Sink/Float Magnetic Immunoassays for In-Field Bioassays
Graphical Abstract
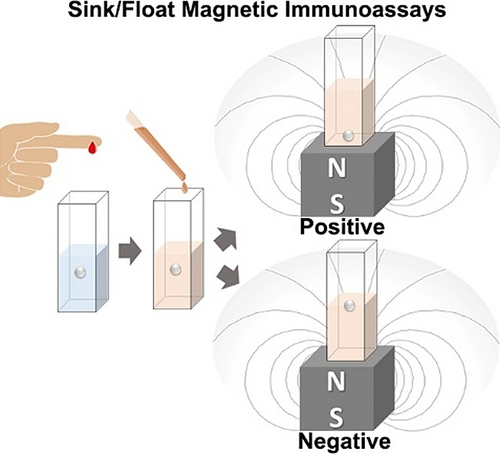
Sink/float magnetic immunoassays detect proteins, antibodies, and bacteria in samples using a simple mix-and-observe protocol that uses a biofunctionalized small sphere, some liquid reagents and a small permanent magnet. A simple sink/float test of the sphere identifies if the analyte is above or below a predetermined level; the sphere sinks only if the analyte is above the concentration level.
Abstract
Analytical tests/devices that are used outside laboratory settings are required to have a very simple analytical protocol to get clearance by regulatory authorities. This study describes sink/float magnetic immunoassays, a new type of rapid, mix-and-observe, instrument-free tests for the detection of biomarkers in untreated biological samples that are very simple and might meet the simple-to-use criterion of authorities to be used in the field. These tests can tell whether an analyte is above or below a predetermined level within 25–45 minutes based on the sinking or floating of a mm-sized sphere on the surface of which an immunoassay that uses reporter antibodies conjugated to superparamagnetic nanoparticles is performed. This manuscript describes the theory and proof-of-concept applications of sink/float magnetic immunoassays for the detection of C-Reactive Protein, anti-Treponema pallidum antibodies and E. coli bacteria.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.