Analyte-Triggered DNA-Probe Release from a Triplex Molecular Beacon for Nanopore Sensing
Bingyuan Guo
Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Sciences, Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Living Biosystems, Institute of Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100190 China
Key Laboratory for Biomedical Effects of Nanomaterials & Nanosafety, Multidisciplinary Center, Institute of High Energy Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
Search for more papers by this authorYingying Sheng
Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Sciences, Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Living Biosystems, Institute of Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100190 China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Ke Zhou
Key Laboratory for Biomedical Effects of Nanomaterials & Nanosafety, Multidisciplinary Center, Institute of High Energy Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Quansheng Liu
Key Laboratory for Biomedical Effects of Nanomaterials & Nanosafety, Multidisciplinary Center, Institute of High Energy Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dr. Lei Liu
Key Laboratory for Biomedical Effects of Nanomaterials & Nanosafety, Multidisciplinary Center, Institute of High Energy Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Hai-Chen Wu
Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Sciences, Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Living Biosystems, Institute of Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100190 China
Search for more papers by this authorBingyuan Guo
Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Sciences, Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Living Biosystems, Institute of Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100190 China
Key Laboratory for Biomedical Effects of Nanomaterials & Nanosafety, Multidisciplinary Center, Institute of High Energy Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
Search for more papers by this authorYingying Sheng
Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Sciences, Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Living Biosystems, Institute of Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100190 China
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Ke Zhou
Key Laboratory for Biomedical Effects of Nanomaterials & Nanosafety, Multidisciplinary Center, Institute of High Energy Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Quansheng Liu
Key Laboratory for Biomedical Effects of Nanomaterials & Nanosafety, Multidisciplinary Center, Institute of High Energy Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dr. Lei Liu
Key Laboratory for Biomedical Effects of Nanomaterials & Nanosafety, Multidisciplinary Center, Institute of High Energy Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Hai-Chen Wu
Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Sciences, Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Living Biosystems, Institute of Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100190 China
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
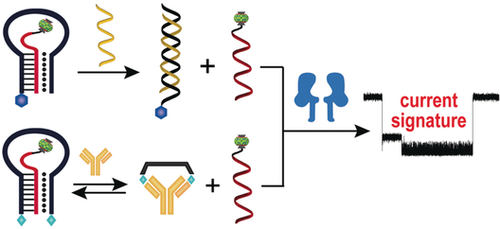
A nanopore sensing strategy based on a triplex molecular beacon was developed for the detection of specific DNA or multivalent proteins. Upon analyte binding, the loop of the molecular beacon is opened and the stem-forming DNA probe is released for nanopore translocation recording. The frequency of current signatures can be used to quantify the concentrations of the analytes.
Abstract
A new nanopore sensing strategy based on triplex molecular beacon was developed for the detection of specific DNA or multivalent proteins. The sensor is composed of a triplex-forming molecular beacon and a stem-forming DNA component that is modified with a host–guest complex. Upon target DNA hybridizing with the molecular beacon loop or multivalent proteins binding to the recognition elements on the stem, the DNA probe is released and produces highly characteristic current signals when translocated through α-hemolysin. The frequency of current signatures can be used to quantify the concentrations of the target molecules. This sensing approach provides a simple, quick, and modular tool for the detection of specific macromolecules with high sensitivity and excellent selectivity. It may find useful applications in point-of-care diagnostics with a portable nanopore kit in the future.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie201711690-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf984.7 KB | Supplementary |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1
- 1aR. Etzioni, N. Urban, S. Ramsey, M. McIntosh, S. Schwartz, B. Reid, J. Radich, G. Anderson, L. Hartwell, Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 243–252;
- 1bD. D. Taylor, C. Gercel-Taylor, Gynecol. Oncol. 2008, 110, 13–21.
- 2H. Schwarzenbach, D. S. B. Hoon, K. Pantel, Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 426–437.
- 3
- 3aA. Ríos, M. Zougagh, M. Avila, Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 740, 1–11;
- 3bM. Grønborg, T. Z. Kristiansen, A. Iwahori, R. Chang, R. Reddy, N. Sato, H. Molina, O. N. Jensen, R. H. Hruban, M. G. Goggins, A. Maitra, A. Pandey, Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2006, 5, 157–171;
- 3cA. Ambrosi, F. Airo, A. Merkoci, Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 1151–1156;
- 3dR. de la Rica, M. M. Stevens, Nat. Nanotechnol. 2012, 7, 821–824.
- 4
- 4aJ. Shen, Y. Li, H. Gu, F. Xia, X. Zuo, Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 7631–7677;
- 4bA. B. Chinen, C. M. Guan, J. R. Ferrer, S. N. Barnaby, T. J. Merkel, C. A. Mirkin, Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 10530–10574.
- 5H. Bayley, P. S. Cremer, Nature 2001, 413, 226–230.
- 6
- 6aO. Braha, L. Q. Gu, L. Zhou, X. F. Lu, S. Cheley, H. Bayley, Nat. Biotechnol. 2000, 18, 1005–1007;
- 6bA. F. Hammerstein, S.-H. Shin, H. Bayley, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 5085–5090; Angew. Chem. 2010, 122, 5211–5216;
- 6cS. Wen, T. Zeng, L. Liu, K. Zhao, Y. Zhao, X. Liu, H.-C. Wu, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 18312–18317;
- 6dC. Yang, L. Liu, T. Zeng, D. Yang, Z. Yao, Y. Zhao, H.-C. Wu, Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 7302–7307.
- 7
- 7aL. Q. Gu, O. Braha, S. Conlan, S. Cheley, H. Bayley, Nature 1999, 398, 686–690;
- 7bH.-C. Wu, H. Bayley, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 6813–6819.
- 8
- 8aL. Movileanu, S. Howorka, O. Braha, H. Bayley, Nat. Biotechnol. 2000, 18, 1091–1095;
- 8bS. Howorka, S. Cheley, H. Bayley, Nat. Biotechnol. 2001, 19, 636–639;
- 8cE. C. Yusko, J. M. Johnson, S. Majd, P. Prangkio, R. C. Rollings, J. Li, J. Yang, M. Mayer, Nat. Nanotechnol. 2011, 6, 253–260;
- 8dR. Wei, V. Gatterdam, R. Wieneke, R. Tampe, U. Rant, Nat. Nanotechnol. 2012, 7, 257–263;
- 8eD. Rotem, L. Jayasinghe, M. Salichou, H. Bayley, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 2781–2787;
- 8fL. Liu, C. Yang, K. Zhao, J. Li, H.-C. Wu, Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2989;
- 8gT. Li, L. Liu, Y. Li, J. Xie, H.-C. Wu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 7568–7571; Angew. Chem. 2015, 127, 7678–7681.
- 9
- 9aY. Wang, D. Zheng, Q. Tan, M. X. Wang, L.-Q. Gu, Nat. Nanotechnol. 2011, 6, 668–674;
- 9bM. Wanunu, T. Dadosh, V. Ray, J. Jin, L. McReynolds, M. Drndic, Nat. Nanotechnol. 2010, 5, 807–814;
- 9cS. Wang, F. Haque, P. G. Rychahou, B. M. Evers, P. Guo, ACS Nano 2013, 7, 9814–9822.
- 10
- 10aS. H. Shin, T. Luchian, S. Cheley, O. Braha, H. Bayley, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2002, 41, 3707–3709;
10.1002/1521-3773(20021004)41:19<3707::AID-ANIE3707>3.0.CO;2-5 CAS PubMed Web of Science® Google ScholarAngew. Chem. 2002, 114, 3859–3861;
- 10bS. Lu, W.-W. Li, D. Rotem, E. Mikhailova, H. Bayley, Nat. Chem. 2010, 2, 921–928;
- 10cM. B. Steffensen, D. Rotem, H. Bayley, Nat. Chem. 2014, 6, 603–608;
- 10dF. Haque, J. Lunn, H. Fang, D. Smithrud, P. Guo, ACS Nano 2012, 6, 3251–3261.
- 11
- 11aJ. Clarke, H.-C. Wu, L. Jayasinghe, A. Patel, S. Reid, H. Bayley, Nat. Nanotechnol. 2009, 4, 265–270;
- 11bE. A. Manrao, I. M. Derrington, A. H. Laszlo, K. W. Langford, M. K. Hopper, N. Gillgren, M. Pavlenok, M. Niederweis, J. H. Gundlach, Nat. Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 349–353;
- 11cG. M. Cherf, K. R. Lieberman, H. Rashid, C. E. Lam, K. Karplus, M. Akeson, Nat. Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 344–348;
- 11dA. H. Laszlo, I. M. Derrington, B. C. Ross, H. Brinkerhoff, A. Adey, I. C. Nova, J. M. Craig, K. W. Langford, J. M. Samson, R. Daza, K. Doering, J. Shendure, J. H. Gundlach, Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 829–833;
- 11eF. Haque, J. Li, H.-C. Wu, X.-J. Liang, P. Guo, Nano Today 2013, 8, 56–74.
- 12N. A. W. Bell, U. F. Keyser, Nat. Nanotechnol. 2016, 11, 645–651.
- 13L. Liu, H.-C. Wu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 15216–15222; Angew. Chem. 2016, 128, 15440–15446.
- 14
- 14aS. Tyagi, F. R. Kramer, Nat. Biotechnol. 1996, 14, 303–308;
- 14bS. Tyagi, D. P. Bratu, F. R. Kramer, Nat. Biotechnol. 1998, 16, 49–53.
- 15Y. Wang, K. Tian, L. L. Hunter, B. Ritzo, L.-Q. Gu, Nanoscale 2014, 6, 11372–11379.
- 16
- 16aT. N. Grossmann, L. Roeglin, O. Seitz, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 5223–5225; Angew. Chem. 2007, 119, 5315–5318;
- 16bY. Hu, A. Cecconello, A. Idili, F. Ricci, I. Willner, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 15210–15233; Angew. Chem. 2017, 129, 15410–15434.
- 17S. Ranallo, M. Rossetti, K. W. Plaxco, A. Vallee-Belisle, F. Ricci, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 13214–13218; Angew. Chem. 2015, 127, 13412–13416.
- 18S. Banala, S. J. A. Aper, W. Schalk, M. Merkx, ACS Chem. Biol. 2013, 8, 2127–2132.
- 19H. G. Gratzner, Science 1982, 218, 474–475.