 13bM. Stępień, E. Gońka, M. Żyła, N. Sprutta, Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 3479;
- 13cX. Wang, X. Yao, A. Narita, K. Müllen, Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 2491;
- 13dA. Borissov, Y. K. Maurya, L. Moshniaha, W.-S. Wong, M. Żyła-Karwowska, M. Stępień, Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 565;
- 13eF. Hernández-Culebras, M. Melle-Franco, A. Mateo-Alonso, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202205018; Angew. Chem. 2022, 134, e202205018.
- 14
- 14aM. Uryu, T. Hiraga, Y. Koga, Y. Saito, K. Murakami, K. Itami, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 6551; Angew. Chem. 2020, 132, 6613;
- 14bY. Koga, T. Kaneda, Y. Saito, K. Murakami, K. Itami, Science 2018, 359, 435;
- 14cC. Zhu, D. Wang, D. Wang, Y. Zhao, W.-Y. Sun, Z. Shi, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 8848; Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 8986;
- 14dG. Li, K.-Y. Yoon, X. Zhong, J. Wang, R. Zhang, J. R. Guest, J. Wen, X.-Y. Zhu, G. Dong, Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1687;
- 14eC. P. Sen, S. Valiyaveettil, Chem. Eur. J. 2017, 23, 1686;
- 14fG. Li, K.-Y. Yoon, X. Zhong, X. Zhu, G. Dong, Chem. Eur. J. 2016, 22, 9116;
- 14gJ. He, S. Mathew, Z. J. Kinney, R. M. Warrell, J. S. Molina, C. S. Hartley, Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 7245;
- 14hT. H. Vo, M. Shekhirev, D. A. Kunkel, M. D. Morton, E. Berglund, L. Kong, P. M. Wilson, P. A. Dowben, A. Enders, A. Sinitskii, Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3189;
- 14iB. T. King, J. Kroulík, C. R. Robertson, P. Rempala, C. L. Hilton, J. D. Korinek, L. M. Gortari, J. Org. Chem. 2007, 72, 2279;
- 14jM. Grzybowski, K. Skonieczny, H. Butenschön, D. T. Gryko, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 9900; Angew. Chem. 2013, 125, 10084.
- 15
- 15aM. Daigle, A. Picard-Lafond, E. Soligo, J.-F. Morin, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 2042; Angew. Chem. 2016, 128, 2082;
- 15bD. Miao, M. Daigle, A. Lucotti, J. Boismenu-Lavoie, M. Tommasini, J. F. Morin, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 3588; Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 3650;
- 15cZ.-L. Qiu, X.-W. Chen, Y.-D. Huang, R.-J. Wei, K.-S. Chu, X.-J. Zhao, Y.-Z. Tan, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202116955; Angew. Chem. 2022, 134, e202116955.
- 16
- 16aA.-K. Steiner, K. Y. Amsharov, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 14732; Angew. Chem. 2017, 129, 14926;
- 16bO. Papaianina, V. A. Akhmetov, A. A. Goryunkov, F. Hampel, F. W. Heinemann, K. Y. Amsharov, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 4834; Angew. Chem. 2017, 129, 4912.
- 17Q. Zhang, H. Peng, G. Zhang, Q. Lu, J. Chang, Y. Dong, X. Shi, J. Wei, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 5057.
- 18W. Yang, A. Lucotti, M. Tommasini, W. A. Chalifoux, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 9137.
- 19
- 19aS. Kumar, S. K. Varshney, Liq. Cryst. 1999, 26, 1841;
- 19bS. J. Mahoney, M. M. Ahmida, H. Kayal, N. Fox, Y. Shimizu, S. H. Eichhorn, J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 9221.
- 20J. Shang, R. Wang, C. Yuan, Z. Liu, H.-L. Zhang, X. Shao, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202117504; Angew. Chem. 2022, 134, e202117504.
- 21Z. Qiu, C.-J. Li, Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 10454.
- 22Deposition numbers 2192379, 2192380, 2192381, 2192382, 2192383, and 2192384 contain the crystallographic data for 6, 2HBT, 3, 3HBT, 2, and 4HBT, respectively. These data are provided free of charge by the joint Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre and Fachinformationszentrum Karlsruhe Access Structures service.
- 23B. Tan, L. Liu, H. Zheng, T. Cheng, D. Zhu, X. Yang, X. Luan, Chem. Sci. 2020, 11, 10198.
- 24
- 24aJ. P. Wolfe, S. L. Buchwald, J. Org. Chem. 1997, 62, 1264;
- 24bJ. Louie, M. S. Driver, B. C. Hamann, J. F. Hartwig, J. Org. Chem. 1997, 62, 1268;
- 24cG. D. Vo, J. F. Hartwig, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 11049;
- 24dJ. L. Klinkenberg, J. F. Hartwig, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 11830.
- 25
- 25aE. Wenkert, E. L. Michelotti, C. S. Swindell, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1979, 101, 2246;
- 25bN. Yoshikai, H. Matsuda, E. Nakamura, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 9590;
- 25cB.-J. Li, L. Xu, Z.-H. Wu, B.-T. Guan, C.-L. Sun, B.-Q. Wang, Z.-J. Shi, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 14656;
- 25dP. Guo, K. Wang, W.-J. Jin, H. Xie, L. Qi, X.-Y. Liu, X.-Z. Shu, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 513;
- 25eW.-Y. Ma, G.-Y. Han, S. Kang, X. Pang, X.-Y. Liu, X.-Z. Shu, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 15930;
- 25fR.-D. He, Y. Bai, G.-Y. Han, Z.-Z. Zhao, X. Pang, X. Pan, X.-Y. Liu, .X.-Z. Shu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202114556; Angew. Chem. 2022, 134, e202114556.
- 26
- 26aZ. Chen, C. S. Wannere, C. Corminboeuf, R. Puchta, P. v. R. Schleyer, Chem. Rev. 2005, 105, 3842;
- 26bH. Fallah-Bagher-Shaidaei, C. S. Wannere, C. Corminboeuf, R. Puchta, P. v. R. Schleyer, Org. Lett. 2006, 8, 863.
- 27
- 27aD. Geuenich, K. Hess, F. Köhler, R. Herges, Chem. Rev. 2005, 105, 3758;
- 27bQ. Li, C.-M. Li, H.-L. Xu, Z.-M. Su, J. Mol. Model. 2017, 23, 231.
- 28J. L. Bredas, R. Silbey, D. S. Boudreux, R. R. Chance, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1983, 105, 6555.
- 29C. Würth, M. Grabolle, J. Pauli, M. Spieles, U. Resch-Genger, Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 1535.
- 30X. Li, Y. Zhu, J. Shao, B. Wang, S. Zhang, Y. Shao, X. Jin, X. Yao, R. Fang, X. Shao, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 535–538; Angew. Chem. 2014, 126, 545–548.
- 31
- 31aX. Guo, Z. Yuan, Y. Zhu, Z. Li, R. Huang, Z. Xia, W. Zhang, Y. Li, J. Wang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 16966; Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 17122;
- 31bY. Zhu, Z. Xia, Z. Cai, Z. Yuan, N. Jiang, T. Li, Y. Wang, X. Guo, Z. Li, S. Ma, D. Zhong, Y. Li, J. Wang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 4222;
- 31cX. Yan, X. Cui, L.-s. Li, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 5944;
- 31dY. Wang, Z. Yin, Y. Zhu, J. Gu, Y. Li, J. Wang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 587; Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 597;
- 31eY.-Z. Tan, B. Yang, K. Parvez, A. Narita, S. Osella, D. Beljonne, X. Feng, K. Müllen, Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2646;
- 31fY. Zhu, X. Guo, Y. Li, J. Wang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 5511.
- 32
- 32aD. L. Dexter, J. H. Schulman, J. Chem. Phys. 1954, 22, 1063;
- 32bM. Kasha, H. R. Rawls, M. Ashraf El-Bayoumi, Pure Appl. Chem. 1965, 11, 371;
- 32cR. F. Chen, J. R. Knutson, Anal. Biochem. 1988, 172, 61.
- 33
- 33aM. Pawlicki, H. A. Collins, R. G. Denning, H. L. Anderson, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 3244; Angew. Chem. 2009, 121, 3292;
- 33bF. Gao, Q. Liao, Z.-Z. Xu, Y.-H. Yue, Q. Wang, H.-L. Zhang, H.-B. Fu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 732; Angew. Chem. 2010, 122, 744;
- 33cZ.-H. Wu, Z.-T. Huang, R.-X. Guo, C.-L. Sun, L.-C. Chen, B. Sun, Z.-F. Shi, X. Shao, H. Li, H.-L. Zhang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 13031; Angew. Chem. 2017, 129, 13211;
- 33dC. M. Cruz, I. R. Márquez, I. F. A. Mariz, V. Blanco, C. Sánchez-Sánchez, J. M. Sobrado, J. A. Martín-Gago, J. M. Cuerva, E. Maçôas, A. G. Campaña, Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 3917;
- 33eC. M. Cruz, I. R. Márquez, S. Castro-Fernández, J. M. Cuerva, E. Maçôas, A. G. Campaña, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 8068; Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 8152;
- 33fS. Castro-Fernández, C. M. Cruz, I. F. A. Mariz, I. R. Márquez, V. G. Jiménez, L. Palomino-Ruiz, J. M. Cuerva, E. Maçôas, A. G. Campaña, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 7139; Angew. Chem. 2020, 132, 7205.
- 34
- 34aD. Yang, H. Wang, C. Sun, H. Zhao, K. Hu, W. Qin, R. Ma, F. Yin, X. Qin, Q. Zhang, Y. Liang, Z. Li, Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 6322;
- 34bF. Yuan, T. Yuan, L. Sui, Z. Wang, Z. Xi, Y. Li, X. Li, L. Fan, Z. Tan, A. Chen, M. Jin, S. Yang, Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2249;
- 34cX. Ren, F. Zhang, H. Luo, L. Liao, X. Song, W. Chen, Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 2159.