A Polymer Solution To Prevent Nanoclustering and Improve the Selectivity of Metal Nanoparticles for Electrocatalytic CO2 Reduction
Dr. Lei Zhang
Jiangsu Key Laboratory of New Power Batteries, Collaborative Innovation Center of Biomedical Functional Materials, School of Chemistry and Materials Science, Nanjing Normal University, Nanjing, 210023 China
Department of Chemistry, University of Connecticut, Storrs, CT, 06269 USA
Search for more papers by this authorZichao Wei
Department of Chemistry, University of Connecticut, Storrs, CT, 06269 USA
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Srinivas Thanneeru
Department of Chemistry, University of Connecticut, Storrs, CT, 06269 USA
Search for more papers by this authorMichael Meng
Department of Chemistry, University of Connecticut, Storrs, CT, 06269 USA
Search for more papers by this authorMegan Kruzyk
Department of Chemistry, University of Connecticut, Storrs, CT, 06269 USA
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Gaël Ung
Department of Chemistry, University of Connecticut, Storrs, CT, 06269 USA
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Ben Liu
Jiangsu Key Laboratory of New Power Batteries, Collaborative Innovation Center of Biomedical Functional Materials, School of Chemistry and Materials Science, Nanjing Normal University, Nanjing, 210023 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Jie He
Department of Chemistry, University of Connecticut, Storrs, CT, 06269 USA
Polymer Program, Institute of Materials Science, University of Connecticut, Storrs, CT, 06269 USA
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Lei Zhang
Jiangsu Key Laboratory of New Power Batteries, Collaborative Innovation Center of Biomedical Functional Materials, School of Chemistry and Materials Science, Nanjing Normal University, Nanjing, 210023 China
Department of Chemistry, University of Connecticut, Storrs, CT, 06269 USA
Search for more papers by this authorZichao Wei
Department of Chemistry, University of Connecticut, Storrs, CT, 06269 USA
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Srinivas Thanneeru
Department of Chemistry, University of Connecticut, Storrs, CT, 06269 USA
Search for more papers by this authorMichael Meng
Department of Chemistry, University of Connecticut, Storrs, CT, 06269 USA
Search for more papers by this authorMegan Kruzyk
Department of Chemistry, University of Connecticut, Storrs, CT, 06269 USA
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Gaël Ung
Department of Chemistry, University of Connecticut, Storrs, CT, 06269 USA
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Ben Liu
Jiangsu Key Laboratory of New Power Batteries, Collaborative Innovation Center of Biomedical Functional Materials, School of Chemistry and Materials Science, Nanjing Normal University, Nanjing, 210023 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Jie He
Department of Chemistry, University of Connecticut, Storrs, CT, 06269 USA
Polymer Program, Institute of Materials Science, University of Connecticut, Storrs, CT, 06269 USA
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
Abstract
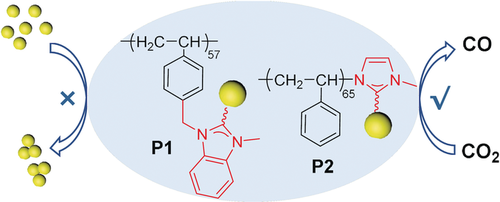
The stability of metal nanocatalysts for electrocatalytic CO2 reduction is of key importance for practical application. We report the use of two polymeric N-heterocyclic carbenes (NHC) (polydentate and monodentate) to stabilize metal nanocatalysts (Au and Pd) for efficient CO2 electroreduction. Compared with other conventional ligands including thiols and amines, metal–carbene bonds that are stable under reductive potentials prevent the nanoclustering of nanoparticles. Au nanocatalysts modified by polymeric NHC ligands show an activity retention of 86 % after CO2 reduction at −0.9 V for 11 h, while it is less than 10 % for unmodified Au. We demonstrate that the hydrophobicity of polymer ligands and the enriched surface electron density of metal NPs through σ-donation of NHCs substantially improve the selectivity for CO2 reduction over proton.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie201909069-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf1.3 MB | Supplementary |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1J. Huang, R. Buonsanti, Chem. Mater. 2019, 31, 13–25.
- 2L. Jin, B. Liu, S. Duay, J. He, Catalysts 2017, 7, 44.
- 3
- 3aS. Ikeda, S. Ishino, T. Harada, N. Okamoto, T. Sakata, H. Mori, S. Kuwabata, T. Torimoto, M. Matsumura, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 7063–7066; Angew. Chem. 2006, 118, 7221–7224;
- 3bZ. Niu, Y. Li, Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 72–83.
- 4C. Rogers, W. S. Perkins, G. Veber, T. E. Williams, R. R. Cloke, F. R. Fischer, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 4052–4061.
- 5
- 5aY. Fang, J. C. Flake, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 3399–3405;
- 5bC. A. Schoenbaum, D. K. Schwartz, J. W. Medlin, Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 1438–1445;
- 5cC. A. Schoenbaum, D. K. Schwartz, J. W. Medlin, J. Catal. 2013, 303, 92–99.
- 6
- 6aJ. A. Trindell, J. Clausmeyer, R. M. Crooks, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 16161–16167;
- 6bM. H. Stewart, K. Susumu, B. C. Mei, I. L. Medintz, J. B. Delehanty, J. B. Blanco-Canosa, P. E. Dawson, H. Mattoussi, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 9804–9813;
- 6cP. Liu, R. Qin, G. Fu, N. Zheng, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 2122–2131.
- 7
- 7aK. Manthiram, Y. Surendranath, A. P. Alivisatos, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 7237–7240;
- 7bZ. Cao, S. B. Zacate, X. Sun, J. Liu, E. M. Hale, W. P. Carson, S. B. Tyndall, J. Xu, X. Liu, X. Liu, C. Song, J. H. Luo, M. J. Cheng, X. Wen, W. Liu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 12675–12679; Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 12857–12861.
- 8
- 8aK. Manthiram, B. J. Beberwyck, A. P. Alivisatos, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 13319–13325;
- 8bJ. Huang, N. Hormann, E. Oveisi, A. Loiudice, G. L. De Gregorio, O. Andreussi, N. Marzari, R. Buonsanti, Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3117;
- 8cZ. Wang, G. Yang, Z. Zhang, M. Jin, Y. Yin, ACS Nano 2016, 10, 4559–4564.
- 9
- 9aS. Liu, H. Tao, L. Zeng, Q. Liu, Z. Xu, Q. Liu, J. L. Luo, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 2160–2163;
- 9bM. Ma, K. Liu, J. Shen, R. Kas, W. A. Smith, ACS Energy Lett. 2018, 3, 1301–1306.
- 10S. Zhang, G. Leem, L. O. Srisombat, T. R. Lee, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 113–120.
- 11
- 11aZ. Cao, D. Kim, D. Hong, Y. Yu, J. Xu, S. Lin, X. Wen, E. M. Nichols, K. Jeong, J. A. Reimer, P. Yang, C. J. Chang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 8120–8125;
- 11bM. J. MacLeod, A. J. Goodman, H. Z. Ye, H. V. Nguyen, T. Van Voorhis, J. A. Johnson, Nat. Chem. 2019, 11, 57–63;
- 11cA. Ferry, K. Schaepe, P. Tegeder, C. Richter, K. M. Chepiga, B. J. Ravoo, F. Glorius, ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 5414–5420;
- 11dA. Rühling, K. Schaepe, L. Rakers, B. Vonhören, P. Tegeder, B. J. Ravoo, F. Glorius, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 5856–5860; Angew. Chem. 2016, 128, 5950–5955;
- 11eC. A. Smith, M. R. Narouz, P. A. Lummis, I. Singh, A. Nazemi, C. H. Li, C. M. Crudden, Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 4986–5056;
- 11fJ. B. Ernst, S. Muratsugu, F. Wang, M. Tada, F. Glorius, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 10718–10721;
- 11gJ. B. Ernst, C. Schwermann, G. I. Yokota, M. Tada, S. Muratsugu, N. L. Doltsinis, F. Glorius, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 9144–9147.
- 12
- 12aM. Fèvre, P. Coupillaud, K. Miqueu, J. M. Sotiropoulos, J. Vignolle, D. Taton, J. Org. Chem. 2012, 77, 10135–10144;
- 12bM. Fèvre, J. Pinaud, A. Leteneur, Y. Gnanou, J. Vignolle, D. Taton, K. Miqueu, J. M. Sotiropoulos, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 6776–6784.
- 13C. M. Crudden, J. H. Horton, M. R. Narouz, Z. Li, C. A. Smith, K. Munro, C. J. Baddeley, C. R. Larrea, B. Drevniok, B. Thanabalasingam, A. B. McLean, O. V. Zenkina, Ebralidze II, Z. She, H. B. Kraatz, N. J. Mosey, L. N. Saunders, A. Yagi, Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12654.
- 14
- 14aJ. He, X. Huang, Y.-C. Li, Y. Liu, T. Babu, M. A. Aronova, S. Wang, Z. Lu, X. Chen, Z. Nie, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 7974–7984;
- 14bW. Li, I. Kanyo, C.-H. Kuo, S. Thanneeru, J. He, Nanoscale 2015, 7, 956–964;
- 14cB. Liu, S. Thanneeru, A. Lopes, L. Jin, M. McCabe, J. He, Small 2017, 13, 1700091.
- 15G. Chen, C. Xu, X. Huang, J. Ye, L. Gu, G. Li, Z. Tang, B. Wu, H. Yang, Z. Zhao, Nat. Mater. 2016, 15, 564.
- 16B. Liu, H. Yao, W. Song, L. Jin, I. M. Mosa, J. F. Rusling, S. L. Suib, J. He, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 4718–4721.
- 17M. K. Corbierre, N. S. Cameron, R. B. Lennox, Langmuir 2004, 20, 2867–2873.
- 18
- 18aY. Yang, L. Jin, B. Liu, P. Kerns, J. He, Electrochim. Acta 2018, 269, 441–451;
- 18bL. Jin, B. Liu, P. Wang, H. Yao, L. A. Achola, P. Kerns, A. Lopes, Y. Yang, J. Ho, A. Moewes, Y. Pei, J. He, Nanoscale 2018, 10, 14678–14686.
- 19
- 19aB. A. Rosen, A. Salehi-Khojin, M. R. Thorson, W. Zhu, D. T. Whipple, P. J. Kenis, R. I. Masel, Science 2011, 334, 643–644;
- 19bC. M. Sánchez-Sánchez, in Encyclopedia of Interfacial Chemistry: Surface Science and Electrochemistry, Ed. , Elsevier, 2018, pp. 539—551;
10.1016/B978-0-12-409547-2.13377-3 Google Scholar
- 19cC. Costentin, J. C. Canales, B. Haddou, J.-M. Savéant, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 17671–17674;
- 19dM. Lessio, E. A. Carter, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 13248–13251.
- 20
- 20aS. Zhao, R. Jin, R. Jin, ACS Energy Lett. 2018, 3, 452–462;
- 20bJ. Fu, Y. Wang, J. Liu, K. Huang, Y. Chen, Y. Li, J.-J. Zhu, ACS Energy Lett. 2018, 3, 946–951;
- 20cG. Iijima, T. Kitagawa, A. Katayama, T. Inomata, H. Yamaguchi, K. Suzuki, K. Hirata, Y. Hijikata, M. Ito, H. Masuda, ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 1990–2000;
- 20dZ. Yin, G. T. R. Palmore, S. Sun, Trends Chem. 2019 DOI: 10.1016/j.trechm.2019.05.00;
- 20eW. Zhu, R. Michalsky, O. Metin, H. Lv, S. Guo, C. J. Wright, X. Sun, A. A. Peterson, S. Sun, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 16833–16836;
- 20fD. R. Kauffman, D. Alfonso, C. Matranga, H. Qian, R. Jin, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 10237–10243.
- 21
- 21aD. Gao, H. Zhou, J. Wang, S. Miao, F. Yang, G. Wang, J. Wang, X. Bao, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 4288–4291;
- 21bF. Cai, D. Gao, H. Zhou, G. Wang, T. He, H. Gong, S. Miao, F. Yang, J. Wang, X. Bao, Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 2569–2573;
- 21cB. Jiang, X.-G. Zhang, K. Jiang, D.-Y. Wu, W.-B. Cai, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 2880–2889.
- 22C. Kim, T. Eom, M. S. Jee, H. Jung, H. Kim, B. K. Min, Y. J. Hwang, ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 779–785.
- 23Z. Cao, J. S. Derrick, J. Xu, R. Gao, M. Gong, E. M. Nichols, P. T. Smith, X. Liu, X. Wen, C. Copéret, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 4981–4985; Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 5075–5079.
- 24
- 24aA. R. Riscoe, C. J. Wrasman, A. A. Herzing, A. S. Hoffman, A. Menon, A. Boubnov, M. Vargas, S. R. Bare, M. Cargnello, Nat. Catal. 2019, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41929-019-0322-7;
- 24bS. Thanneeru, N. Milazzo, A. Lopes, Z. Wei, A. M. Angeles-Boza, J. He, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 4252–4256.