Influence of Isomerism on Radioluminescence of Purely Organic Phosphorescence Scintillators
Chaomin Dong
Key Laboratory of Flexible Electronics & Institute of Advanced Materials, Nanjing Tech University, Nanjing, 211800 China
These authors contributed equally.
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Xiao Wang
Frontiers Science Center for Flexible Electronics, Xi'an Institute of Flexible Electronics and Xi'an Institute of Biomedical Materials & Engineering, Northwestern Polytechnical University, Xi'an, 710072 China
These authors contributed equally.
Search for more papers by this authorWenqi Gong
Key Laboratory of Flexible Electronics & Institute of Advanced Materials, Nanjing Tech University, Nanjing, 211800 China
Search for more papers by this authorWenbo Ma
State Key Laboratory of Modern Optical Instrumentation, College of Optical Science and Engineering, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, 310027 China
Search for more papers by this authorMeng Zhang
Key Laboratory of Flexible Electronics & Institute of Advanced Materials, Nanjing Tech University, Nanjing, 211800 China
Search for more papers by this authorJingjie Li
Key Laboratory of Flexible Electronics & Institute of Advanced Materials, Nanjing Tech University, Nanjing, 211800 China
Search for more papers by this authorYuan Zhang
Key Laboratory of Flexible Electronics & Institute of Advanced Materials, Nanjing Tech University, Nanjing, 211800 China
Search for more papers by this authorZixing Zhou
Key Laboratory of Flexible Electronics & Institute of Advanced Materials, Nanjing Tech University, Nanjing, 211800 China
Search for more papers by this authorZhijian Yang
MOE Key Laboratory for Analytical Science of Food Safety and Biology, State Key Laboratory of Photocatalysis on Energy and Environment, College of Chemistry, Fuzhou University, Fuzhou, 350002 China
Search for more papers by this authorShuli Qu
Key Laboratory of Flexible Electronics & Institute of Advanced Materials, Nanjing Tech University, Nanjing, 211800 China
Search for more papers by this authorQian Wang
Key Laboratory of Flexible Electronics & Institute of Advanced Materials, Nanjing Tech University, Nanjing, 211800 China
Search for more papers by this authorZhu Zhao
Key Laboratory of Flexible Electronics & Institute of Advanced Materials, Nanjing Tech University, Nanjing, 211800 China
Search for more papers by this authorGuohui Yang
Key Laboratory of Flexible Electronics & Institute of Advanced Materials, Nanjing Tech University, Nanjing, 211800 China
Search for more papers by this authorAnqi Lv
Key Laboratory of Flexible Electronics & Institute of Advanced Materials, Nanjing Tech University, Nanjing, 211800 China
Search for more papers by this authorHuili Ma
Key Laboratory of Flexible Electronics & Institute of Advanced Materials, Nanjing Tech University, Nanjing, 211800 China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Qiushui Chen
MOE Key Laboratory for Analytical Science of Food Safety and Biology, State Key Laboratory of Photocatalysis on Energy and Environment, College of Chemistry, Fuzhou University, Fuzhou, 350002 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Huifang Shi
Key Laboratory of Flexible Electronics & Institute of Advanced Materials, Nanjing Tech University, Nanjing, 211800 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Yang (Michael) Yang
State Key Laboratory of Modern Optical Instrumentation, College of Optical Science and Engineering, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, 310027 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Zhongfu An
Key Laboratory of Flexible Electronics & Institute of Advanced Materials, Nanjing Tech University, Nanjing, 211800 China
Search for more papers by this authorChaomin Dong
Key Laboratory of Flexible Electronics & Institute of Advanced Materials, Nanjing Tech University, Nanjing, 211800 China
These authors contributed equally.
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Xiao Wang
Frontiers Science Center for Flexible Electronics, Xi'an Institute of Flexible Electronics and Xi'an Institute of Biomedical Materials & Engineering, Northwestern Polytechnical University, Xi'an, 710072 China
These authors contributed equally.
Search for more papers by this authorWenqi Gong
Key Laboratory of Flexible Electronics & Institute of Advanced Materials, Nanjing Tech University, Nanjing, 211800 China
Search for more papers by this authorWenbo Ma
State Key Laboratory of Modern Optical Instrumentation, College of Optical Science and Engineering, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, 310027 China
Search for more papers by this authorMeng Zhang
Key Laboratory of Flexible Electronics & Institute of Advanced Materials, Nanjing Tech University, Nanjing, 211800 China
Search for more papers by this authorJingjie Li
Key Laboratory of Flexible Electronics & Institute of Advanced Materials, Nanjing Tech University, Nanjing, 211800 China
Search for more papers by this authorYuan Zhang
Key Laboratory of Flexible Electronics & Institute of Advanced Materials, Nanjing Tech University, Nanjing, 211800 China
Search for more papers by this authorZixing Zhou
Key Laboratory of Flexible Electronics & Institute of Advanced Materials, Nanjing Tech University, Nanjing, 211800 China
Search for more papers by this authorZhijian Yang
MOE Key Laboratory for Analytical Science of Food Safety and Biology, State Key Laboratory of Photocatalysis on Energy and Environment, College of Chemistry, Fuzhou University, Fuzhou, 350002 China
Search for more papers by this authorShuli Qu
Key Laboratory of Flexible Electronics & Institute of Advanced Materials, Nanjing Tech University, Nanjing, 211800 China
Search for more papers by this authorQian Wang
Key Laboratory of Flexible Electronics & Institute of Advanced Materials, Nanjing Tech University, Nanjing, 211800 China
Search for more papers by this authorZhu Zhao
Key Laboratory of Flexible Electronics & Institute of Advanced Materials, Nanjing Tech University, Nanjing, 211800 China
Search for more papers by this authorGuohui Yang
Key Laboratory of Flexible Electronics & Institute of Advanced Materials, Nanjing Tech University, Nanjing, 211800 China
Search for more papers by this authorAnqi Lv
Key Laboratory of Flexible Electronics & Institute of Advanced Materials, Nanjing Tech University, Nanjing, 211800 China
Search for more papers by this authorHuili Ma
Key Laboratory of Flexible Electronics & Institute of Advanced Materials, Nanjing Tech University, Nanjing, 211800 China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Qiushui Chen
MOE Key Laboratory for Analytical Science of Food Safety and Biology, State Key Laboratory of Photocatalysis on Energy and Environment, College of Chemistry, Fuzhou University, Fuzhou, 350002 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Huifang Shi
Key Laboratory of Flexible Electronics & Institute of Advanced Materials, Nanjing Tech University, Nanjing, 211800 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Yang (Michael) Yang
State Key Laboratory of Modern Optical Instrumentation, College of Optical Science and Engineering, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, 310027 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Zhongfu An
Key Laboratory of Flexible Electronics & Institute of Advanced Materials, Nanjing Tech University, Nanjing, 211800 China
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
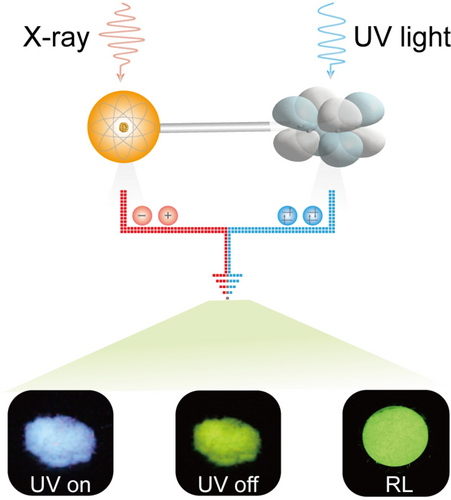
We present an isomerism strategy to study the effect of molecular structures on radioluminescence. Under UV-light excitation, all isomers showed bright phosphorescence with an efficiency of up to 22.8 %. Unexpectedly, both m-BA and p-BA scintillators showed bright luminescence under X-ray irradiation, which was ascribed to both excellent electrical conductivity and efficient suppression of non-radiative decay.
Abstract
There are few reports about purely organic phosphorescence scintillators, and the relationship between molecular structures and radioluminescence in organic scintillators is still unclear. Here, we presented isomerism strategy to study the effect of molecular structures on radioluminescence. The isomers can achieve phosphorescence efficiency of up to 22.8 % by ultraviolet irradiation. Under X-ray irradiation, both m-BA and p-BA show excellent radioluminescence, while o-BA has almost no radioluminescence. Through experimental and theoretical investigation, we found that radioluminescence was not only affected by non-radiation in emissive process, but also highly depended on the material conductivity caused by the different molecular packing. This study not only allows us to clearly understand the relationship between the molecular structures and radioluminescence, but also provides a guidance to rationally design new organic scintillators.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie202109802-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf4.5 MB | Supporting Information |
| anie202109802-sup-0001-Video_S1.avi1.6 MB | Supporting Information |
| anie202109802-sup-0001-Video_S2.avi1.6 MB | Supporting Information |
| anie202109802-sup-0001-Video_S3.avi1.1 MB | Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1
- 1aQ. Chen, J. Wu, X. Ou, B. Huang, J. Almutlaq, A. A. Zhumekenov, X. Guan, S. Han, L. Liang, Z. Yi, J. Li, X. Xie, Y. Wang, Y. Li, D. Fan, D. B. L. Teh, A. H. All, O. F. Mohammed, O. M. Bakr, T. Wu, M. Bettinelli, H. Yang, W. Huang, X. Liu, Nature 2018, 561, 88–93;
- 1bX. Wang, H. Shi, H. Ma, W. Ye, L. Song, J. Zan, X. Yao, X. Ou, G. Yang, Z. Zhao, M. Singh, C. Lin, H. Wang, W. Jia, Q. Wang, J. Zhi, C. Dong, X. Jiang, Y. Tang, X. Xie, Y. Yang, J. Wang, Q. Chen, Y. Wang, H. Yang, G. Zhang, Z. An, X. Liu, W. Huang, Nat. Photonics 2021, 15, 187–192;
- 1cT. J. Hajagos, C. Liu, N. J. Cherepy, Q. Pei, Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1706956;
- 1dJ. Perego, I. Villa, A. Pedrini, E. C. Padovani, R. Crapanzano, A. Vedda, C. Dujardin, C. X. Bezuidenhout, S. Bracco, P. E. Sozzani, A. Comotti, L. Gironi, M. Beretta, M. Salomoni, N. Kratochwil, S. Gundacker, E. Auffray, F. Meinardi, A. Monguzzi, Nat. Photonics 2021, 15, 393–400.
- 2
- 2aM. Zhang, X. Wang, B. Yang, J. Zhu, G. Niu, H. Wu, L. Yin, X. Du, M. Niu, Y. Ge, Q. Xie, Y. Yan, J. Tang, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2007921;
- 2bP. Büchele, M. Richter, S. F. Tedde, G. J. Matt, G. N. Ankah, R. Fischer, M. Biele, W. Metzger, S. Lilliu, O. Bikondoa, J. E. Macdonald, C. J. Brabec, T. Kraus, U. Lemmer, O. Schmidt, Nat. Photonics 2015, 9, 843–848;
- 2cH. Lusic, M. W. Grinstaff, Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 1641–1666;
- 2dP. Pei, Y. Chen, C. Sun, Y. Fan, Y. Yang, X. Liu, L. Lu, M. Zhao, H. Zhang, D. Zhao, X. Liu, F. Zhang, Nat. Nanotechnol. 2021, 16, 1011–1018.
- 3
- 3aB. G. Durie, S. E. Salmon, Science 1975, 190, 1093–1095;
- 3bY. Zou, Y. Wei, G. Wang, F. Meng, M. Gao, G. Storm, Z. Zhong, Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1603997;
- 3cJ. Xu, M. Yu, P. Carter, E. Hernandez, A. Dang, P. Kapur, J. T. Hsieh, J. Zheng, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 13356–13360; Angew. Chem. 2017, 129, 13541–13545;
- 3dW. Zhu, W. Ma, Y. Su, Z. Chen, X. Chen, Y. Ma, L. Bai, W. Xiao, T. Liu, H. Zhu, X. Liu, H. Liu, X. Liu, Y. Yang, Light: Sci. Appl. 2020, 9, 112;
- 3eX. Ou, X. Qin, B. Huang, J. Zan, Q. Wu, Z. Hong, L. Xie, H. Bian, Z. Yi, X. Chen, Y. Wu, X. Song, J. Li, Q. Chen, H. Yang, X. Liu, Nature 2021, 590, 410–415;
- 3fY. He, M. Petryk, Z. Liu, D. G. Chica, I. Hadar, C. Leak, W. Ke, I. Spanopoulos, W. Lin, D. Y. Chung, B. W. Wessels, Z. He, M. G. Kanatzidis, Nat. Photonics 2021, 15, 36–42;
- 3gB. D. Milbrath, A. J. Peurrung, M. Bliss, W. Weber, J. Mater. Res. 2008, 23, 2561–2581.
- 4
- 4aT. Chen, H. Yu, X. Wen, C. Redding, T. J. Hajagos, H. Zhao, J. P. Hayward, C. Yang, Q. Pei, Adv. Opt. Mater. 2021, 9, 2001975;
- 4bM. Gandini, I. Villa, M. Beretta, C. Gotti, M. Imran, F. Carulli, E. Fantuzzi, M. Sassi, M. Zaffalon, C. Brofferio, Nat. Nanotechnol. 2020, 15, 462–468.
- 5
- 5aD. G. Ott, F. N. Hayes, E. Hansbury, V. N. Kerr, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1957, 79, 5448–5454;
- 5bS. Cho, S. Kim, J. Kim, Y. Jo, I. Ryu, S. Hong, J.-J. Lee, S. Cha, E. B. Nam, S. U. Lee, Light: Sci. Appl. 2020, 9, 156;
- 5cF. Reines, R. Schuch, C. Cowan, F. Harrison, E. C. Anderson, F. Hayes, Nature 1953, 172, 521–523.
- 6M. Chen, C. Wang, W. Hu, J. Mater. Chem. C 2021, 9, 4709–4729.
- 7
- 7aA. Rao, P. C. Chow, S. Gelinas, C. W. Schlenker, C. Z. Li, H. L. Yip, A. K. Jen, D. S. Ginger, R. H. Friend, Nature 2013, 500, 435–439;
- 7bN. J. Thompson, M. W. Wilson, D. N. Congreve, P. R. Brown, J. M. Scherer, T. S. Bischof, M. Wu, N. Geva, M. Welborn, T. Van Voorhis, Nat. Mater. 2014, 13, 1039–1043.
- 8
- 8aL. Gu, H. Shi, L. Bian, M. Gu, K. Ling, X. Wang, H. Ma, S. Cai, W. Ning, L. Fu, H. Wang, S. Wang, Y. Gao, W. Yao, F. Huo, Y. Tao, Z. An, X. Liu, W. Huang, Nat. Photonics 2019, 13, 406–411;
- 8bJ. Yang, X. Zhen, B. Wang, X. Gao, Z. Ren, J. Wang, Y. Xie, J. Li, Q. Peng, K. Pu, Z. Li, Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 840;
- 8cW. Zhao, T. S. Cheung, N. Jiang, W. Huang, J. W. Y. Lam, X. Zhang, Z. He, B. Tang, Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1595;
- 8dX. Ma, J. Wang, H. Tian, Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 738–748;
- 8eC. A. M. Salla, G. Farias, M. Rouzières, P. Dechambenoit, F. Durola, H. Bock, B. de Souza, I. H. Bechtold, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 6982–6986; Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 7056–7060;
- 8fT. Wang, Z. Hu, X. Nie, L. Huang, M. Hui, X. Sun, G. Zhang, Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1364;
- 8gH. Ma, Q. Peng, Z. An, W. Huang, Z. Shuai, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 1010–1015;
- 8hO. Bolton, K. Lee, H. J. Kim, K. Y. Lin, J. Kim, Nat. Chem. 2011, 3, 205–210;
- 8iZ. Yang, Z. Mao, X. Zhang, D. Ou, Y. Mu, Y. Zhang, C. Zhao, S. Liu, Z. Chi, J. Xu, Y. C. Wu, P. Y. Lu, A. Lien, M. R. Bryce, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 2181–2185; Angew. Chem. 2016, 128, 2221–2225;
- 8jK. Narushima, Y. Kiyota, T. Mori, S. Hirata, M. Vacha, Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1807268;
- 8kY. Su, S. Z. F. Phua, Y. Li, X. Zhou, D. Jana, G. Liu, W. Q. Lim, W. K. Ong, C. Yang, Y. Zhao, Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaas9732;
- 8lT. Zhang, X. Ma, H. Wu, L. Zhu, Y. Zhao, H. Tian, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 11206–11216; Angew. Chem. 2020, 132, 11302–11312;
- 8mY. Zhang, Y. Su, H. Wu, Z. Wang, C. Wang, Y. Zheng, X. Zheng, L. Gao, Q. Zhou, Y. Yang, X. Chen, C. Yang, Y. Zhao, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 13675–13685;
- 8nB. Ding, L. Ma, Z. Huang, X. Ma, H. Tian, Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabf9668.
- 9
- 9aG. Blasse, Chem. Mater. 1994, 6, 1465;
- 9bX. Chen, J. Song, X. Chen, H. Yang, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 3073–3101.
- 10
- 10aR. Zhuang, X. Wang, W. Ma, Y. Wu, X. Chen, L. Tang, H. Zhu, J. Liu, L. Wu, W. Zhou, X. Liu, Y. Yang, Nat. Photonics 2019, 13, 602–608;
- 10bY.-M. Yang, Z.-Y. Li, J.-Y. Zhang, Y. Lu, S.-Q. Guo, Q. Zhao, X. Wang, Z.-J. Yong, H. Li, J.-P. Ma, Y. Kuroiwa, C. Moriyoshi, L.-L. Hu, L.-Y. Zhang, L.-R. Zheng, H.-T. Sun, Light: Sci. Appl. 2018, 7, 88.
- 11
- 11aG. Baryshnikov, B. Minaev, H. Ågren, Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 6500–6537;
- 11bM. Kasha, J. Chem. Phys. 1952, 20, 71–74.
- 12
- 12aZ. Yang, C. Xu, W. Li, Z. Mao, X. Ge, Q. Huang, H. Deng, J. Zhao, F. L. Gu, Y. Zhang, Z. Chi, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 17451–17455; Angew. Chem. 2020, 132, 17604–17608;
- 12bN. Gan, X. Wang, H. Ma, A. Lv, H. Wang, Q. Wang, M. Gu, S. Cai, Y. Zhang, L. Fu, M. Zhang, C. Dong, W. Yao, H. Shi, Z. An, W. Huang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 14140–14145; Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 14278–14283;
- 12cY. Xiong, Z. Zhao, W. Zhao, H. Ma, Q. Peng, Z. He, X. Zhang, Y. Chen, X. He, J. W. Y. Lam, B. Tang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 7997–8001; Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 8129–8133;
- 12dZ. He, H. Gao, S. Zhang, S. Zheng, Y. Wang, Z. Zhao, D. Ding, B. Yang, Y. Zhang, W. Yuan, Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1807222;
- 12eC. Chen, R. Huang, A. S. Batsanov, P. Pander, Y. T. Hsu, Z. Chi, F. B. Dias, M. R. Bryce, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 16407–16411; Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 16645–16649.
- 13H. Inokuchi, H. Akamatu, J. Solid State Phys. 1961, 12, 93–148.
- 14
- 14aS. K. Maity, S. Bera, A. Paikar, A. Pramanik, D. Haldar, Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 9051–9053;
- 14bS. Cai, H. Shi, D. Tian, H. Ma, Z. Cheng, Q. Wu, M. Gu, L. Huang, Z. An, Q. Peng, W. Huang, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1705045;
- 14cJ. Wang, X. Gu, H. Ma, Q. Peng, X. Huang, X. Zheng, S. H. P. Sung, G. Shan, J. W. Y. Lam, Z. Shuai, B. Tang, Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2963.
- 15H. Wei, Y. Fang, P. Mulligan, C. William, H. Fang, C. Wang, B. R. Ecker, Y. Gao, M. A. Loi, C. Lei, J. Huang, Nat. Photonics 2016, 10, 333–339.
- 16M. J. Berger, XCOM: photon cross sections database, 2010, https://www.nist.gov/pml/xcom-photon-cross-sections-database.