C−C Coupling Is Unlikely to Be the Rate-Determining Step in the Formation of C2+ Products in the Copper-Catalyzed Electrochemical Reduction of CO
Xiaoxia Chang
College of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering, Peking University, Beijing, 100871 China
Center for Catalytic Science and Technology, Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, University of Delaware, Newark, DE, 19716 USA
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorJing Li
State Key Laboratory of Chemical Engineering, Department of Chemical Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorHaocheng Xiong
College of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering, Peking University, Beijing, 100871 China
State Key Laboratory of Chemical Engineering, Department of Chemical Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084 China
Search for more papers by this authorHaochen Zhang
State Key Laboratory of Chemical Engineering, Department of Chemical Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084 China
Search for more papers by this authorYifei Xu
College of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering, Peking University, Beijing, 100871 China
Search for more papers by this authorHai Xiao
Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Qi Lu
State Key Laboratory of Chemical Engineering, Department of Chemical Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Bingjun Xu
College of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering, Peking University, Beijing, 100871 China
Center for Catalytic Science and Technology, Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, University of Delaware, Newark, DE, 19716 USA
Search for more papers by this authorXiaoxia Chang
College of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering, Peking University, Beijing, 100871 China
Center for Catalytic Science and Technology, Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, University of Delaware, Newark, DE, 19716 USA
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorJing Li
State Key Laboratory of Chemical Engineering, Department of Chemical Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorHaocheng Xiong
College of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering, Peking University, Beijing, 100871 China
State Key Laboratory of Chemical Engineering, Department of Chemical Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084 China
Search for more papers by this authorHaochen Zhang
State Key Laboratory of Chemical Engineering, Department of Chemical Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084 China
Search for more papers by this authorYifei Xu
College of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering, Peking University, Beijing, 100871 China
Search for more papers by this authorHai Xiao
Department of Chemistry, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Qi Lu
State Key Laboratory of Chemical Engineering, Department of Chemical Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing, 100084 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Bingjun Xu
College of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering, Peking University, Beijing, 100871 China
Center for Catalytic Science and Technology, Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, University of Delaware, Newark, DE, 19716 USA
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
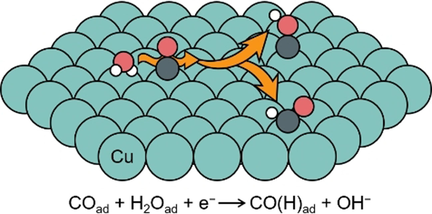
Electrokinetic and surface-enhanced infrared spectroscopic results indicate that the C−C coupling is unlikely to be the rate-determining step (RDS) in the formation of C2+ products in the electrochemical CO reduction reaction. Electrochemical hydrogenation of CO with adsorbed water as the proton donor is proposed as the RDS.
Abstract
The identity of the rate-determining step (RDS) in the electrochemical CO reduction reaction (CORR) on Cu catalysts remains unresolved because: 1) the presence of mass transport limitation of CO; and 2) the absence of quantitative correlation between CO partial pressure (pCO) and surface CO coverage. In this work, we determined CO adsorption isotherms on Cu in a broad pH range of 7.2–12.9. Together with electrokinetic data, we demonstrate that the reaction orders of adsorbed CO at pCO <0.4 and >0.6 atm are 1st and 0th, respectively, for multi-carbon (C2+) products on three Cu catalysts. These results indicate that the C−C coupling is unlikely to be the RDS in the formation of C2+ products in the CORR. We propose that the hydrogenation of CO with adsorbed water is the RDS, and the site competition between CO and water leads to the observed transition of the CO reaction order.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie202111167-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf2.9 MB | Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1
- 1aS. Nitopi, E. Bertheussen, S. B. Scott, X. Liu, A. K. Engstfeld, S. Horch, B. Seger, I. E. L. Stephens, K. Chan, C. Hahn, J. K. Norskov, T. F. Jaramillo, I. Chorkendorff, Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 7610–7672;
- 1bM. R. Shaner, H. A. Atwater, N. S. Lewis, E. W. McFarland, Energy Environ. Sci. 2016, 9, 2354–2371;
- 1cX. Chang, T. Wang, J. Gong, Energy Environ. Sci. 2016, 9, 2177–2196;
- 1dY. Yang, Y. Zhang, J.-S. Hu, L.-J. Wan, Acta Phys. Chim. Sin. 2020, 36, 1906085.
- 2
- 2aK. J. P. Schouten, Y. Kwon, C. J. M. van der Ham, Z. Qin, M. T. M. Koper, Chem. Sci. 2011, 2, 1902–1909;
- 2bJ. H. Montoya, C. Shi, K. Chan, J. K. Norskov, J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2015, 6, 2032–2037;
- 2cL. Wang, S. A. Nitopi, E. Bertheussen, M. Orazov, C. G. Morales-Guio, X. Liu, D. C. Higgins, K. Chan, J. K. Nørskov, C. Hahn, T. F. Jaramillo, ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 7445–7454;
- 2dX. Liu, P. Schlexer, J. Xiao, Y. Ji, L. Wang, R. B. Sandberg, M. Tang, K. S. Brown, H. Peng, S. Ringe, C. Hahn, T. F. Jaramillo, J. K. Norskov, K. Chan, Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 32.
- 3
- 3aM. Dunwell, Q. Lu, J. M. Heyes, J. Rosen, J. G. Chen, Y. Yan, F. Jiao, B. Xu, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 3774–3783;
- 3bA. Wuttig, Y. Yoon, J. Ryu, Y. Surendranath, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 17109–17113.
- 4J. Li, D. Wu, A. S. Malkani, X. Chang, M. J. Cheng, B. Xu, Q. Lu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 4464–4469; Angew. Chem. 2020, 132, 4494–4499.
- 5Y. Hori, A. Murata, R. Takahashi, J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1 1989, 85, 2309.
- 6J. E. Huang, F. Li, A. Ozden, A. Sedighian Rasouli, F. P. Garcia de Arquer, S. Liu, S. Zhang, M. Luo, X. Wang, Y. Lum, Y. Xu, K. Bertens, R. K. Miao, C. T. Dinh, D. Sinton, E. H. Sargent, Science 2021, 372, 1074–1078.
- 7
- 7aJ. Li, K. Chang, H. Zhang, M. He, W. A. Goddard, J. G. Chen, M.-J. Cheng, Q. Lu, ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 4709–4718;
- 7bM. Schreier, Y. Yoon, M. N. Jackson, Y. Surendranath, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 10221–10225; Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 10378–10382.
- 8Y. Hori, R. Takahashi, Y. Yoshinami, A. Murata, J. Phys. Chem. B 1997, 101, 7075–7081.
- 9
- 9aH. Xiao, T. Cheng, W. A. Goddard, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 130–136;
- 9bJ. D. Goodpaster, A. T. Bell, M. Head-Gordon, J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2016, 7, 1471–1477;
- 9cH. Xiao, T. Cheng, W. A. Goddard 3rd, R. Sundararaman, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 483–486.
- 10J. Li, X. Chang, H. Zhang, A. S. Malkani, M. J. Cheng, B. Xu, Q. Lu, Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3264.
- 11
- 11aM. Jouny, W. Luc, F. Jiao, Nat. Catal. 2018, 1, 748–755;
- 11bF. P. García de Arquer, C. T. Dinh, A. Ozden, J. Wicks, C. McCallum, A. R. Kirmani, D. H. Nam, C. Gabardo, A. Seifitokaldani, X. Wang, Y. C. Li, F. Li, J. Edwards, L. J. Richter, S. J. Thorpe, D. Sinton, E. H. Sargent, Science 2020, 367, 661–666;
- 11cD. T. Whipple, E. C. Finke, P. J. A. Kenis, Electrochem. Solid-State Lett. 2010, 13, B109.
- 12R. M. Hammaker, S. A. Francis, R. P. Eischens, Spectrochim. Acta 1965, 21, 1295–1309.
- 13A. Bagger, W. Ju, A. S. Varela, P. Strasser, J. Rossmeisl, ChemPhysChem 2017, 18, 3266–3273.
- 14E. Borguet, H. L. Dai, J. Chem. Phys. 1994, 101, 9080–9095.
- 15P. Hollins, J. Pritchard, Surf. Sci. 1979, 89, 486–495.
- 16A. Crossley, D. A. King, Surf. Sci. 1977, 68, 528–538.
- 17
- 17aA. S. Malkani, J. Li, J. Anibal, Q. Lu, B. Xu, ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 941–946;
- 17bA. S. Malkani, J. Li, N. J. Oliveira, M. He, X. Chang, B. Xu, Q. Lu, Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eabd2569.
- 18R. B. Sandberg, J. H. Montoya, K. Chan, J. K. Nørskov, Surf. Sci. 2016, 654, 56–62.
- 19B. V. Tilak, B. E. Conway, Electrochim. Acta 1992, 37, 51–63.
- 20M. Dunwell, W. Luc, Y. Yan, F. Jiao, B. Xu, ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 8121–8129.
- 21
- 21aW. Sheng, M. Myint, J. G. Chen, Y. Yan, Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 1509–1512;
- 21bJ. Durst, A. Siebel, C. Simon, F. Hasché, J. Herranz, H. A. Gasteiger, Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 2255–2260.
- 22
- 22aF. T. Wagner, T. E. Moylan, S. J. Schmieg, Surf. Sci. 1988, 195, 403–428;
- 22bA. Miki, S. Ye, M. Osawa, Chem. Commun. 2002, 1500–1501.
- 23
- 23aX. Chang, Y. Zhao, A. S. Malkani, X. Yang, L. Thompson, F. Jiao, B. Xu, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 9735–9743;
- 23bX. Chang, Y. Zhao, B. Xu, ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 13737–13747.