Selective Functionalization of Graphene at Defect-Activated Sites by Arylazocarboxylic tert-Butyl Esters
Dr. Christian E. Halbig
Institut für Chemie und Biochemie, Freie Universität Berlin, Takustraße 3, 14195 Berlin, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Roman Lasch
Department Chemie und Pharmazie, Friedrich-Alexander Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg, Nikolaus-Fiebiger-Straße 10, 91058 Erlangen, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorM. Sc. Jasmin Krüll
Department Chemie und Pharmazie, Friedrich-Alexander Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg, Nikolaus-Fiebiger-Straße 10, 91058 Erlangen, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorAnna S. Pirzer
Department Chemie und Pharmazie, Friedrich-Alexander Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg, Nikolaus-Fiebiger-Straße 10, 91058 Erlangen, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorM. Sc. Zhenping Wang
Institut für Chemie und Biochemie, Freie Universität Berlin, Takustraße 3, 14195 Berlin, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorM. Sc. Jan N. Kirchhof
Institut für Experimentalphysik, Freie Universität Berlin, Arnimallee 14, 14195 Berlin, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Dr. Kirill I. Bolotin
Institut für Experimentalphysik, Freie Universität Berlin, Arnimallee 14, 14195 Berlin, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Markus R. Heinrich
Department Chemie und Pharmazie, Friedrich-Alexander Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg, Nikolaus-Fiebiger-Straße 10, 91058 Erlangen, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Siegfried Eigler
Institut für Chemie und Biochemie, Freie Universität Berlin, Takustraße 3, 14195 Berlin, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Christian E. Halbig
Institut für Chemie und Biochemie, Freie Universität Berlin, Takustraße 3, 14195 Berlin, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Roman Lasch
Department Chemie und Pharmazie, Friedrich-Alexander Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg, Nikolaus-Fiebiger-Straße 10, 91058 Erlangen, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorM. Sc. Jasmin Krüll
Department Chemie und Pharmazie, Friedrich-Alexander Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg, Nikolaus-Fiebiger-Straße 10, 91058 Erlangen, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorAnna S. Pirzer
Department Chemie und Pharmazie, Friedrich-Alexander Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg, Nikolaus-Fiebiger-Straße 10, 91058 Erlangen, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorM. Sc. Zhenping Wang
Institut für Chemie und Biochemie, Freie Universität Berlin, Takustraße 3, 14195 Berlin, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorM. Sc. Jan N. Kirchhof
Institut für Experimentalphysik, Freie Universität Berlin, Arnimallee 14, 14195 Berlin, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Dr. Kirill I. Bolotin
Institut für Experimentalphysik, Freie Universität Berlin, Arnimallee 14, 14195 Berlin, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Markus R. Heinrich
Department Chemie und Pharmazie, Friedrich-Alexander Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg, Nikolaus-Fiebiger-Straße 10, 91058 Erlangen, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Siegfried Eigler
Institut für Chemie und Biochemie, Freie Universität Berlin, Takustraße 3, 14195 Berlin, Germany
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
Abstract
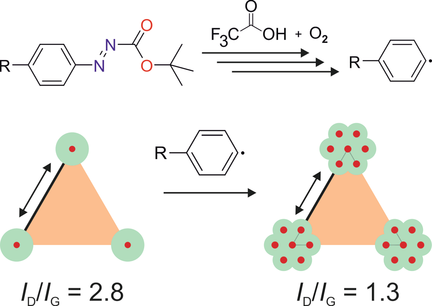
The development of versatile functionalization concepts for graphene is currently in the focus of research. Upon oxo-functionalization of graphite, the full surface of graphene becomes accessible for C−C bond formation to introduce out-of-plane functionality. Herein, we present the arylation of graphene with arylazocarboxylic tert-butyl esters, which generates aryl radicals after activation with an acid. Surprisingly, the degree of functionalization is related to the concentration of lattice vacancy defects in the graphene material. Consequently, graphene materials that are free from lattice defects are not reactive. The reaction can be applied to graphene dispersed in solvents and leads to bitopic functionalization as well as monotopic functionalization when the graphene is deposited on surfaces. As the arylazocarboxylic tert-butyl ester moiety can be attached to various molecules, the presented method paves the way to functional graphene derivatives, with the density of defects determining the degree of functionalization.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie201811192-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf3.8 MB | Supplementary |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1
- 1aD. R. Dreyer, S. Park, C. W. Bielawski, R. S. Ruoff, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 228;
- 1bS. Eigler, A. Hirsch, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 7720;
- 1cS. Eigler, A. Hirsch, Angew. Chem. 2014, 126, 7852;
- 1dJ. M. Englert, K. C. Knirsch, C. Dotzer, B. Butz, F. Hauke, E. Spiecker, A. Hirsch, Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 5025;
- 1eY. Si, E. T. Samulski, Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 1679;
- 1fJ. M. Englert, C. Dotzer, G. Yang, M. Schmid, C. Papp, J. M. Gottfried, H. P. Steinruck, E. Spiecker, F. Hauke, A. Hirsch, Nat. Chem. 2011, 3, 279.
- 2F. Bonaccorso, L. Colombo, G. Yu, M. Stoller, V. Tozzini, A. C. Ferrari, R. S. Ruoff, V. Pellegrini, Science 2015, 347, 1246501.
- 3
- 3aC. Lee, X. Wei, J. W. Kysar, J. Hone, Science 2008, 321, 385;
- 3bC. Gómez-Navarro, M. Burghard, K. Kern, Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 2045.
- 4
- 4aS. V. Morozov, K. S. Novoselov, M. I. Katsnelson, F. Schedin, D. C. Elias, J. A. Jaszczak, A. K. Geim, Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 100, 016602;
- 4bE. V. Castro, K. S. Novoselov, S. V. Morozov, N. M. Peres, J. M. dos Santos, J. Nilsson, F. Guinea, A. K. Geim, A. H. Neto, Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 99, 216802.
- 5
- 5aM. H. Overgaard, M. Kühnel, R. Hvidsten, S. V. Petersen, T. Vosch, K. Nørgaard, B. W. Laursen, Adv. Mater. Technol. 2017, 2, 1700011;
- 5bH. Chen, Y. Hou, C. E. Halbig, S. Chen, H. Zhang, N. Li, F. Guo, X. Tang, N. Gasparini, I. Levchuk, S. Kahmann, C. O. Ramirez Quiroz, A. Osvet, S. Eigler, C. J. Brabec, J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 11604;
- 5cJ. Liu, L. Cui, D. Losic, Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 9243;
- 5dS. Homaeigohar, M. Elbahri, NPG Asia Mater. 2017, 9, e 427;
- 5eT. Kuilla, S. Bhadra, D. Yao, N. H. Kim, S. Bose, J. H. Lee, Prog. Polym. Sci. 2010, 35, 1350.
- 6
- 6aB. Alfano, E. Massera, T. Polichetti, M. L. Miglietta, G. Di Francia, Sens. Actuators B 2017, 253, 1163;
- 6bD. Chen, H. Feng, J. Li, Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 6027;
- 6cK. ul Hasan, M. H. Asif, O. Nur, M. Willander, J. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 3, 114.
- 7
- 7aS. Eigler, Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 3162;
- 7bS. Eigler, M. Enzelberger-Heim, S. Grimm, P. Hofmann, W. Kroener, A. Geworski, C. Dotzer, M. Rockert, J. Xiao, C. Papp, O. Lytken, H. P. Steinruck, P. Muller, A. Hirsch, Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 3583;
- 7cB. Butz, C. Dolle, C. E. Halbig, E. Spiecker, S. Eigler, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 15771; Angew. Chem. 2016, 128, 16003;
- 7dB. Butz, C. Dolle, C. E. Halbig, E. Spiecker, S. Eigler, Angew. Chem. 2016, 128, 16003;
10.1002/ange.201608377 Google Scholar
- 7eW. S. Hummers, R. E. Offeman, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1958, 80, 1339.
- 8
- 8aP. Feicht, S. Eigler, ChemNanoMat 2018, 4, 244;
- 8bS. Seiler, C. E. Halbig, F. Grote, P. Rietsch, F. Borrnert, U. Kaiser, B. Meyer, S. Eigler, Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 836.
- 9
- 9aK. C. Knirsch, R. A. Schäfer, F. Hauke, A. Hirsch, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 5861; Angew. Chem. 2016, 128, 5956;
- 9bK. C. Knirsch, R. A. Schäfer, F. Hauke, A. Hirsch, Angew. Chem. 2016, 128, 5956.
10.1002/ange.201511807 Google Scholar
- 10
- 10aG. Abellán, M. Schirowski, K. F. Edelthalhammer, M. Fickert, K. Werbach, H. Peterlik, F. Hauke, A. Hirsch, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 5175;
- 10bJ. Greenwood, T. H. Phan, Y. Fujita, Z. Li, O. Ivasenko, W. Vanderlinden, H. Van Gorp, W. Frederickx, G. Lu, K. Tahara, Y. Tobe, I. H. Uji, S. F. Mertens, S. De Feyter, ACS Nano 2015, 9, 5520;
- 10cC. E. Halbig, O. Martin, F. Hauke, S. Eigler, A. Hirsch, Chem. Eur. J. 2018, 24, 13348.
- 11P. Vecera, K. Edelthalhammer, F. Hauke, A. Hirsch, Phys. Status Solidi B 2014, 251, 2536.
- 12J. Holzwarth, K. Y. Amsharov, D. I. Sharapa, D. Reger, K. Roshchyna, D. Lungerich, N. Jux, F. Hauke, T. Clark, A. Hirsch, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 12184; Angew. Chem. 2017, 129, 12352.
- 13
- 13aS. K. Fehler, G. Pratsch, M. R. Heinrich, Angew. Chem. 2014, 126, 11543;
10.1002/ange.201406175 Google Scholar
- 13bS. K. Fehler, G. Pratsch, M. R. Heinrich, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 11361; Angew. Chem. 2014, 126, 11543;
- 13cS. B. Höfling, A. L. Bartuschat, M. R. Heinrich, Angew. Chem. 2010, 122, 9963;
10.1002/ange.201004508 Google Scholar
- 13dS. B. Höfling, A. L. Bartuschat, M. R. Heinrich, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 9769; Angew. Chem. 2010, 122, 9963;
- 13eH. Jasch, S. B. Hofling, M. R. Heinrich, J. Org. Chem. 2012, 77, 1520;
- 13fN. Nebel, B. Strauch, S. Maschauer, R. Lasch, H. Rampp, S. K. Fehler, L. R. Bock, H. Hubner, P. Gmeiner, M. R. Heinrich, O. Prante, ACS Omega 2017, 2, 8649;
- 13gP. K. C. Huang, E. M. Kosower, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1967, 89, 3910.
- 14G. L. Paulus, Q. H. Wang, M. S. Strano, Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 160.
- 15
- 15aF. Grote, C. Gruber, F. Borrnert, U. Kaiser, S. Eigler, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 9222; Angew. Chem. 2017, 129, 9350;
- 15bF. Grote, C. Gruber, F. Börrnert, U. Kaiser, S. Eigler, Angew. Chem. 2017, 129, 9350.
10.1002/ange.201704419 Google Scholar
- 16S. Eigler, S. Grimm, M. Enzelberger-Heim, P. Muller, A. Hirsch, Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 7391.
- 17
- 17aS. Eigler, C. Dotzer, A. Hirsch, Carbon 2012, 50, 3666;
- 17bM. M. Lucchese, F. Stavale, E. H. M. Ferreira, C. Vilani, M. V. O. Moutinho, R. B. Capaz, C. A. Achete, A. Jorio, Carbon 2010, 48, 1592.
- 18
- 18aL. G. Cançado, A. Jorio, E. H. Ferreira, F. Stavale, C. A. Achete, R. B. Capaz, M. V. Moutinho, A. Lombardo, T. S. Kulmala, A. C. Ferrari, Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 3190;
- 18bP. Vecera, S. Eigler, M. Kolesnik-Gray, V. Krstic, A. Vierck, J. Maultzsch, R. A. Schäfer, F. Hauke, A. Hirsch, Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45165.
- 19
- 19aL. Gustavo Cançado, M. Gomes da Silva, E. H. Martins Ferreira, F. Hof, K. Kampioti, K. Huang, A. Pénicaud, C. Alberto Achete, R. B. Capaz, A. Jorio, 2D Mater. 2017, 4, 025039;
- 19bL. P. Biró, P. Lambin, New J. Phys. 2013, 15, 035024.
- 20
- 20aS. Eigler, S. Grimm, F. Hof, A. Hirsch, J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 11559;
- 20bT. J. Nacken, C. E. Halbig, S. E. Wawra, C. Damm, S. Romeis, J. Walter, M. J. Tehrani, Y. C. Hu, Y. Ishii, S. Eigler, W. Peukert, Carbon 2017, 125, 360.