Construction of a Nanoporous Highly Crystalline Hexagonal Boron Nitride from an Amorphous Precursor for Catalytic Dehydrogenation
Dr. Hao Chen
Key Laboratory of Biomass Chemical Engineering of Ministry of Education, College of Chemical and Biological Engineering, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, 310027 China
Chemical Sciences Division, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Oak Ridge, TN, 37831 USA
Department of Chemistry, The University of Tennessee, Knoxville, TN, 37996 USA
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dr. Zhenzhen Yang
Chemical Sciences Division, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Oak Ridge, TN, 37831 USA
Department of Chemistry, The University of Tennessee, Knoxville, TN, 37996 USA
Search for more papers by this authorZihao Zhang
Key Laboratory of Biomass Chemical Engineering of Ministry of Education, College of Chemical and Biological Engineering, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, 310027 China
Search for more papers by this authorZitao Chen
Center for Nanophase Materials Sciences, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Oak Ridge, TN, 37831 USA
Search for more papers by this authorMiaofang Chi
Center for Nanophase Materials Sciences, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Oak Ridge, TN, 37831 USA
Search for more papers by this authorSong Wang
Department of Chemistry, University of California, Riverside, CA, 92521 USA
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dr. Jie Fu
Key Laboratory of Biomass Chemical Engineering of Ministry of Education, College of Chemical and Biological Engineering, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, 310027 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dr. Sheng Dai
Chemical Sciences Division, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Oak Ridge, TN, 37831 USA
Department of Chemistry, The University of Tennessee, Knoxville, TN, 37996 USA
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Hao Chen
Key Laboratory of Biomass Chemical Engineering of Ministry of Education, College of Chemical and Biological Engineering, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, 310027 China
Chemical Sciences Division, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Oak Ridge, TN, 37831 USA
Department of Chemistry, The University of Tennessee, Knoxville, TN, 37996 USA
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dr. Zhenzhen Yang
Chemical Sciences Division, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Oak Ridge, TN, 37831 USA
Department of Chemistry, The University of Tennessee, Knoxville, TN, 37996 USA
Search for more papers by this authorZihao Zhang
Key Laboratory of Biomass Chemical Engineering of Ministry of Education, College of Chemical and Biological Engineering, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, 310027 China
Search for more papers by this authorZitao Chen
Center for Nanophase Materials Sciences, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Oak Ridge, TN, 37831 USA
Search for more papers by this authorMiaofang Chi
Center for Nanophase Materials Sciences, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Oak Ridge, TN, 37831 USA
Search for more papers by this authorSong Wang
Department of Chemistry, University of California, Riverside, CA, 92521 USA
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dr. Jie Fu
Key Laboratory of Biomass Chemical Engineering of Ministry of Education, College of Chemical and Biological Engineering, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, 310027 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dr. Sheng Dai
Chemical Sciences Division, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Oak Ridge, TN, 37831 USA
Department of Chemistry, The University of Tennessee, Knoxville, TN, 37996 USA
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
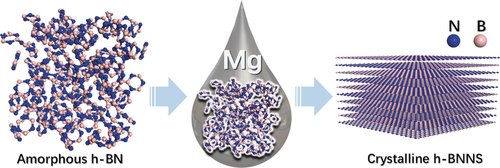
Highly crystalline nanoporous hexagonal boron nitride nanosheets (h-BNNS) were prepared using amorphous h-BN precursors through a dissolution–precipitation/crystallization process in the presence of magnesium. The crystalline h-BNNS is a catalyst for the dehydrogenation of dodecahydro-N-ethylcarbazole.
Abstract
Hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) is regarded as a graphene analogue and exhibits important characteristics and vast application potentials. However, discovering a facile method for the preparation of nanoporous crystalline h-BN nanosheets (h-BNNS) is still a challenge. Herein, a novel and simple route for the conversion of amorphous h-BN precursors into highly crystalline h-BNNS was achieved through a successive dissolution–precipitation/crystallization process in the presence of magnesium. The h-BNNS has high crystallinity, high porosity with a surface area of 347 m2 g−1, high purity, and enhanced thermal stability. Improved catalytic performance of crystalline h-BNNS was evidenced by its much higher catalytic efficiency in the dehydrogenation of dodecahydro-N-ethylcarbazole, compared with its amorphous h-BN precursor, as well as other precious-metal-loaded heterogeneous catalysts.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie201904996-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf430.9 KB | Supplementary |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1K. S. Novoselov, A. K. Geim, S. V. Morozov, D. Jiang, Y. Zhang, S. V. Dubonos, I. V. Grigorieva, A. A. Firsov, Science 2004, 306, 666.
- 2C. Tan, X. Cao, X.-J. Wu, Q. He, J. Yang, X. Zhang, J. Chen, W. Zhao, S. Han, G.-H. Nam, M. Sindoro, H. Zhang, Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 6225–6331.
- 3X. Huang, X. Qi, F. Boey, H. Zhang, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 666–686.
- 4F. K. Kessler, Y. Zheng, D. Schwarz, C. Merschjann, W. Schnick, X. Wang, M. J. Bojdys, Nat. Rev. Mater. 2017, 2, 17030.
- 5A. Savateev, I. Ghosh, B. König, M. Antonietti, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 15936–15947; Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 16164–16176.
- 6Q. Weng, X. Wang, X. Wang, Y. Bando, D. Golberg, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 3989–4012.
- 7Q. Li, L. Chen, M. R. Gadinski, S. Zhang, G. Zhang, H. U. Li, E. Iagodkine, A. Haque, L.-Q. Chen, T. N. Jackson, Q. Wang, Nature 2015, 523, 576.
- 8W. Zhu, Z. Wu, G. S. Foo, X. Gao, M. Zhou, B. Liu, G. M. Veith, P. Wu, K. L. Browning, H. N. Lee, H. Li, S. Dai, H. Zhu, Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15291.
- 9P. Wu, S. Yang, W. Zhu, H. Li, Y. Chao, H. Zhu, H. Li, S. Dai, Small 2017, 13, 1701857.
- 10Y. Kubota, K. Watanabe, O. Tsuda, T. Taniguchi, Science 2007, 317, 932–934.
- 11J. T. Grant, C. A. Carrero, F. Goeltl, J. Venegas, P. Mueller, S. P. Burt, S. E. Specht, W. P. McDermott, A. Chieregato, I. Hermans, Science 2016, 354, 1570–1573.
- 12A. M. Love, B. Thomas, S. E. Specht, M. P. Hanrahan, J. M. Venegas, S. P. Burt, J. T. Grant, M. C. Cendejas, W. P. McDermott, A. J. Rossini, I. Hermans, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 182–190.
- 13S. Chen, R. Xu, J. Liu, X. Zou, L. Qiu, F. Kang, B. Liu, H.-M. Cheng, Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1804810.
- 14A. Pakdel, Y. Bando, D. Golberg, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 934–959.
- 15J. Yin, J. Li, Y. Hang, J. Yu, G. Tai, X. Li, Z. Zhang, W. Guo, Small 2016, 12, 2942–2968.
- 16W. Zhu, X. Gao, Q. Li, H. Li, Y. Chao, M. Li, S. M. Mahurin, H. Li, H. Zhu, S. Dai, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 10766–10770; Angew. Chem. 2016, 128, 10924–10928.
- 17P. Wu, W. Zhu, Y. Chao, J. Zhang, P. Zhang, H. Zhu, C. Li, Z. Chen, H. Li, S. Dai, Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 144–147.
- 18M. Liu, K. Jiang, X. Ding, S. Wang, C. Zhang, J. Liu, Z. Zhan, G. Cheng, B. Li, H. Chen, S. Jin, B. Tan, Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1807865.
- 19M. Zhao, Y. Huang, Y. Peng, Z. Huang, Q. Ma, H. Zhang, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 6267–6295.
- 20C. S. Diercks, O. M. Yaghi, Science 2017, 355, eaal 1585.
- 21Z. Miao, G. Liu, Y. Cui, Z. Liu, J. Li, F. Han, Y. Liu, X. Sun, X. Gong, Y. Zhai, Y. Zhao, Y. Zeng, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 4906–4910; Angew. Chem. 2019, 131, 4960–4964.
- 22J. Xiong, W. Zhu, H. Li, W. Ding, Y. Chao, P. Wu, S. Xun, M. Zhang, H. Li, Green Chem. 2015, 17, 1647–1656.
- 23A. Ōya, S. Ōtani, Carbon 1979, 17, 131–137.
- 24A. Oberlin, Carbon 1984, 22, 521–541.
- 25J. Peng, N. Chen, R. He, Z. Wang, S. Dai, X. Jin, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 1751–1755; Angew. Chem. 2017, 129, 1777–1781.
- 26L. Zhao, X. Zhao, L. T. Burke, J. C. Bennett, R. A. Dunlap, M. N. Obrovac, ChemSusChem 2017, 10, 3409–3418.
- 27W. Lei, V. N. Mochalin, D. Liu, S. Qin, Y. Gogotsi, Y. Chen, Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8849.
- 28L. H. Li, J. Cervenka, K. Watanabe, T. Taniguchi, Y. Chen, ACS Nano 2014, 8, 1457–1462.
- 29C. Gervais, J. Maquet, F. Babonneau, C. Duriez, E. Framery, M. Vaultier, P. Florian, D. Massiot, Chem. Mater. 2001, 13, 1700–1707.
- 30A. Ōya, H. Marsh, J. Mater. Sci. 1982, 17, 309–322.
- 31see Ref. [15].
- 32E. Gianotti, M. Taillades-Jacquin, J. Rozière, D. J. Jones, ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 4660–4680.
- 33U. Eberle, M. Felderhoff, F. Schüth, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 6608–6630; Angew. Chem. 2009, 121, 6732–6757.
- 34P. Preuster, C. Papp, P. Wasserscheid, Acc. Chem. Res. 2017, 50, 74–85.
- 35D. Teichmann, K. Stark, K. Müller, G. Zöttl, P. Wasserscheid, W. Arlt, Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 9044–9054.
- 36M. C. Williams, J. P. Strakey, W. A. Surdoval, J. Power Sources 2005, 143, 191–196.
- 37J. Tian, J. Tan, M. Xu, Z. Zhang, S. Wan, S. Wang, J. Lin, Y. Wang, Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaav 8063.
- 38Y. Wang, W.-C. Li, Y.-X. Zhou, R. Lu, A.-H. Lu, Catal. Today 2018, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2018.1012.1028.
- 39F. Sotoodeh, K. J. Smith, J. Catal. 2011, 279, 36–47.