Chiroptical Switching and Quantitative Chirality Sensing with (Pseudo)halogenated Quinones
Graphical Abstract
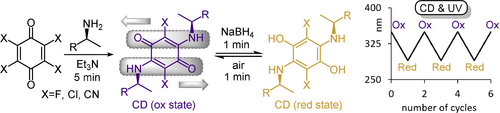
Quinones are used for quantitative UV/CD sensing of the concentration and enantiomeric excess of more than thirty aliphatic and aromatic chiral amines, amino alcohols and amino acids. The integration of redox switching into the sensing protocol allows spectral deconvolution of otherwise overlapping CD spectra that are obtained with challenging compound mixtures.
Abstract
(Pseudo)halogenated quinones react smoothly with chiral amines, amino alcohols, and amino acids toward push–pull conjugates with optical sensing and switching applications. The chiroptically active conjugates serve as redox switches between two reversibly interconverting states with remarkably different UV and CD signatures. Addition of sodium borohydride generates a hydroquinone derivative that is quantitatively re-oxidized to the original quinone upon exposure to air. This chiroptical quinone/hydroquinone redox switch system combines several attractive features such as simple set-up, use of inexpensive chemicals, short response time, and thermal and photochemical stability. A conceptually new sensing approach that is based on integrated chiroptical amplification and redox switching enables on-the-fly deconvolution of otherwise overlapping CD spectra and is used for quantitative er analysis of challenging samples containing constitutional isomers in varying enantiomeric compositions.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.