Strong SHG Responses in a Beryllium-Free Deep-UV-Transparent Hydroxyborate via Covalent Bond Modification
Dr. Chao Wu
China-Australia Joint Research Center for Functional Molecular Materials, School of Chemical Science and Engineering, Tongji University, Shanghai, 200092 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Xingxing Jiang
Technical Institute of Physics and Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100190 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorLin Lin
China-Australia Joint Research Center for Functional Molecular Materials, School of Chemical Science and Engineering, Tongji University, Shanghai, 200092 China
Search for more papers by this authorWenyan Dan
China-Australia Joint Research Center for Functional Molecular Materials, School of Chemical Science and Engineering, Tongji University, Shanghai, 200092 China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Zheshuai Lin
Technical Institute of Physics and Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100190 China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Zhipeng Huang
China-Australia Joint Research Center for Functional Molecular Materials, School of Chemical Science and Engineering, Tongji University, Shanghai, 200092 China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Mark G. Humphrey
Research School of Chemistry, Australian National University, Canberra, ACT, 2601 Australia
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Chi Zhang
China-Australia Joint Research Center for Functional Molecular Materials, School of Chemical Science and Engineering, Tongji University, Shanghai, 200092 China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Chao Wu
China-Australia Joint Research Center for Functional Molecular Materials, School of Chemical Science and Engineering, Tongji University, Shanghai, 200092 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Xingxing Jiang
Technical Institute of Physics and Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100190 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorLin Lin
China-Australia Joint Research Center for Functional Molecular Materials, School of Chemical Science and Engineering, Tongji University, Shanghai, 200092 China
Search for more papers by this authorWenyan Dan
China-Australia Joint Research Center for Functional Molecular Materials, School of Chemical Science and Engineering, Tongji University, Shanghai, 200092 China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Zheshuai Lin
Technical Institute of Physics and Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100190 China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Zhipeng Huang
China-Australia Joint Research Center for Functional Molecular Materials, School of Chemical Science and Engineering, Tongji University, Shanghai, 200092 China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Mark G. Humphrey
Research School of Chemistry, Australian National University, Canberra, ACT, 2601 Australia
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Chi Zhang
China-Australia Joint Research Center for Functional Molecular Materials, School of Chemical Science and Engineering, Tongji University, Shanghai, 200092 China
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
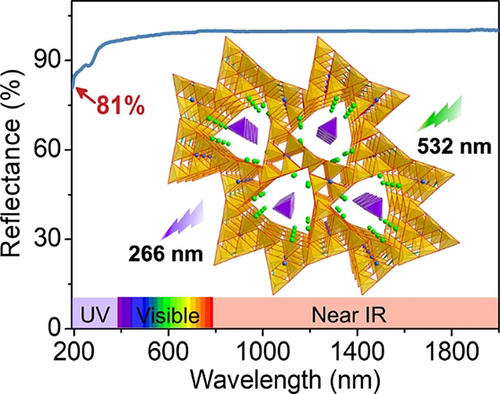
A beryllium-free deep-ultraviolet nonlinear optical hydroxyborate, NaSr3(OH)(B9O16)[B(OH)4] (NSBOH), was constructed by a covalent bond modification strategy via a facile hydrothermal reaction. Moisture-stable NSBOH is SHG-active at both 1064 nm and 532 nm, with deep-UV transparency to wavelengths below 190 nm, and good phase-matchability in the near deep-UV region, a rare combination for NLO hydroxyborates.
Abstract
Deep-ultraviolet (deep-UV) nonlinear optical (NLO) crystals are key materials in creating tunable deep-UV lasers for frequency conversion technology. However, practical application of the sole usable crystal, KBe2BO3F2, has been hindered by the high toxicity of beryllium and its layering tendency in crystal growth. Herein, we report a beryllium-free deep-UV NLO material NaSr3(OH)(B9O16)[B(OH)4] (NSBOH), synthesized by a covalent bond modification strategy under hydrothermal conditions. Moisture-stable NSBOH exhibits strong second-harmonic generation (SHG) at 1064 nm (3.3 × KH2PO4) and 532 nm (0.55 × β-BaB2O4), both amongst the largest powder SHG responses for a deep-UV borate, with good phase-matchability and a short wavelength cutoff edge (below 190 nm). NSBOH possesses a 3D covalent anionic [B9O19]∞ honeycomb-like framework with no layering. The Sr2+ and Na+ ions, residing in the cavities of the anionic framework, act as templates for the assembly and favorable alignment of NLO-active groups, resulting in an optimal balance between strong SHG activities and wide UV transparency. These merits indicate NSBOH is a very attractive candidate for deep-UV NLO applications.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie202113397-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf1.3 MB | Supporting Information |
| anie202113397-sup-0001-SI.cif31.6 KB | Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1
- 1aN. Savage, Nat. Photonics 2007, 1, 83–85;
- 1bD. Cyranoski, Nature 2009, 457, 953–955;
- 1cM. Mutailipu, M. Zhang, Z. H. Yang, S. L. Pan, Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 791–801;
- 1dC. Wu, G. Yang, M. G. Humphrey, C. Zhang, Coord. Chem. Rev. 2018, 375, 459–488.
- 2
- 2aX. M. Liu, L. Kang, P. F. Gong, Z. S. Lin, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 13574–13578; Angew. Chem. 2021, 133, 13686–13690;
- 2bT. T. Tran, J. Young, J. M. Rondinelli, P. S. Halasyamani, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 1285–1295;
- 2cG. Peng, C. C. Lin, N. Ye, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 20542–20546.
- 3
- 3aX. M. Liu, P. F. Gong, Y. Yang, G. M. Song, Z. S. Lin, Coord. Chem. Rev. 2019, 400, 213045;
- 3bL. Huang, G. H. Zou, H. Q. Cai, S. C. Wang, C. S. Lin, N. Ye, J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 5268–5274;
- 3cC. Wu, X. X. Jiang, Z. J. Wang, L. Lin, Z. S. Lin, Z. P. Huang, X. F. Long, M. G. Humphrey, C. Zhang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 3464–3468; Angew. Chem. 2021, 133, 3506–3510.
- 4
- 4aL. Li, Y. Wang, B. H. Lei, S. J. Han, Z. H. Yang, K. R. Poeppelmeier, S. L. Pan, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 9101–9104;
- 4bS. G. Zhao, P. F. Gong, S. Y. Luo, L. Bai, Z. S. Lin, Y. Y. Tang, Y. L. Zhou, M. C. Hong, J. H. Luo, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 4217–4221; Angew. Chem. 2015, 127, 4291–4295;
- 4cX. F. Lu, Z. H. Chen, X. R. Shi, Q. Jing, M. H. Lee, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 17648–17656; Angew. Chem. 2020, 132, 17801–17809;
- 4dJ. Chen, L. Xiong, L. Chen, L. M. Wu, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 14082–14086;
- 4eC. Wu, X. X. Jiang, Z. J. Wang, H. Y. Sha, Z. S. Lin, Z. P. Huang, X. F. Long, M. G. Humphrey, C. Zhang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 14806–14810; Angew. Chem. 2021, 133, 14932–14936.
- 5
- 5aY. Q. Li, F. Liang, S. G. Zhao, L. N. Li, Z. Y. Wu, Q. R. Ding, S. Liu, Z. S. Lin, M. C. Hong, J. H. Luo, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 3833–3837;
- 5bX. H. Dong, L. Huang, C. F. Hu, H. M. Zeng, Z. E. Lin, X. Wang, K. M. Ok, G. H. Zou, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 6528–6534; Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 6598–6604;
- 5cC. Wu, T. H. Wu, X. X. Jiang, Z. J. Wang, H. Y. Sha, L. Lin, Z. S. Lin, Z. P. Huang, X. F. Long, M. G. Humphrey, C. Zhang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 4138–4142.
- 6
- 6aM. Mutailipu, M. Zhang, B. B. Zhang, L. Y. Wang, Z. H. Yang, X. Zhou, S. L. Pan, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 6095–6099; Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 6203–6207;
- 6bB. B. Zhang, G. Q. Shi, Z. H. Yang, F. F. Zhang, S. L. Pan, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 3916–3919; Angew. Chem. 2017, 129, 3974–3977;
- 6cM. Luo, F. Liang, Y. Song, D. Zhao, F. Xu, N. Ye, Z. S. Lin, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 3884–3887;
- 6dX. F. Wang, Y. Wang, B. B. Zhang, F. F. Zhang, Z. H. Yang, S. L. Pan, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 14119–14123; Angew. Chem. 2017, 129, 14307–14311.
- 7
- 7aC. T. Chen, B. C. Wu, A. D. Jiang, G. M. You, Sci. Sin. Ser. B (Engl. Ed.) 1985, 28, 235–243;
- 7bC. T. Chen, Y. B. Wang, B. C. Wu, K. C. Wu, W. L. Zeng, L. H. Yu, Nature 1995, 373, 322–324;
- 7cC. T. Chen, Y. C. Wu, A. D. Jiang, B. C. Wu, G. M. You, R. K. Li, S. J. Lin, J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 1989, 6, 616–621.
- 8
- 8aG. Q. Shi, Y. Wang, F. F. Zhang, B. B. Zhang, Z. H. Yang, X. L. Hou, S. L. Pan, K. R. Poeppelmeier, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 10645–10648;
- 8bJ. J. Zhou, Y. Q. Liu, H. P. Wu, H. W. Yu, Z. S. Lin, Z. G. Hu, J. Y. Wang, Y. C. Wu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 19006–19010; Angew. Chem. 2020, 132, 19168–19172;
- 8cP. S. Halasyamani, J. M. Rondinelli, Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2972.
- 9
- 9aP. F. Gong, L. Kang, Z. S. Lin, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 15157–15163;
- 9bH. W. Yu, W. G. Zhang, J. Young, J. M. Rondinelli, P. S. Halasyamani, Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 7380–7385.
- 10
- 10aC. T. Chen, G. L. Wang, X. Y. Wang, Z. Y. Xu, Appl. Phys. B 2009, 97, 9–25;
- 10bG. H. Zou, C. S. Lin, H. Jo, G. Nam, T. S. You, K. M. Ok, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 12078–12082; Angew. Chem. 2016, 128, 12257–12261.
- 11H. W. Yu, N. Z. Koocher, J. M. Rondinelli, P. S. Halasyamani, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 6100–6103; Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 6208–6211.
- 12
- 12aS. C. Wang, N. Ye, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 11458–11461;
- 12bH. W. Huang, L. J. Liu, S. F. Jin, W. J. Yao, Y. H. Zhang, C. T. Chen, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 18319–18322;
- 12cS. C. Wang, N. Ye, W. Li, D. Zhao, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 8779–8786;
- 12dG. Peng, N. Ye, Z. S. Lin, L. Kang, S. L. Pan, M. Zhang, C. S. Lin, X. F. Long, M. Luo, Y. Chen, Y. H. Tang, F. Xu, T. Yan, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 8968–8972; Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 9106–9110.
- 13
- 13aT. T. Tran, N. Z. Koocher, J. M. Rondinelli, P. S. Halasyamani, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 2969–2973; Angew. Chem. 2017, 129, 3015–3019;
- 13bS. G. Zhao, P. F. Gong, L. Bai, X. Xu, S. Q. Zhang, Z. H. Sun, Z. S. Lin, M. C. Hong, C. T. Chen, J. H. Luo, Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4019;
- 13cS. G. Zhao, L. Kang, Y. G. Shen, X. D. Wang, M. A. Asghar, Z. S. Lin, Y. Y. Xu, S. Y. Zeng, M. C. Hong, J. H. Luo, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 2961–2964;
- 13dH. W. Yu, J. Young, H. P. Wu, W. G. Zhang, J. M. Rondinelli, P. S. Halasyamani, Adv. Opt. Mater. 2017, 5, 1700840;
- 13eH. P. Wu, H. W. Yu, S. L. Pan, P. S. Halasyamani, Inorg. Chem. 2017, 56, 8755–8758;
- 13fS. G. Zhao, P. F. Gong, S. Y. Luo, S. J. Liu, L. N. Li, M. A. Asghar, T. Khan, M. C. Hong, Z. S. Lin, J. H. Luo, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 2207–2210;
- 13gH. K. Liu, Y. Wang, B. B. Zhang, Z. H. Yang, Chem. Sci. 2020, 11, 694–698.
- 14C. Wu, L. H. Li, J. L. Song, G. Yang, M. G. Humphrey, C. Zhang, Inorg. Chem. 2017, 56, 1340–1348.
- 15
- 15aH. W. Huang, J. Y. Yao, Z. S. Lin, X. Y. Wang, R. He, W. J. Yao, N. X. Zhai, C. T. Chen, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 9141–9144; Angew. Chem. 2011, 123, 9307–9310;
- 15bX. S. Wang, L. J. Liu, X. Y. Wang, L. Bai, C. T. Chen, CrystEngComm 2015, 17, 925–929.
- 16
- 16aH. P. Wu, B. B. Zhang, H. W. Yu, Z. G. Hu, J. Y. Wang, Y. C. Wu, P. S. Halasyamani, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 8922–8926; Angew. Chem. 2020, 132, 9007–9011;
- 16bJ. H. Huang, C. C. Jin, P. L. Xu, P. F. Gong, Z. S. Lin, J. W. Cheng, G. Y. Yang, Inorg. Chem. 2019, 58, 1755–1758;
- 16cX. D. Zhang, L. C. Guo, B. B. Zhang, J. Yu, Y. Wang, K. Wu, H. J. Wang, M. H. Lee, Chem. Commun. 2021, 57, 639–642;
- 16dB. L. Wu, C. L. Hu, F. F. Mao, R. L. Tang, J. G. Mao, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 10188–10192;
- 16eC. Wu, L. H. Li, G. Yang, J. L. Song, B. Yan, M. G. Humphrey, L. Zhang, J. D. Shao, C. Zhang, Dalton Trans. 2017, 46, 12605–12611.
- 17
- 17aD. Vitzthum, K. Wurst, J. M. Pann, P. Brüggeller, M. Seibald, H. Huppertz, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 11451–11455; Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 11622–11626;
- 17bM. A. Silver, T. E. Albrecht-Schmitt, Coord. Chem. Rev. 2016, 323, 36–51.
- 18Crystal data of NSBOH: a=9.9561(2) Å, b=9.9561(2) Å, c=8.7252(2) Å, α=β=90°, γ=120°, V=749.00(3) Å3. Deposition Number 1525548 contains the supplementary crystallographic data for this paper. These data are provided free of charge by the joint Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre and Fachinformationszentrum Karlsruhe Access Structures service.
- 19N. E. Brese, M. O'Keeffe, Acta Crystallogr. Sect. B 1991, 47, 192–197.
- 20S. J. Clark, M. D. Segall, C. J. Pickard, P. J. Hasnip, M. I. J. Probert, K. Refson, M. C. Payne, Z. Kristallogr. 2005, 220, 567–570.
- 21S. K. Kurtz, T. T. Perry, J. Appl. Phys. 1968, 39, 3798–3813.
- 22
- 22aH. P. Wu, H. W. Yu, Z. H. Yang, X. L. Hou, X. Su, S. L. Pan, K. R. Poeppelmeier, J. M. Rondinelli, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 4215–4218;
- 22bZ. H. Yang, S. L. Pan, Mater. Chem. Front. 2021, 5, 3507–3523;
- 22cM. Mutailipu, M. Zhang, H. P. Wu, Z. H. Yang, Y. H. Shen, J. L. Sun, S. L. Pan, Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3089.
- 23
- 23aP. A. Maggard, T. S. Nault, C. L. Stern, K. R. Poeppelmeier, J. Solid State Chem. 2003, 175, 27–33;
- 23bY. L. Hu, C. Wu, X. X. Jiang, Z. J. Wang, Z. P. Huang, Z. S. Lin, X. F. Long, M. G. Humphrey, C. Zhang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 12455–12459.
- 24D. A. Kleinman, Phys. Rev. 1962, 126, 1977–1979.
- 25J. Lin, M. H. Lee, Z. P. Liu, C. T. Chen, C. J. Pickard, Phys. Rev. B 1999, 60, 13380–13389.
- 26R. He, Z. S. Lin, M. H. Lee, C. T. Chen, J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 109, 103510.