Probing Interfacial Electronic and Catalytic Properties on Well-Defined Surfaces by Using In Situ Raman Spectroscopy
Ya-Hao Wang
The MOE Key Laboratory of Spectrochemical Analysis and Instrumentation, State Key Laboratory of Physical Chemistry of Solid Surfaces, iChEM, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Xiamen University, Xiamen, 361005 China
Search for more papers by this authorMiao-Miao Liang
Department of Physics, Research Institute for Biomimetics and Soft Matter, Xiamen University, Xiamen, 361005 China
Search for more papers by this authorYue-Jiao Zhang
The MOE Key Laboratory of Spectrochemical Analysis and Instrumentation, State Key Laboratory of Physical Chemistry of Solid Surfaces, iChEM, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Xiamen University, Xiamen, 361005 China
Search for more papers by this authorShu Chen
Department of Physics, Research Institute for Biomimetics and Soft Matter, Xiamen University, Xiamen, 361005 China
Search for more papers by this authorPetar Radjenovic
The MOE Key Laboratory of Spectrochemical Analysis and Instrumentation, State Key Laboratory of Physical Chemistry of Solid Surfaces, iChEM, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Xiamen University, Xiamen, 361005 China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Hua Zhang
The MOE Key Laboratory of Spectrochemical Analysis and Instrumentation, State Key Laboratory of Physical Chemistry of Solid Surfaces, iChEM, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Xiamen University, Xiamen, 361005 China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Zhi-Lin Yang
Department of Physics, Research Institute for Biomimetics and Soft Matter, Xiamen University, Xiamen, 361005 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Xiao-Shun Zhou
Key Laboratory of the Ministry of Education for Advanced Catalysis Materials, College of Chemistry and Life Sciences, Zhejiang Normal University, Jinhua, 321004 China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Zhong-Qun Tian
The MOE Key Laboratory of Spectrochemical Analysis and Instrumentation, State Key Laboratory of Physical Chemistry of Solid Surfaces, iChEM, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Xiamen University, Xiamen, 361005 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Jian-Feng Li
The MOE Key Laboratory of Spectrochemical Analysis and Instrumentation, State Key Laboratory of Physical Chemistry of Solid Surfaces, iChEM, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Xiamen University, Xiamen, 361005 China
Department of Physics, Research Institute for Biomimetics and Soft Matter, Xiamen University, Xiamen, 361005 China
Shenzhen Research Institute of Xiamen University, Shenzhen, 518000 China
Search for more papers by this authorYa-Hao Wang
The MOE Key Laboratory of Spectrochemical Analysis and Instrumentation, State Key Laboratory of Physical Chemistry of Solid Surfaces, iChEM, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Xiamen University, Xiamen, 361005 China
Search for more papers by this authorMiao-Miao Liang
Department of Physics, Research Institute for Biomimetics and Soft Matter, Xiamen University, Xiamen, 361005 China
Search for more papers by this authorYue-Jiao Zhang
The MOE Key Laboratory of Spectrochemical Analysis and Instrumentation, State Key Laboratory of Physical Chemistry of Solid Surfaces, iChEM, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Xiamen University, Xiamen, 361005 China
Search for more papers by this authorShu Chen
Department of Physics, Research Institute for Biomimetics and Soft Matter, Xiamen University, Xiamen, 361005 China
Search for more papers by this authorPetar Radjenovic
The MOE Key Laboratory of Spectrochemical Analysis and Instrumentation, State Key Laboratory of Physical Chemistry of Solid Surfaces, iChEM, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Xiamen University, Xiamen, 361005 China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Hua Zhang
The MOE Key Laboratory of Spectrochemical Analysis and Instrumentation, State Key Laboratory of Physical Chemistry of Solid Surfaces, iChEM, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Xiamen University, Xiamen, 361005 China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Zhi-Lin Yang
Department of Physics, Research Institute for Biomimetics and Soft Matter, Xiamen University, Xiamen, 361005 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Xiao-Shun Zhou
Key Laboratory of the Ministry of Education for Advanced Catalysis Materials, College of Chemistry and Life Sciences, Zhejiang Normal University, Jinhua, 321004 China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Zhong-Qun Tian
The MOE Key Laboratory of Spectrochemical Analysis and Instrumentation, State Key Laboratory of Physical Chemistry of Solid Surfaces, iChEM, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Xiamen University, Xiamen, 361005 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Jian-Feng Li
The MOE Key Laboratory of Spectrochemical Analysis and Instrumentation, State Key Laboratory of Physical Chemistry of Solid Surfaces, iChEM, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Xiamen University, Xiamen, 361005 China
Department of Physics, Research Institute for Biomimetics and Soft Matter, Xiamen University, Xiamen, 361005 China
Shenzhen Research Institute of Xiamen University, Shenzhen, 518000 China
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
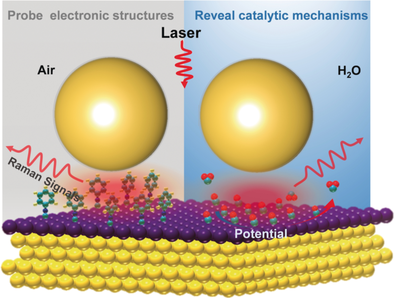
Shell seekers: Shell-isolated nanoparticle-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SHINERS) was used to probe the electronic structures and reveal the catalytic mechanisms on Pd/Pt-overlayer-coated Au single crystals. This work opens up a novel way to detect the electronic structures of heterogeneous metal interfaces and understand catalytic mechanisms at the molecular level.
Abstract
Heterogeneous metal interfaces play a key role in determining the mechanism and performance of catalysts. However, in situ characterization of such interfaces at the molecular level is challenging. Herein, two model interfaces, Pd and Pt overlayers on Au single crystals, were constructed. The electronic structures of these interfaces as well as effects of crystallographic orientation on them were analyzed by shell-isolated nanoparticle-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SHINERS) using phenyl isocyanide (PIC) as a probe molecule. A clear red shift in the frequency of the C≡N stretch (νNC) was observed, which is consistent with X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) data and indicates that the ultrathin Pt and Pd layers donate their free electrons to the Au substrates. Furthermore, in situ electrochemical SHINERS studies showed that the electronic effects weaken Pt−C/Pd−C bonds, leading to improved surface activity towards CO electrooxidation.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie201805464-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf903.4 KB | Supplementary |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1
- 1aR. Schlögl, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 3465–3520; Angew. Chem. 2015, 127, 3531–3589;
- 1bJ. Gong, X. Bao, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 1770–1771.
- 2M. Shao, A. Peles, K. Shoemaker, Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 3714–3719.
- 3
- 3aY. Xiong, B. J. Wiley, Y. Xia, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 7157–7159; Angew. Chem. 2007, 119, 7291–7293;
- 3bI. Lee, F. Delbecq, R. Morales, M. A. Albiter, F. Zaera, Nat. Mater. 2009, 8, 132–138.
- 4
- 4aY. Xia, H. Yang, C. T. Campbell, Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 1671–1672;
- 4bS. Zhang, L. Nguyen, Y. Zhu, S. Zhan, C.-K. Tsung, F. Tao, Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 1731–1739.
- 5B. Hammer, J. K. Nørskov, Adv. Catal. 2000, 45, 71–129.
- 6C. H. Christensen, J. K. Nørskov, J. Chem. Phys. 2008, 128, 182503.
- 7S. Schauermann, N. Nilius, S. Shaikhutdinov, H. J. Freund, Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 1673–1681.
- 8T. H. M. Housmans, A. H. Wonders, M. T. M. Koper, J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 10021–10031.
- 9
- 9aV. R. Stamenkovic, B. Fowler, G. Wang, P. N. Ross, C. A. Lucas, N. M. Marković, Science 2007, 315, 493;
- 9bM. D. Maciá, J. M. Campiña, E. Herrero, J. M. Feliu, J. Electroanal. Chem. 2004, 564, 141–150.
- 10
- 10aN. Hoshi, T. Suzuki, Y. Hori, Electrochim. Acta 1996, 41, 1647–1653;
- 10bK. J. P. Schouten, Z. Qin, E. Pérez Gallent, M. T. M. Koper, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 9864–9867.
- 11L. A. Kibler, A. M. El-Aziz, R. Hoyer, D. M. Kolb, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 2080–2084; Angew. Chem. 2005, 117, 2116–2120.
- 12S. H. Ahn, Y. Liu, T. P. Moffat, ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 2124–2136.
- 13
- 13aM. Fleischmann, P. J. Hendra, A. J. McQuillan, Chem. Phys. Lett. 1974, 26, 163–166;
- 13bD. L. Jeanmaire, R. P. Van Duyne, J. Electroanal. Chem. Interfacial Electrochem. 1977, 84, 1–20.
- 14
- 14aY. Wang, Z. Yu, W. Ji, Y. Tanaka, H. Sui, B. Zhao, Y. Ozaki, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 13866–13870; Angew. Chem. 2014, 126, 14086–14090;
- 14bJ. Mirza, S. R. Smith, J. Y. Baron, Y. Choi, J. Lipkowski, Surf. Sci. 2015, 631, 196–206.
- 15J. F. Li, Y. F. Huang, Z. L. Yang, X. S. Zhou, W. Zhang, Z. Y. Zhou, D. Y. Wu, B. Ren, Z. L. Wang, Z. Q. Tian, Nature 2010, 464, 392–395.
- 16
- 16aJ. F. Li, A. Rudnev, T. Wandlowski, ACS Nano 2013, 7, 8940–8952;
- 16bC. Y. Li, J. C. Dong, R. Panneerselvam, Z. L. Yang, J. F. Li, T. Wandlowski, Z. Q. Tian, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 7648–7651.
- 17
- 17aE. Herrero, L. J. Buller, H. D. Abruña, Chem. Rev. 2001, 101, 1897–1930;
- 17bC. Schlaup, I. Chorkendorff, Surf. Sci. 2015, 631, 155–164.
- 18S. R. Brankovic, R. R. Adžić, Surf. Sci. 2001, 474, L173–L179.
- 19
- 19aZ. Q. Tian, B. Ren, J. F. Li, Z. L. Yang, Chem. Commun. 2007, 3514;
- 19bY. J. Zhang, S. B. Li, R. Panneerselvam, Z. Y. Zhou, D. L. Phillips, J. F. Li, Z. Q. Tian, J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 20684–20691.
- 20L. A. Kibler, R. Randler, D. M. Kolb, Surf. Sci. 1999, 443, 19–30.
- 21H. F. Waibel, M. Kleinert, L. A. Kibler, D. M. Kolb, Electrochim. Acta 2002, 47, 1461–1467.
- 22
- 22aJ. Hu, N. Hoshi, K. Uosaki, K. Ikeda, Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 7982–7986;
- 22bJ. Hu, M. Tanabe, J. Sato, K. Uosaki, K. Ikeda, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 10299–10307;
- 22cJ. H. Zhong, X. Jin, Z. L. Yang, C. T. Williams, B. Ren, Nat. Nanotechnol. 2016, 12, 132.
- 23M. Li, P. Liu, R. R. Adzic, J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2012, 3, 3480–3485.
- 24
- 24aR. Loukrakpam, Q. Yuan, V. Petkov, L. Gan, S. Rudi, R. Yang, Y. Huang, S. R. Brankovic, P. Strasser, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 18866–18876;
- 24bJ. Zeng, J. Yang, J. Y. Lee, W. Zhou, J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 24606–24611.
- 25
- 25aD. J. Chen, Y. J. Tong, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 9394–9398; Angew. Chem. 2015, 127, 9526–9530;
- 25bP. P. Fang, S. Duan, J. R. Anema, D. Y. Wu, B. Ren, Z. L. Wang, C. Amatore, Z. Q. Tian, Chem. Sci. 2011, 2, 531–539;
- 25cZ. Liu, G. S. Jackson, B. W. Eichhorn, Energy Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 1900–1903.
- 26
- 26aH. Yang, Y. Yang, S. Zou, J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 19058–19065;
- 26bM. M. Liang, Y. H. Wang, H. Zhang, Z. L. Yang, J. F. Li, Z. Q. Tian, Electrochem. Commun. 2017, 81, 38–42.
- 27Y. Zhang, X. Gao, M. J. Weaver, J. Phys. Chem. 1993, 97, 8656–8663.
- 28
- 28aK. Jiang, H. X. Zhang, S. Zou, W. B. Cai, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 20360–20376;
- 28bF. J. Vidal-Iglesias, J. Solla-Gullon, A. Aldaz, J. M. Feliu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 6998–7001; Angew. Chem. 2010, 122, 7152–7155.
- 29K. Tedsree, T. Li, S. Jones, K. M. K. Yu, P. A. J. Bagot, E. A. Marquis, G. D. W. Smith, S. C. E. Tsang, Nat. Nanotechnol. 2011, 6, 302.
- 30H. Zhang, C. Wang, G. Fu, S. Chen, Y. J. Zhang, B. H. Chen, J. R. Anema, Z. L. Yang, J. F. Li, Z. Q. Tian, Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15447.