Stable 2D Heteroporous Covalent Organic Frameworks for Efficient Ionic Conduction
Zhen Xie
Department of Chemistry, Institute of Molecular Plus, Tianjin Key Laboratory of Molecular Optoelectronic Science, Tianjin University, Tianjin, 300072 China
Search for more papers by this authorBo Wang
Department of Chemistry, Institute of Molecular Plus, Tianjin Key Laboratory of Molecular Optoelectronic Science, Tianjin University, Tianjin, 300072 China
Search for more papers by this authorZongfan Yang
Department of Chemistry, Institute of Molecular Plus, Tianjin Key Laboratory of Molecular Optoelectronic Science, Tianjin University, Tianjin, 300072 China
Search for more papers by this authorXiao Yang
Department of Chemistry, Institute of Molecular Plus, Tianjin Key Laboratory of Molecular Optoelectronic Science, Tianjin University, Tianjin, 300072 China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Xiang Yu
Analytical and Testing Center, Jinan University, Guangzhou, 510632 China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Guolong Xing
Department of Chemistry, Institute of Molecular Plus, Tianjin Key Laboratory of Molecular Optoelectronic Science, Tianjin University, Tianjin, 300072 China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Yinghui Zhang
School of Materials Science and Engineering & National Institute for Advanced Materials, Nankai University, Tianjin, 300350 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Long Chen
Department of Chemistry, Institute of Molecular Plus, Tianjin Key Laboratory of Molecular Optoelectronic Science, Tianjin University, Tianjin, 300072 China
Search for more papers by this authorZhen Xie
Department of Chemistry, Institute of Molecular Plus, Tianjin Key Laboratory of Molecular Optoelectronic Science, Tianjin University, Tianjin, 300072 China
Search for more papers by this authorBo Wang
Department of Chemistry, Institute of Molecular Plus, Tianjin Key Laboratory of Molecular Optoelectronic Science, Tianjin University, Tianjin, 300072 China
Search for more papers by this authorZongfan Yang
Department of Chemistry, Institute of Molecular Plus, Tianjin Key Laboratory of Molecular Optoelectronic Science, Tianjin University, Tianjin, 300072 China
Search for more papers by this authorXiao Yang
Department of Chemistry, Institute of Molecular Plus, Tianjin Key Laboratory of Molecular Optoelectronic Science, Tianjin University, Tianjin, 300072 China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Xiang Yu
Analytical and Testing Center, Jinan University, Guangzhou, 510632 China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Guolong Xing
Department of Chemistry, Institute of Molecular Plus, Tianjin Key Laboratory of Molecular Optoelectronic Science, Tianjin University, Tianjin, 300072 China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Yinghui Zhang
School of Materials Science and Engineering & National Institute for Advanced Materials, Nankai University, Tianjin, 300350 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Long Chen
Department of Chemistry, Institute of Molecular Plus, Tianjin Key Laboratory of Molecular Optoelectronic Science, Tianjin University, Tianjin, 300072 China
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
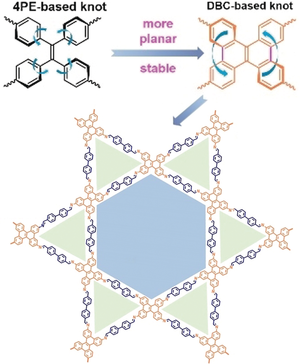
Planarization-enhanced stability: Dibenzo[g,p]chrysene (DBC), a “closed” version of tetraphenylethene (4PE), was integrated into a 2D heteroporous imine covalent organic framework (COF). The resulting DBC-COF exhibited much better crystallinity and stability than its counterpart 4PE-COF, and is a promising host material for ionic conduction.
Abstract
Two-dimensional (2D) covalent organic frameworks (COFs) feature open and ordered one-dimensional column nanochannels which offer immense possibilities for incorporation of various guests for specific functions. However, the relatively low chemical stability of most COFs originating from the dynamic covalent linkages hinders their practical application. In this work, a highly crystalline and heteroporous dibenzo[g,p]chrysene-based COF (DBC-2P) was synthesized and served as a host material for ionic conduction. DBC-2P exhibits excellent stability both in strong acid and base due to the large conjugated DBC-based knot that reinforces the interlayer interactions. Subsequent encapsulation of linear polyethylene glycol (PEG) and PEG-LiBF4 salt into the nanochannels of DBC-2P affords a hybrid material with a high ionic conductivity of 2.31×10−3 S cm−1. This work demonstrates an efficient post-synthetic strategy for the development of new COF–polymer composites with intriguing properties.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie201909554-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf3.2 MB | Supplementary |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1A. P. Côtè, A. I. Benin, N. W. Ockwig, M. O'Keeffe, A. J. Matzger, O. M. Yaghi, Science 2005, 310, 1166–1170.
- 2
- 2aF. J. Uribe-Romo, J. R. Hunt, H. Furukawa, C. Klöck, M. O'Keeffe, O. M. Yaghi, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 4570–4571;
- 2bF. J. Uribe-Romo, C. J. Doonan, H. Furukawa, K. Oisaki, O. M. Yaghi, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 11478–11481;
- 2cS. Dalapati, S. Jin, J. Gao, Y. Xu, A. Nagai, D. Jiang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 17310–17313.
- 3
- 3aT. Zhou, S. Xu, Q. Wen, Z. Pang, X. Zhao, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 15885–15888;
- 3bY. Liu, Y. Ma, Y. Zhao, X. Sun, F. Gándara, H. Furukawa, Z. Liu, H. Zhu, C. Zhu, K. Suenaga, P. Oleynikov, A. S. Alshammari, X. Zhang, O. Terasaki, O. M. Yaghi, Science 2016, 351, 365–369;
- 3cZ. Pang, S. Xu, T. Zhou, R. Liang, T. Zhan, X. Zhao, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 4710–4713;
- 3dC. Qian, Q. Qi, G. Jiang, F. Cui, Y. Tian, X. Zhao, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 6736–6743.
- 4
- 4aP. F. Wei, M. Z. Qi, Z. P. Wang, S. Y. Ding, W. Yu, Q. Liu, L. K. Wang, H. Z. Wang, W. K. An, W. Wang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 4623–4631;
- 4bS. Kandambeth, A. Mallick, B. Lukose, M. V. Mane, T. Heine, R. Banerjee, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 19524–19527;
- 4cY. Zeng, R. Zou, Z. Luo, H. Zhang, X. Yao, X. Ma, R. Zou, Y. Zhao, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 1020–1023.
- 5
- 5aN. Huang, X. Chen, R. Krishna, D. Jiang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 2986–2990; Angew. Chem. 2015, 127, 3029–3033;
- 5bN. Huang, R. Krishna, D. Jiang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 7079–7082.
- 6
- 6aH. Xu, J. Gao, D. Jiang, Nat. Chem. 2015, 7, 905–912;
- 6bQ. Sun, B. Aguila, J. A. Perman, N. T. Nguyen, S. Ma, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 15790–11579;
- 6cX. Wang, X. Han, J. Zhang, X. Wu, Y. Liu, Y. Cui, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 12332–12335.
- 7S. Ding, M. Dong, Y. Wang, Y. Chen, H. Wang, C. Su, W. Wang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 3031–3037.
- 8C. R. DeBlase, K. E. Silberstein, T. Truong, H. D. Abruña, W. R. Dichtel, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 16821–16824.
- 9
- 9aL. Chen, K. Furukawa, J. Gao, A. Nagai, T. Nakamura, Y. Dong, D. Jiang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 9806–9809;
- 9bV. S. Vyas, F. Haase, L. Stegbauer, G. Savasci, F. Podjaski, C. Ochsenfeld, B. V. Lotsch, Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8508;
- 9cD. Bessinger, L. Ascherl, F. Auras, T. Bein, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 12035–12042;
- 9dT. Sick, A. G. Hufnagel, J. Kampmann, I. Kondofersky, M. Calik, J. M. Rotter, A. Evans, M. Döblinger, S. Herbert, K. Peters, D. Böhm, P. Knochel, D. D. Medina, D. Fattakhova-Rohlfing, T. Bein, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 2085–2092.
- 10N. Huang, P. Wang, D. Jiang, Nat. Rev. Mater. 2016, 1, 16068.
- 11
- 11aB. Lukose, A. Kuc, T. Heine, Chem. Eur. J. 2011, 17, 2388–2392;
- 11bF. Auras, L. Ascherl, A. H. Hakimioun, J. T. Margraf, F. C. Hanusch, S. Reuter, D. Bessinger, M. Döblinger, C. Hettstedt, K. Karaghiosoff, S. Herbert, P. Knochel, T. Clark, T. Bein, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 16703–16710.
- 12M. S. Lohse, T. Bein, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1705553.
- 13
- 13aS. Lu, Y. Hu, S. Wan, R. McCaffrey, Y. Jin, H. Gu, W. Zhang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 17082–17088;
- 13bH. Xu, S. Tao, D. Jiang, Nat. Mater. 2016, 15, 722–726;
- 13cQ. Xu, S. Tao, Q. Jiang, D. Jiang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 7429–7432.
- 14
- 14aT. Kitao, Y. Zhang, S. Kitagawa, B. Wang, T. Uemura, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 3108–3133;
- 14bT. Uemura, N. Yanai, S. Watanabe, H. Tanaka, R. Numaguchi, M. T. Miyahara, Y. Ohta, M. Nagaoka, S. Kitagawa, Nat. Commun. 2010, 1, 83;
- 14cK. Tajima, T. Aida, Chem. Commun. 2000, 0, 2399–2412;
- 14dT. Uemura, K. Kitagawa, S. Horike, T. Kawamura, S. Kitagawa, M. Mizuno, K. Endo, Chem. Commun. 2005, 0, 5968–5970;
- 14eW. Morris, W. E. Briley, E. Auyeung, M. D. Cabezas, C. A. Mirkin, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 7261–7264.
- 15
- 15aT. Bae, J. S. Lee, W. Qiu, W. J. Koros, C. W. Jones, S. Nair, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 9863–9866; Angew. Chem. 2010, 122, 10059–10062;
- 15bY. Zhang, X. Feng, H. Li, Y. Chen, J. Zhao, S. Wang, L. Wang, B. Wang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 4259–4263; Angew. Chem. 2015, 127, 4333–4337;
- 15cN. Yanai, T. Uemura, S. Horike, S. Shimomura, S. Kitagawa, Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 1722–1724.
- 16N. C. Burtch, H. Jasuja, K. S. Walton, Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 10575–10612.
- 17R. P. Bisbey, W. R. Dichtel, ACS Cent. Sci. 2017, 3, 533–543.
- 18
- 18aA. van der Craats, N. Stutzmann, O. Bunk, M. Nielsen, M. Watson, K. Müllen, H. Chanzy, H. Sirringhaus, R. Friend, Adv. Mater. 2003, 15, 495–499;
- 18bS. Kumar, S. Varshney, Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 2002, 378, 59–64.
- 19L. Ascherl, T. Sick, J. Margraf, S. Lapidus, M. Calik, C. Hettstedt, K. Karaghiosoff, M. Döblinger, T. Clark, K. Chapman, F. Auras, T. Bein, Nat. Chem. 2016, 8, 310–316.
- 20
- 20aM. Alcoutlabi, G. B. McKenna, J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2005, 17, R 461–R524;
- 20bC. Alba-Simionesco, B. Coasne, G. Dosseh, G. Dudziak, K. E. Gubbins, R. Radhakrishnan, M. Sliwinska-Bartkowiak, J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2006, 18, R 15–R68.
- 21S. K. Nataraj, C. Wang, H. Huang, H. Du, S. Wang, Y. Chen, Li. Chen, K. Chen, ChemSusChem 2012, 5, 392–395.
- 22S. Horike, D. Umeyama, M. Inukai, T. Itakura, S. Kitagawa, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 7612–7615.
- 23
- 23aC. Montoro, D. Rodríguez-San-Miguel, E. Polo, R. Escudero-Cid, M. L. Ruiz-González, J. A. R. Navarro, P. Ocón, F. Zamora, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 10079–10086;
- 23bS. Horike, Y. Kamitsubo, M. Inukai, T. Fukushima, D. Umeyama, T. Itakura, S. Kitagawa, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 4612–4615.