Electrolyte Additives for Lithium Metal Anodes and Rechargeable Lithium Metal Batteries: Progress and Perspectives
Dr. Heng Zhang
CIC Energigune, Parque Tecnológico de Álava, Albert Einstein 48, 01510 Miñano, Álava, Spain
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dr. Gebrekidan Gebresilassie Eshetu
CIC Energigune, Parque Tecnológico de Álava, Albert Einstein 48, 01510 Miñano, Álava, Spain
Search for more papers by this authorXabier Judez
CIC Energigune, Parque Tecnológico de Álava, Albert Einstein 48, 01510 Miñano, Álava, Spain
Department of Chemical Engineering, Faculty of Science and Technology, University of the Basque Country (UPV-EHU), P.P. Box 644, 48080 Bilbao, Spain
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Chunmei Li
CIC Energigune, Parque Tecnológico de Álava, Albert Einstein 48, 01510 Miñano, Álava, Spain
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Lide M. Rodriguez-Martínez
CIC Energigune, Parque Tecnológico de Álava, Albert Einstein 48, 01510 Miñano, Álava, Spain
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Michel Armand
CIC Energigune, Parque Tecnológico de Álava, Albert Einstein 48, 01510 Miñano, Álava, Spain
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Heng Zhang
CIC Energigune, Parque Tecnológico de Álava, Albert Einstein 48, 01510 Miñano, Álava, Spain
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dr. Gebrekidan Gebresilassie Eshetu
CIC Energigune, Parque Tecnológico de Álava, Albert Einstein 48, 01510 Miñano, Álava, Spain
Search for more papers by this authorXabier Judez
CIC Energigune, Parque Tecnológico de Álava, Albert Einstein 48, 01510 Miñano, Álava, Spain
Department of Chemical Engineering, Faculty of Science and Technology, University of the Basque Country (UPV-EHU), P.P. Box 644, 48080 Bilbao, Spain
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Chunmei Li
CIC Energigune, Parque Tecnológico de Álava, Albert Einstein 48, 01510 Miñano, Álava, Spain
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Lide M. Rodriguez-Martínez
CIC Energigune, Parque Tecnológico de Álava, Albert Einstein 48, 01510 Miñano, Álava, Spain
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Michel Armand
CIC Energigune, Parque Tecnológico de Álava, Albert Einstein 48, 01510 Miñano, Álava, Spain
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
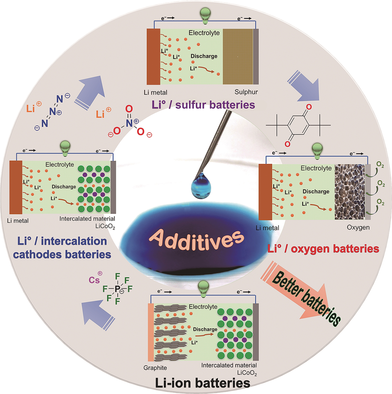
Better batteries: The use of electrolyte additives is considered one of the most viable, economical, and effective approaches to circumvent the problems of rechargeable Li metal batteries (LMBs). This Review assesses the current status of research on electrolyte additives for rechargeable LMBs and considers new avenues for the realization of these appealing devices.
Abstract
Lithium metal (Li0) rechargeable batteries (LMBs), such as systems with a Li0 anode and intercalation and/or conversion type cathode, lithium-sulfur (Li-S), and lithium-oxygen (O2)/air (Li-O2/air) batteries, are becoming increasingly important for electrifying the modern transportation system, with the aim of sustainable mobility. Although some rechargeable LMBs (e.g. Li0/LiFePO4 batteries from Bolloré Bluecar, Li-S batteries from OXIS Energy and Sion Power) are already commercially viable in niche applications, their large-scale deployment is hampered by a number of formidable challenges, including growth of lithium dendrites, electrolyte instability towards high voltage intercalation-type cathodes, the poor electronic and ionic conductivities of sulfur (S8) and O2, as well as their corresponding reduction products (e.g. Li2S and Li2O), dissolution, and shuttling of polysulfide (PS) intermediates. This leads to a short lifecycle, low coulombic/energy efficiency, poor safety, and a high self-discharge rate. The use of electrolyte additives is considered one of the most economical and effective approaches for circumventing these problems. This Review gives an overview of the various functional additives that are being applied and aims to stimulate new avenues for the practical realization of these appealing devices.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- 1M. Armand, J.-M. Tarascon, Nature 2008, 451, 652–657.
- 2G. G. Eshetu, M. Armand, B. Scrosati, S. Passerini, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 13342–13359; Angew. Chem. 2014, 126, 13558–13576.
- 3J. Kalhoff, G. G. Eshetu, D. Bresser, S. Passerini, ChemSusChem 2015, 8, 2154–2175.
- 4S. Stefano, G. G. Eshetu, M. Armand, H. Ohno, Energy Environ. Sci. 2015, 9, 49–61.
- 5J. W. Choi, D. Aurbach, Nat. Rev. Mater. 2016, 1, 16013.
- 6M. Winter, R. J. Brodd, Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 4245–4269.
- 7M. S. Whittingham, Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 4271–4302.
- 8W. Xu, J. Wang, F. Ding, X. Chen, E. Nasybulin, Y. Zhang, J.-G. Zhang, Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 513–537.
- 9X.-B. Cheng, R. Zhang, C.-Z. Zhao, Q. Zhang, Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 10403–10473.
- 10P. G. Bruce, S. A. Freunberger, L. J. Hardwick, J.-M. Tarascon, Nat. Mater. 2012, 11, 19–29.
- 11Q. Pang, X. Liang, C. Y. Kwok, L. F. Nazar, Nat. Energy 2016, 1, 16132.
- 12H. Peng, J. Huang, X. Cheng, Q. Zhang, Adv. Energy Mater. 2017, 7, 1700260.
- 13Y. Yang, G. Zheng, Y. Cui, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 3018–3032.
- 14Z. W. Seh, Y. Sun, Q. Zhang, Y. Cui, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 5605–5634.
- 15H. Zhang, C. Li, M. Piszcz, E. Coya, T. Rojo, L. M. Rodriguez-Martinez, M. Armand, Z. Zhou, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 797–815.
- 16X. Judez, H. Zhang, C. Li, G. G. Eshetu, J. A. González-Marcos, M. Armand, L. M. Rodriguez-Martinez, J. Electrochem. Soc. 2018, 165, A 6008–A6016.
- 17D. Geng, N. Ding, T. S. A. Hor, S. W. Chien, Z. Liu, D. Wuu, X. Sun, Y. Zong, Adv. Energy Mater. 2016, 6, 1502164.
- 18L. Wang, Y. Zhang, Z. Liu, L. Guo, Z. Peng, Green Energy Environ. 2017, 2, 186–203.
- 19K. Xu, Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 4303–4417.
- 20K. Xu, Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 11503–11618.
- 21E. Peled, J. Electrochem. Soc. 1979, 126, 2047–2051.
- 22M. Winter, Z. Phys. Chem. 2009, 223, 1395–1406.
- 23M. Xu, L. Xing, W. Li in Electrolytes Lithium Lithium-Ion Battery, Springer, Amsterdam, 2014, pp. 227–282.
- 24G. G. Eshetu, X. Judez, C. Li, O. Bondarchuk, L. M. Rodriguez-Martinez, H. Zhang, M. Armand, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 15368–15372; Angew. Chem. 2017, 129, 15570–15574.
- 25P. Adelhelm, P. Hartmann, C. L. Bender, M. Busche, C. Eufinger, J. Janek, Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2015, 6, 1016–1055.
- 26N.-S. Choi, Z. Chen, S. A. Freunberger, X. Ji, Y.-K. Sun, K. Amine, G. Yushin, L. F. Nazar, J. Cho, P. G. Bruce, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 9994–10024; Angew. Chem. 2012, 124, 10134–10166.
- 27M. Balaish, A. Kraytsberg, Y. Ein-eli, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 2801–2822.
- 28D. G. Kwabi, N. Ortiz-Vitoriano, S. A. Freunberger, Y. Chen, N. Imanishi, P. G. Bruce, Y. Shao-Horn, MRS Bull. 2014, 39, 443–452.
- 29D. Aurbach, B. D. Mccloskey, L. F. Nazar, P. G. Bruce, Nat. Energy 2016, 1, 16128.
- 30K. G. Gallagher, S. Goebel, T. Greszler, M. Mathias, W. Oelerich, D. Eroglu, V. Srinivasan, Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 1555–1563.
- 31D. Aurbach, K. Gamolsky, B. Markovsky, Y. Gofer, M. Schmidt, U. Heider, Electrochim. Acta 2002, 47, 1423–1439.
- 32K. Sato, L. Zhao, S. Okada, J. I. Yamaki, J. Power Sources 2011, 196, 5617–5622.
- 33J. C. Burns, R. Petibon, K. J. Nelson, N. N. Sinha, A. Kassam, B. M. Way, J. R. Dahn, J. Electrochem. Soc. 2013, 160, A 1668–A1674.
- 34S. S. Zhang, J. Power Sources 2006, 162, 1379–1394.
- 35R. Mogi, M. Inaba, S.-K. Jeong, Y. Iriyama, T. Abe, Z. Ogumi, J. Electrochem. Soc. 2002, 149, A 1578–A1583.
- 36H. Ota, K. Shima, M. Ue, J. Yamaki, Electrochim. Acta 2004, 49, 565–572.
- 37J. Heine, P. Hilbig, X. Qi, P. Niehoff, M. Winter, P. Bieker, J. Electrochem. Soc. 2015, 162, A 1094–A1101.
- 38X. Q. Zhang, X. B. Cheng, X. Chen, C. Yan, Q. Zhang, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1605989.
- 39C. Tiyapiboonchaiya, J. M. Pringle, J. Sun, N. Byrne, P. C. Howlett, D. R. MacFarlane, M. Forsyth, Nat. Mater. 2004, 3, 29–32.
- 40N. Byrne, P. C. Howlett, D. R. MacFarlane, M. Forsyth, Adv. Mater. 2005, 17, 2497–2501.
- 41N. Byrne, P. C. Howlett, D. R. MacFarlane, M. E. Smith, A. Howes, A. F. Hollenkamp, T. Bastow, P. Hale, M. Forsyth, J. Power Sources 2008, 184, 288–296.
- 42Y. Lu, S. K. Das, S. S. Moganty, L. A. Archer, Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 4430–4435.
- 43Y. Lu, K. Korf, Y. Kambe, Z. Tu, L. A. Archer, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 488–492; Angew. Chem. 2014, 126, 498–502.
- 44H. Zhang, X. Cheng, Q. Ma, W. Feng, L. Zheng, J. Nie, X. Huang, M. Armand, Z. Zhou, Electrochim. Acta 2016, 207, 66–75.
- 45Y. Lu, Z. Tu, L. A. Archer, Nat. Mater. 2014, 13, 961–969.
- 46Y. Lu, Z. Tu, J. Shu, L. A. Archer, J. Power Sources 2015, 279, 413–418.
- 47C. Monroe, J. Newman, J. Electrochem. Soc. 2005, 152, A 396.
- 48F. Ding, W. Xu, G. L. Graff, J. Zhang, M. Sushko, X. Chen, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 4450–4456.
- 49Y. H. Zhang, J. F. Qian, W. Xu, S. M. Russell, X. L. Chen, E. Nasybulin, P. Bhattacharya, M. H. Engelhard, D. H. Mei, R. G. Cao, et al., Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 6889–6896.
- 50L. Xiao, X. Chen, R. Cao, J. Qian, H. Xiang, J. Zheng, J.-G. Zhang, W. Xu, J. Power Sources 2015, 293, 1062–1067.
- 51F. Ding, W. Xu, X. Chen, J. Zhang, Y. Shao, M. H. Engelhard, Y. Zhang, T. A. Blake, G. L. Graff, X. Liu, et al., J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 4043–4049.
- 52H. Ye, Y.-X. Yin, S.-F. Zhang, Y. Shi, L. Liu, X.-X. Zeng, R. Wen, Y.-G. Guo, L.-J. Wan, Nano Energy 2017, 36, 411–417.
- 53H.-B. Han, S.-S. Zhou, D.-J. Zhang, S.-W. Feng, L.-F. Li, K. Liu, W.-F. Feng, J. Nie, H. Li, X.-J. Huang, M. Armand, Z.-B. Zhou, J. Power Sources 2011, 196, 3623–3632.
- 54J. Zheng, M. H. Engelhard, D. Mei, S. Jiao, B. J. Polzin, J.-G. Zhang, W. Xu, Nat. Energy 2017, 2, 17012.
- 55X. Ren, Y. Zhang, M. H. Engelhard, Q. Li, J.-G. Zhang, W. Xu, ACS Energy Lett. 2018, 3, 14–19.
- 56N. Choi, J. Han, S. Ha, RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 2732–2748.
- 57L. Xing, W. Li, C. Wang, F. Gu, M. Xu, C. Tan, J. Yi, J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 16596–16602.
- 58T. Huang, X. Zheng, M. Wu, W. Wang, Y. Pan, G. Fang, J. Power Sources 2016, 318, 264–269.
- 59S. Tan, Y. J. Ji, Z. R. Zhang, Y. Yang, ChemPhysChem 2014, 15, 1956–1969.
- 60X. Wang, X. Zheng, Y. Liao, Q. Huang, L. Xing, M. Xu, W. Li, J. Power Sources 2017, 338, 108–116.
- 61E. A. Olivetti, G. Ceder, G. G. Gaustad, X. Fu, Joule 2017, 1, 229–243.
- 62Y. Qian, P. Niehoff, M. Borner, M. Grutzke, X. Monnighoff, P. Behrends, S. Nowak, M. Winter, F. M. Schappacher, J. Power Sources 2016, 329, 31–40.
- 63P. Dong, D. Wang, Y. Yao, X. Li, Y. Zhang, J. Ru, T. Ren, J. Power Sources 2017, 344, 111–118.
- 64Z. Wang, L. Xing, J. H. Li, M. Xu, W. Li, J. Power Sources 2016, 307, 587–592.
- 65C. Yan, Y. Xu, J. Xia, C. Gong, K. Chen, J. Energy Chem. 2016, 25, 659–666.
- 66J. G. Han, S. J. Lee, J. Lee, J. S. Kim, K. T. Lee, N. S. Choi, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 8319–8329.
- 67J. Li, L. Zhang, L. Yu, W. Fan, Z. Wang, X. Yang, Y. Lin, L. Xing, M. Xu, W. Li, J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 26899–26907.
- 68J. Pires, A. Castets, L. Timperman, J. Santos-Peña, E. Dumont, S. Levasseur, C. Tessier, R. Dedryvère, M. Anouti, J. Power Sources 2015, 296, 413–425.
- 69Z. Zhou, Y. Ma, L. Wang, P. Zuo, X. Cheng, C. Du, G. Yin, Y. Gao, Electrochim. Acta 2016, 216, 44–50.
- 70J. Li, L. Xing, R. Zhang, M. Chen, Z. Wang, M. Xu, W. Li, J. Power Sources 2015, 285, 360–366.
- 71W. Tu, L. Xing, P. Xia, M. Xu, Y. Liao, W. Li, Electrochim. Acta 2016, 204, 192–198.
- 72X. Zheng, X. Wang, X. Cai, L. Xing, M. Xu, Y. Liao, X. Li, W. Li, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 30116–30125.
- 73P. Hong, M. Xu, X. Zheng, Y. Zhu, Y. Liao, L. Xing, Q. Huang, H. Wan, Y. Yang, W. Li, J. Power Sources 2016, 329, 216–224.
- 74A. Birrozzi, N. Laszczynski, M. Hekmatfar, J. Von Zamory, G. A. Giffin, S. Passerini, J. Power Sources 2016, 325, 525–533.
- 75Y.-M. Song, J.-G. Han, S. Park, K. T. Lee, N.-S. Choi, J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 9506–9513.
- 76X. Liao, Q. Huang, S. Mai, X. Wang, M. Xu, L. Xing, Y. Liao, W. Li, J. Power Sources 2014, 272, 501–507.
- 77Y. Xu, L. Wan, J. Liu, L. Zeng, Z. Yang, J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 698, 207–214.
- 78R. Chen, F. Liu, Y. Chen, Y. Ye, Y. Huang, F. Wu, L. Li, J. Power Sources 2016, 306, 70–77.
- 79S. Li, D. Zhao, P. Wang, X. Cui, F. Tang, Electrochim. Acta 2016, 222, 668–677.
- 80W. Tu, P. Xia, J. Li, L. Zeng, M. Xu, L. Xing, L. Zhang, L. Yu, W. Fan, W. Li, Electrochim. Acta 2016, 208, 251–259.
- 81H. Rong, M. Xu, B. Xie, H. Lin, Y. Zhu, X. Zheng, W. Huang, Y. Liao, L. Xing, W. Li, J. Power Sources 2016, 329, 586–593.
- 82S. Kim, M. Kim, I. Choi, J. J. Kim, J. Power Sources 2016, 336, 316–324.
- 83D. J. Lee, D. Im, Y.-G. Ryu, S. Lee, J. Yoon, J. Lee, W. Choi, I. Jung, S. Lee, S.-G. Doo, J. Power Sources 2013, 243, 831–835.
- 84N. von Aspern, S. Röser, B. R. Rad, P. Murmann, B. Streipert, X. Mönnighoff, S. D. Tillmann, M. Shevchuk, O. Stubbmann-Kazakova, G. V. Röschenthaler, S. Nowak, M. Winter, I. Cekic-Laskovic, J. Fluorine Chem. 2017, 198, 24–33.
- 85D. Moy, A. Manivannan, S. R. Narayanan, J. Electrochem. Soc. 2015, 162, A 1–A7.
- 86D. Aurbach, E. Pollak, R. Elazari, G. Salitra, C. S. Kelley, J. Affinito, J. Electrochem. Soc. 2009, 156, A 694–A702.
- 87N. Ding, L. Zhou, C. Zhou, D. Geng, J. Yang, S. W. Chien, Z. Liu, M. Ng, A. Yu, T. S. A. Hor, M. B. Sullivan, Y. Zong, Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33154.
- 88M. Ebadi, M. J. Lacey, D. Brandell, C. M. Araujo, J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 23324–23332.
- 89A. Rosenman, R. Elazari, G. Salitra, E. Markevich, D. Aurbach, A. Garsuch, J. Electrochem. Soc. 2015, 162, A 470–A473.
- 90S. S. Zhang, J. Electrochem. Soc. 2012, 159, A 920–A923.
- 91S. S. Zhang, Electrochim. Acta 2012, 70, 344–348.
- 92M. Barghamadi, A. S. Best, A. I. Bhatt, A. F. Hollenkamp, P. J. Mahon, M. Musameh, T. Rüther, J. Power Sources 2015, 295, 212–220.
- 93M. Barghamadi, A. S. Best, A. F. Hollenkamp, P. Mahon, M. Musameh, T. Rüther, Electrochim. Acta 2016, 222, 257–263.
- 94W. Jia, C. Fan, L. Wang, Q. Wang, M. Zhao, A. Zhou, J. Li, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 15399–15405.
- 95J. Kim, D. Yoo, J. Min, R. A. Shakoor, R. Kahraman, J. W. Choi, ChemNanoMat 2015, 1, 240–245.
- 96S. Liu, G. Li, X. Gao, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 7783–7789.
- 97T. Jaumann, J. Balach, M. Klose, S. Oswald, J. Eckert, L. Giebeler, J. Electrochem. Soc. 2016, 163, A 557–A564.
- 98V. Etacheri, U. Geiger, Y. Gofer, G. A. Roberts, I. C. Stefan, R. Fasching, D. Aurbach, Langmuir 2012, 28, 6175–6184.
- 99A. Rabenau, G. H. Talat, Appl. Phys. Lett. 2017, 621, 10–13.
- 100Y. Zhu, X. He, Y. Mo, Adv. Sci. 2017, 4, 1600517.
- 101G. Ma, Z. Wen, M. Wu, C. Shen, Q. Wang, J. Jin, X. Wu, Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 14209–14212.
- 102M. Baloch, D. Shanmukaraj, O. Bondarchuk, E. Bekaert, M. Armand, Energy Storage Mater. 2017, 9, 141–149.
- 103Z. Lin, Z. Liu, W. Fu, N. J. Dudney, C. Liang, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 1064–1069.
- 104W. Li, H. Yao, K. Yan, G. Zheng, Z. Liang, Y.-M. Chiang, Y. Cui, Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7436.
- 105C. Yan, X. Cheng, C. Zhao, J. Huang, S. Yang, J. Power Sources 2016, 327, 212–220.
- 106X.-B. Cheng, C. Yan, H.-J. Peng, J.-Q. Huang, S.-T. Yang, Q. Zhang, Energy Storage Mater. 2018, 10, 199–205.
- 107Y. Diao, K. Xie, S. Xiong, X. Hong, J. Electrochem. Soc. 2012, 159, 1816–1821.
- 108S. Xiong, K. Xie, Y. Diao, X. Hong, J. Power Sources 2014, 246, 840–845.
- 109S. Gu, Z. Wen, R. Qian, J. Jin, Q. Wang, M. Wu, S. Zhuo, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 34379–34386.
- 110B. L. Mehdi, A. Steve, J. Qian, C. Park, W. Xu, W. A. Henderson, J. Zhang, K. T. Mueller, N. D. Browning, Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34267.
- 111J. Qian, W. Xu, P. Bhattacharya, M. Engelhard, W. A. Henderson, Y. Zhang, J. G. Zhang, Nano Energy 2015, 15, 135–144.
- 112H. Koshikawa, S. Matsuda, K. Kamiya, Y. Kubo, J. Power Sources 2017, 350, 73–79.
- 113H. Wu, R. T. Haasch, B. R. Perdue, C. A. Apblett, A. A. Gewirth, J. Power Sources 2017, 369, 50–56.
- 114F. Wu, J. T. Lee, N. Nitta, H. Kim, O. Borodin, G. Yushin, Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 101–108.
- 115H. L. Wu, M. Shin, Y. M. Liu, K. A. See, A. A. Gewirth, Nano Energy 2017, 32, 50–58.
- 116H. M. Kim, J.-Y. Hwang, D. Aurbach, Y.-K. Sun, J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2017, 8, 5331–5337.
- 117W. Zhang, D. Qiao, J. Pan, Y. Cao, H. Yang, X. Ai, Electrochim. Acta 2013, 87, 497–502.
- 118Q. Pang, L. F. Nazar, ACS Nano 2016, 10, 4111–4118.
- 119H. Pan, K. S. Han, M. Vijayakumar, J. Xiao, R. Cao, J. Chen, J. Zhang, K. T. Mueller, Y. Shao, J. Liu, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 4290–4295.
- 120S. Walus̈, C. Barchasz, R. Bouchet, J. F. Martin, J. C. Leprêtre, F. Alloin, Electrochim. Acta 2015, 180, 178–186.
- 121M. Eom, S. Son, C. Park, S. Noh, W. T. Nichols, D. Shin, Electrochim. Acta 2017, 230, 279–284.
- 122K. Zhang, L. Wang, Z. Hu, F. Cheng, J. Chen, Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6467.
- 123Y. Fu, Y. S. Su, A. Manthiram, Adv. Energy Mater. 2014, 4, 1300655.
- 124Y. Yang, M. T. McDowell, A. Jackson, J. J. Cha, S. S. Hong, Y. Cui, Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 1486–1491.
- 125C. Zu, M. Klein, A. Manthiram, J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2014, 5, 3986–3991.
- 126S. Meini, R. Elazari, A. Rosenman, A. Garsuch, D. Aurbach, J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2014, 5, 915–918.
- 127M. J. Klein, A. Dolocan, C. Zu, A. Manthiram, Adv. Energy Mater. 2017, 7, 1701122.
- 128M. Liu, Y. X. Ren, H. R. Jiang, C. Luo, F. Y. Kang, T. S. Zhao, Nano Energy 2017, 40, 240–247.
- 129Y. X. Ren, T. S. Zhao, M. Liu, Y. K. Zeng, H. R. Jiang, J. Power Sources 2017, 361, 203–210.
- 130K. R. Kim, K.-S. Lee, C.-Y. Ahn, S.-H. Yu, Y.-E. Sung, Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32433.
- 131Z. W. Seh, J. H. Yu, W. Li, P.-C. Hsu, H. Wang, Y. Sun, H. Yao, Q. Zhang, Y. Cui, Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5017.
- 132G. Hernández, N. Lago, D. Shanmukaraj, M. Armand, D. Mecerreyes, Mater. Today Energy 2017, 6, 264–270.
- 133F. Wu, S. Thieme, A. Ramanujapuram, E. Zhao, C. Weller, Nano Energy 2017, 40, 170–179.
- 134M. Kazazi, M. R. Vaezi, A. Kazemzadeh, Ionics 2014, 20, 1291–1300.
- 135W. T. Xu, H. J. Peng, J. Q. Huang, C. Z. Zhao, X. B. Cheng, Q. Zhang, ChemSusChem 2015, 8, 2892–2901.
- 136M. J. Lacey, A. Yalamanchili, J. Maibach, C. Tengstedt, K. Edström, D. Brandell, RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 3632–3641.
- 137N. Azimi, Z. Xue, N. D. Rago, C. Takoudis, M. L. Gordin, J. Song, D. Wang, Z. Zhang, J. Electrochem. Soc. 2014, 162, A 64–A68.
- 138F. Lin, J. Wang, H. Jia, C. W. Monroe, J. Yang, Y. Nuli, J. Power Sources 2013, 223, 18–22.
- 139H. Jia, J. Wang, F. Lin, C. W. Monroe, J. Yang, Y. NuLi, Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 7011–7013.
- 140J. Wang, F. Lin, H. Jia, J. Yang, C. W. Monroe, Y. Nuli, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 10099–10104; Angew. Chem. 2014, 126, 10263–10268.
- 141T. Yim, K. S. Kang, J.-S. Yu, K. J. Kim, M.-S. Park, S.-G. Woo, G. Jeong, Y. N. Jo, K. Y. Im, J.-H. Kim, et al., Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 53, 08NK01.
- 142C. O. Laoire, S. Mukerjee, K. M. Abraham, E. J. Plichta, M. A. Hendrickson, J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 20127–20134.
- 143C. O. Laoire, S. Mukerjee, K. M. Abraham, E. J. Plichta, M. A. Hendrickson, J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 9178–9186.
- 144S. A. Freunberger, Y. Chen, Z. Peng, J. M. Griffin, L. J. Hardwick, F. Bardé, P. Novák, P. G. Bruce, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 8040–8047.
- 145Y. Chen, S. A. Freunberger, Z. Peng, O. Fontaine, P. G. Bruce, Nat. Chem. 2013, 5, 489–494.
- 146J.-B. Park, S. H. Lee, H.-G. Jung, D. Aurbach, Y.-K. Sun, Adv. Mater. 2017, 30, 1704162.
- 147D. Kundu, R. Black, B. Adams, L. F. Nazar, ACS Cent. Sci. 2015, 1, 510–515.
- 148B. J. Bergner, A. Schürmann, K. Peppler, A. Garsuch, J. Janek, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 15054–15064.
- 149B. J. Bergner, C. Hofmann, A. Schurmann, D. Schroder, K. Peppler, P. R. Schreiner, J. Janek, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 31769–31779.
- 150Y. Li, S. Dong, B. Chen, C. Lu, K. Liu, Z. Zhang, H. Du, X. Wang, X. Chen, X. Zhou, et al., J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2017, 8, 4218–4225.
- 151H.-D. Lim, B. Lee, Y. Zheng, J. Hong, J. Kim, H. Gwon, Y. Ko, M. Lee, K. Cho, K. Kang, Nat. Energy 2016, 1, 16066.
- 152M. Tułodziecki, G. M. Leverick, C. V. Amanchukwu, Y. Katayama, D. G. Kwabi, F. Bardé, P. T. Hammond, Y. Shao-Horn, Energy Environ. Sci. 2017, 10, 1828–1842.
- 153Y. Qiao, S. Wu, Y. Sun, S. Guo, J. Yi, P. He, H. Zhou, ACS Energy Lett. 2017, 2, 1869–1878.
- 154Z. Liang, Y.-C. Lu, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 7574–7583.
- 155S. Ha, Y. Kim, D. Koo, K.-H. Ha, Y. Park, D.-M. Kim, S. Son, T. Yim, K. T. Lee, J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 10609–10621.
- 156N.-S. Choi, G. Jeong, B. Koo, Y.-W. Lee, K. T. Lee, J. Power Sources 2013, 225, 95–100.
- 157M. Kartal, M. Uysal, A. Alp, H. Akbulut, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 7600–7608.
- 158D. Zheng, H.-S. Lee, X.-Q. Yang, D. Qu, Electrochem. Commun. 2013, 28, 17–19.
- 159C. Li, O. Fontaine, S. A. Freunberger, L. Johnson, S. Grugeon, S. Laruelle, P. G. Bruce, M. Armand, J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 3393–3401.
- 160T. Zhang, K. Liao, P. He, H. Zhou, Energy Environ. Sci. 2016, 9, 1024–1030.
- 161V. S. Bryantsev, V. Giordani, W. Walker, J. Uddin, I. Lee, A. C. T. van Duin, G. V. Chase, D. Addison, J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 11977–11988.
- 162M. Tokur, H. Algul, S. Ozcan, T. Cetinkaya, M. Uysal, M. O. Guler, H. Akbulut, Solid State Ionics 2016, 286, 51–56.
- 163A. A. Uludağ, H. Akbulut, M. Tokur, H. Algül, T. Çetinkaya, M. Uysal, Microsyst. Technol. 2016, 22, 953–963.
- 164M. Kartal, M. Uysal, T. Cetinkaya, A. Alp, H. Akbulut, Acta Phys. Pol. A 2015, 127, 1016–1018.
- 165O. Wijaya, P. Hartmann, R. Younesi, I. I. E. Markovits, A. Rinaldi, J. Janek, R. Yazami, J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 19061–19067.
- 166O. Wijaya, A. Rinaldi, R. Younesi, R. Yazami, J. Electrochem. Soc. 2016, 163, A 2660–A2664.
- 167S. S. Zhang, D. Foster, J. Read, Electrochim. Acta 2011, 56, 1283–1287.
- 168V. Roev, S. B. Ma, D. J. Lee, D. Im, J. Electrochem. Sci. Technol. 2014, 5, 58–64.
- 169L. Johnson, C. Li, Z. Liu, Y. Chen, S. A. Freunberger, P. C. Ashok, B. B. Praveen, K. Dholakia, J.-M. Tarascon, P. G. Bruce, Nat. Chem. 2014, 6, 1091–1099.
- 170X. Gao, Y. Chen, L. Johnson, P. G. Bruce, Nat. Mater. 2016, 15, 918.