Discovery and Mechanism of Action of Small Molecule Inhibitors of Ceramidases**
Dr. Robert D. Healey
IGF, University of Montpellier, CNRS, INSERM, Montpellier, 34094 France
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Essa M. Saied
Institute for chemistry, Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Brook-Taylor-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany
Chemistry Department, Faculty of Science, Suez Canal University, 41522 Ismailia, Egypt
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Xiaojing Cong
IGF, University of Montpellier, CNRS, INSERM, Montpellier, 34094 France
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Gergely Karsai
Institute of Clinical Chemistry, University Hospital Zurich, University of Zurich, Zurich, 8091 Switzerland
Search for more papers by this authorLudovic Gabellier
IGMM, Univ Montpellier, CNRS, Montpellier, France
Search for more papers by this authorJulie Saint-Paul
IGF, University of Montpellier, CNRS, INSERM, Montpellier, 34094 France
Search for more papers by this authorElise Del Nero
IGF, University of Montpellier, CNRS, INSERM, Montpellier, 34094 France
Search for more papers by this authorSylvain Jeannot
IGF, University of Montpellier, CNRS, INSERM, Montpellier, 34094 France
Search for more papers by this authorMarion Drapeau
IGF, University of Montpellier, CNRS, INSERM, Montpellier, 34094 France
Search for more papers by this authorSimon Fontanel
IGF, University of Montpellier, CNRS, INSERM, Montpellier, 34094 France
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Damien Maurel
IGF, University of Montpellier, CNRS, INSERM, Montpellier, 34094 France
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Shibom Basu
EMBL Grenoble, 71 Avenue des Martyrs, CS 90181, 38042 Grenoble, France
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Cedric Leyrat
IGF, University of Montpellier, CNRS, INSERM, Montpellier, 34094 France
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Dr. Jérôme Golebiowski
Université Côte d'Azur, CNRS, Institut de Chimie de Nice UMR7272, Nice, 06108 France
Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences, Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science and Technology, Daegu, 711-873 South Korea
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Guillaume Bossis
IGMM, Univ Montpellier, CNRS, Montpellier, France
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Cherine Bechara
IGF, University of Montpellier, CNRS, INSERM, Montpellier, 34094 France
Institut Universitaire de France (IUF), Paris, France
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Dr. Thorsten Hornemann
Institute of Clinical Chemistry, University Hospital Zurich, University of Zurich, Zurich, 8091 Switzerland
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Dr. Christoph Arenz
Institute for chemistry, Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Brook-Taylor-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dr. Sebastien Granier
IGF, University of Montpellier, CNRS, INSERM, Montpellier, 34094 France
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Robert D. Healey
IGF, University of Montpellier, CNRS, INSERM, Montpellier, 34094 France
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Essa M. Saied
Institute for chemistry, Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Brook-Taylor-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany
Chemistry Department, Faculty of Science, Suez Canal University, 41522 Ismailia, Egypt
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Xiaojing Cong
IGF, University of Montpellier, CNRS, INSERM, Montpellier, 34094 France
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Gergely Karsai
Institute of Clinical Chemistry, University Hospital Zurich, University of Zurich, Zurich, 8091 Switzerland
Search for more papers by this authorLudovic Gabellier
IGMM, Univ Montpellier, CNRS, Montpellier, France
Search for more papers by this authorJulie Saint-Paul
IGF, University of Montpellier, CNRS, INSERM, Montpellier, 34094 France
Search for more papers by this authorElise Del Nero
IGF, University of Montpellier, CNRS, INSERM, Montpellier, 34094 France
Search for more papers by this authorSylvain Jeannot
IGF, University of Montpellier, CNRS, INSERM, Montpellier, 34094 France
Search for more papers by this authorMarion Drapeau
IGF, University of Montpellier, CNRS, INSERM, Montpellier, 34094 France
Search for more papers by this authorSimon Fontanel
IGF, University of Montpellier, CNRS, INSERM, Montpellier, 34094 France
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Damien Maurel
IGF, University of Montpellier, CNRS, INSERM, Montpellier, 34094 France
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Shibom Basu
EMBL Grenoble, 71 Avenue des Martyrs, CS 90181, 38042 Grenoble, France
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Cedric Leyrat
IGF, University of Montpellier, CNRS, INSERM, Montpellier, 34094 France
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Dr. Jérôme Golebiowski
Université Côte d'Azur, CNRS, Institut de Chimie de Nice UMR7272, Nice, 06108 France
Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences, Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science and Technology, Daegu, 711-873 South Korea
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Guillaume Bossis
IGMM, Univ Montpellier, CNRS, Montpellier, France
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Cherine Bechara
IGF, University of Montpellier, CNRS, INSERM, Montpellier, 34094 France
Institut Universitaire de France (IUF), Paris, France
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Dr. Thorsten Hornemann
Institute of Clinical Chemistry, University Hospital Zurich, University of Zurich, Zurich, 8091 Switzerland
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Dr. Christoph Arenz
Institute for chemistry, Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin, Brook-Taylor-Str. 2, 12489 Berlin, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dr. Sebastien Granier
IGF, University of Montpellier, CNRS, INSERM, Montpellier, 34094 France
Search for more papers by this authorA previous version of this manuscript has been deposited on a preprint server (https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.06.15.448479).
Graphical Abstract
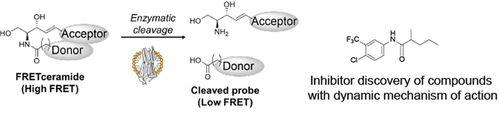
Use of synthetic fluorescent ceramide molecules allows the discovery of the first selective drug-like small molecule inhibitors for alkaline ceramidase 3, an intra-membrane enzyme involved in sphingolipid metabolism in health and disease. These inhibitors represent a new paradigm for controlling lipid metabolism with drug-like small molecules targeting conformationally dynamic membrane proteins.
Abstract
Sphingolipid metabolism is tightly controlled by enzymes to regulate essential processes in human physiology. The central metabolite is ceramide, a pro-apoptotic lipid catabolized by ceramidase enzymes to produce pro-proliferative sphingosine-1-phosphate. Alkaline ceramidases are transmembrane enzymes that recently attracted attention for drug development in fatty liver diseases. However, due to their hydrophobic nature, no specific small molecule inhibitors have been reported. We present the discovery and mechanism of action of the first drug-like inhibitors of alkaline ceramidase 3 (ACER3). In particular, we chemically engineered novel fluorescent ceramide substrates enabling screening of large compound libraries and characterized enzyme:inhibitor interactions using mass spectrometry and MD simulations. In addition to revealing a new paradigm for inhibition of lipid metabolising enzymes with non-lipidic small molecules, our data lay the ground for targeting ACER3 in drug discovery efforts.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie202109967-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf12.7 MB | Supporting Information |
| anie202109967-sup-0001-xlsx.zip219.9 KB | Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1B. Chaurasia, S. A. Summers, Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2021, 83, 303–330.
- 2Y. A. Hannun, L. M. Obeid, Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 175–191.
- 3A. H. Futerman, IUPHAR/BPS Guid. to Pharmacol. CITE 2019, 2019, https://doi.org/10.2218/gtopdb/F767/2019.4.
10.2218/gtopdb/F767/2019.4 Google Scholar
- 4S. A. Summers, B. Chaurasia, W. L. Holland, Nat. Metab. 2019, 1, 1051–1058.
- 5A. C. Lewis, C. T. Wallington-Beddoe, J. A. Powell, S. M. Pitson, Cell Death Discov. 2018, 4, 72.
- 6C. Duarte, J. Akkaoui, C. Yamada, A. Ho, C. Mao, A. Movila, Cells 2020, 9, 1379.
- 7B. Ogretmen, Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 33–50.
- 8S. A. Summers, Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 276–280.
- 9S. A. F. Morad, M. C. Cabot, Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 51–65.
- 10J. Vykoukal, J. F. Fahrmann, J. R. Gregg, Z. Tang, S. Basourakos, E. Irajizad, S. Park, G. Yang, C. J. Creighton, A. Fleury, J. Mayo, A. Paulucci-Holthauzen, J. B. Dennison, E. Murage, C. B. Peterson, J. W. Davis, J. Kim, S. Hanash, T. C. Thompson, Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4279.
- 11Y. A. Hannun, L. M. Obeid, Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 139–150.
- 12D. C. Pant, I. Dorboz, A. Schluter, S. Fourcade, N. Launay, J. Joya, S. Aguilera-Albesa, M. E. Yoldi, C. Casasnovas, M. J. Willis, M. Ruiz, D. Ville, G. Lesca, K. Siquier-Pernet, I. Desguerre, H. Yan, J. Wang, M. Burmeister, L. Brady, M. Tarnopolsky, C. Cornet, D. Rubbini, J. Terriente, K. N. James, D. Musaev, M. S. Zaki, M. C. Patterson, B. C. Lanpher, E. W. Klee, F. Pinto e Vairo, E. Wohler, N. Lygia de M. Sobreira, J. S. Cohen, R. Maroofian, H. Galehdari, N. Mazaheri, G. Shariati, L. Colleaux, D. Rodriguez, J. G. Gleeson, C. Pujades, A. Fatemi, O. Boespflug-Tanguy, A. Pujol, J. Clin. Invest. 2019, 129, 1240–1256.
- 13G. Karsai, F. Kraft, N. Haag, G. C. Korenke, B. Hänisch, A. Othman, S. Suriyanarayanan, R. Steiner, C. Knopp, M. Mull, M. Bergmann, J. M. Schröder, J. Weis, M. Elbracht, M. Begemann, T. Hornemann, I. Kurth, J. Clin. Invest. 2019, 129, 1229–1239.
- 14I. Vasiliauskaité-Brooks, R. Sounier, P. Rochaix, G. Bellot, M. Fortier, F. Hoh, L. De Colibus, C. Bechara, E. M. Saied, C. Arenz, C. Leyrat, S. Granier, Nature 2017, 544, 120–123.
- 15J. Pei, D. P. Millay, E. N. Olson, N. V. Grishin, Biol. Direct 2011, 6, 37.
- 16F. Parveen, D. Bender, S.-H. Law, V. K. Mishra, C.-C. Chen, L.-Y. Ke, Cells 2019, 8, 1573.
- 17A. Dementiev, A. Joachimiak, H. Nguyen, A. Gorelik, K. Illes, S. Shabani, M. Gelsomino, E.-Y. E. Ahn, B. Nagar, N. Doan, J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 987–992.
- 18S. Edvardson, J. K. Yi, C. Jalas, R. Xu, B. D. Webb, J. Snider, A. Fedick, E. Kleinman, N. R. Treff, C. Mao, O. Elpeleg, J. Med. Genet. 2016, 53, 389–396.
- 19I. Vasiliauskaité-Brooks, R. D. Healey, P. Rochaix, J. Saint-Paul, R. Sounier, C. Grison, T. Waltrich-Augusto, M. Fortier, F. Hoh, E. M. Saied, C. Arenz, S. Basu, C. Leyrat, S. Granier, Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5437.
- 20I. Vasiliauskaité-Brooks, R. D. Healey, S. Granier, Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2019, 491, 110397.
- 21C. Chen, Y. Yin, C. Li, J. Chen, J. Xie, Z. Lu, M. Li, Y. Wang, C. C. Zhang, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 478, 33–38.
- 22Y. Yin, M. Xu, J. Gao, M. Li, Pathol. Res. Pract. 2018, 214, 1381–1387.
- 23K. Wang, C. Li, X. Lin, H. Sun, R. Xu, Q. Li, Y. Wei, Y. Li, J. Qian, C. Liu, Q. Zhang, S. Yu, Z. Cui, X. Huang, B. Zhu, J. Zhou, C. Mao, Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 28.
- 24K. P. Bhabak, A. Hauser, S. Redmer, S. Banhart, D. Heuer, C. Arenz, ChemBioChem 2013, 14, 1049–1052.
- 25E. M. Saied, S. Banhart, S. E. Bürkle, D. Heuer, C. Arenz, Future Med. Chem. 2015, 7, 1971–1980.
- 26Z. H. Mohamed, C. Rhein, E. M. Saied, J. Kornhuber, C. Arenz, Chem. Phys. Lipids 2018, 216, 152–161.
- 27T. Pinkert, D. Furkert, T. Korte, A. Herrmann, C. Arenz, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 2790–2794; Angew. Chem. 2017, 129, 2834–2838.
- 28M. Casasampere, L. Camacho, F. Cingolani, J. Casas, M. Egido-Gabás, J. L. Abad, C. Bedia, R. Xu, K. Wang, D. Canals, Y. A. Hannun, C. Mao, G. Fabrias, J. Lipid Res. 2015, 56, 2019–2028.
- 29W. Hu, R. Xu, W. Sun, Z. M. Szulc, J. Bielawski, L. M. Obeid, C. Mao, J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 7964–7976.
- 30C. Andrieu, A. Montigny, A. Bibonne, E. Despin-Guitard, D. Alfandari, E. Théveneau, Development 2020, 147, dev183954.
- 31S. Salentin, S. Schreiber, V. J. Haupt, M. F. Adasme, M. Schroeder, Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W443–W447.
- 32G. Cavallo, P. Metrangolo, R. Milani, T. Pilati, A. Priimagi, G. Resnati, G. Terraneo, Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 2478–2601.
- 33L. Konermann, J. Pan, Y.-H. Liu, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 1224–1234.
- 34J. Zheng, T. Strutzenberg, B. D. Pascal, P. R. Griffin, Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2019, 58, 305–313.
- 35G. R. Masson, J. E. Burke, N. G. Ahn, G. S. Anand, C. Borchers, S. Brier, G. M. Bou-Assaf, J. R. Engen, S. W. Englander, J. Faber, R. Garlish, P. R. Griffin, M. L. Gross, M. Guttman, Y. Hamuro, A. J. R. Heck, D. Houde, R. E. Iacob, T. J. D. Jørgensen, I. A. Kaltashov, J. P. Klinman, L. Konermann, P. Man, L. Mayne, B. D. Pascal, D. Reichmann, M. Skehel, J. Snijder, T. S. Strutzenberg, E. S. Underbakke, C. Wagner, T. E. Wales, B. T. Walters, D. D. Weis, D. J. Wilson, P. L. Wintrode, Z. Zhang, J. Zheng, D. C. Schriemer, K. D. Rand, Nat. Methods 2019, 16, 595–602.
- 36L. Wang, R. A. Friesner, B. J. Berne, J. Phys. Chem. B 2011, 115, 9431–9438.
- 37N. Bielsa, M. Casasampere, M. Aseeri, J. Casas, A. Delgado, J. L. Abad, G. Fabriàs, Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 216, 113296.
- 38D. J. Lightwood, R. J. Munro, J. Porter, D. McMillan, B. Carrington, A. Turner, A. Scott-Tucker, E. S. Hickford, A. Schmidt, D. Fox, A. Maloney, T. Ceska, T. Bourne, J. O'Connell, A. D. G. Lawson, Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 583.
- 39N. B. Doan, H. Alhajala, M. M. Al-Gizawiy, W. M. Mueller, S. D. Rand, J. M. Connelly, E. J. Cochran, C. R. Chitambar, P. Clark, J. Kuo, K. M. Schmainda, S. P. Mirza, Oncotarget 2017, 8, 112662–112674.
- 40M. Lai, N. Realini, M. La Ferla, I. Passalacqua, G. Matteoli, A. Ganesan, M. Pistello, C. M. Mazzanti, D. Piomelli, Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7411.
- 41A. Bai, A. Bielawska, M. Rahmaniyan, J. M. Kraveka, J. Bielawski, Y. A. Hannun, Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 6067–6075.
- 42S. Zhang, P. Huang, H. Dai, Q. Li, L. Hu, J. Peng, S. Jiang, Y. Xu, Z. Wu, H. Nie, Z. Zhang, W. Yin, X. Zhang, J. Lu, Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 892.