Ionic Janus Liquid Droplets Assembled and Propelled by Electric Field
Graphical Abstract
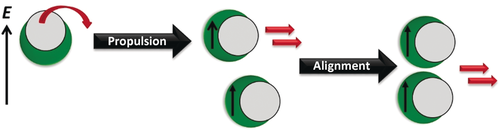
Particles in motion: Janus liquid droplets can be used as building blocks in an active propulsion system. Using an ionic liquid, the droplet system can be tuned from core–shell to Janus and multipatches by using surfactant-based methods. The approach was stimulated by the success of electrohydrodynamic flow produced by an alternating electric field to produce motion of colloidal particles; its usefulness to also propel ionic liquid droplets is demonstrated.
Abstract
Traditional Janus particle approaches to produce active motion are based on using solid particles, but it is interesting to consider liquid droplets instead, because for solid particles, the self-assembly of synthetic active matter requires moving objects to sit in a near-planar 2D geometry. Emulsions, cross-linked polymers, and porous materials have been proposed for 3D self-assembly but with limitations to propel them. It is now demonstrated that Janus liquid droplets can be used as building block in an active propulsion system. Using an ionic liquid motif, the droplet system can be tuned from core–shell to Janus and multipatches, using facile surfactant-based methods. The approach was stimulated by the success of electro-hydrodynamic flow produced by an alternating electric field to produce motion of colloidal particles; its usefulness to also propel ionic liquids is demonstrated.