Mechanisms of DNA Repair by Photolyase and Excision Nuclease (Nobel Lecture)†
Corresponding Author
Prof. Aziz Sancar
Department of Biochemistry and Biophysics, University of North Carolina School of Medicine, Chapel Hill, North Carolina, USA
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Aziz Sancar
Department of Biochemistry and Biophysics, University of North Carolina School of Medicine, Chapel Hill, North Carolina, USA
Search for more papers by this authorCopyright© The Nobel Foundation 2015. We thank the Nobel Foundation, Stockholm, for permission to print this lecture.
Graphical Abstract
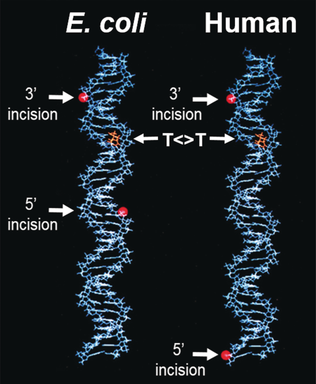
Ultraviolet light damages DNA by converting two adjacent thymines into a thymine dimer which is potentially mutagenic, carcinogenic, or lethal to the organism. This damage is repaired by photolyase and the nucleotide excision repair system in E. coli by nucleotide excision repair in humans. The work leading to these results is presented by Aziz Sancar in his Nobel Lecture.
References
- 1“Effect of Visible Light on the Recovery of Streptomyces Griseus Conidia from Ultra-violet Irradiation Injury”: A. Kelner, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1949, 35, 73–79.
- 2“Photoreactivation of Ultraviolet-Irradiated Escherichia coli, with Special Reference to the Dose-Reduction Principle and to Ultraviolet-Induced Mutation”: A. Kelner, J. Bacteriol. 1949, 58, 511–522.
- 3“Photoreactivation in vitro of ultraviolet-inactivated Hemophilus influenzae transforming factor”: C. S. Rupert, S. H. Goodgal, M. R. Herriott, J. Gen. Physiol. 1958, 41, 451–471.
- 4“Photoreactivation of transforming DNA by an enzyme from bakers’ yeast”: S. C. Rupert, J. Gen. Physiol. 1960, 43, 573–595.
- 5“Photoenzymatic repair of ultraviolet damage in DNA. I. Kinetics of the reaction”: S. C. Rupert, J. Gen. Physiol. 1962, 45, 703–724.
- 6“Photoenzymatic repair of ultraviolet damage in DNA. II. Formation of an enzyme-substrate complex”. S. C. Rupert, J. Gen. Physiol. 1962, 45, 725–741.
- 7“Disappearance of thymine photodimer in ultraviolet irradiated DNA upon treatment with a photoreactivating enzyme from baker's yeast”: D. L. Wulff, S. C. Rupert, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1962, 7, 237–240.
- 8A. Sancar, A study of photoreactivating enzyme (DNA photolyase) of Escherichia coli, PhD Dissertation, University of Texas at Dallas, 1977.
- 9“Cloning of the phr gene and amplification of photolyase in Escherichia coli”: A. Sancar, S. C. Rupert, Gene 1978, 4, 295–308.
- 10“Escherichia coli DNA photolyase is a flavoprotein”: A. Sancar, B. G. Sancar, J. Mol. Biol. 1984, 172, 223–227.
- 11“Purification of Escherichia coli DNA photolyase”: A. Sancar, F. W. Smith, B. G. Sancar, J. Biol. Chem. 1984, 259, 6028–6032.
- 12“Identification of a neutral flavin radical and characterization of a second chromophore in Escherichia coli DNA photolyase”: M. S. Jorns, G. B. Sancar, A. Sancar, Biochemistry 1984, 23, 2673–2679.
- 13“Action mechanism of Escherichia coli DNA photolyase. I. Formation of the enzyme-substrate complex”: G. B. Sancar, F. W. Smith, R. Reid, G. Payne, M. Levy, A. Sancar, J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 478–485.
- 14“Action mechanism of Escherichia coli DNA photolyase. II. Role of the chromophores in catalysis”: M. S. Jorns, E. T. Baldwin, G. B. Sancar, A. Sancar, J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 486–491.
- 15“Action mechanism of Escherichia coli DNA photolyase. III. Photolysis of the enzyme-substrate complex and the absolute action spectrum”: G. B. Sancar, M. S. Jorns, G. Payne, D. J. Fluke, C. S. Rupert, A. Sancar, J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 492–498.
- 16“Photochemical properties of Escherichia coli DNA photolyase: selective photodecomposition of the second chromophore”: P. F. Heelis, G. Payne, A. Sancar, Biochemistry 1987, 26, 4634–4640.
- 17“The active form of Escherichia coli DNA photolyase contains a fully reduced flavin and not a flavin radical, both in vivo and in vitro”: G. Payne, P. F. Heelis, B. R. Rohrs, A. Sancar, Biochemistry 1987, 26, 7121–7127.
- 18“Mechanism of damage recognition by Escherichia coli DNA photolyase”: I. Husain, G. B. Sancar, S. R. Holbrook, A. Sancar, J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 13188–13197.
- 19“Identification of the second chromophore of Escherichia coli and yeast DNA photolyases as 5,10-methenyltetrahydrofolate”: J. L. Johnson, S. Hamm-Alvarez, G. Payne, G. B. Sancar, K. V. Rajagopalan, A. Sancar, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1988, 85, 2046–2050.
- 20“Active site of Escherichia coli DNA photolyase: mutations at Trp 277 alter the selectivity of the enzyme without affecting the quantum yield of photorepair”: Y. F. Li, A. Sancar, Biochemistry 1990, 29, 5698–5706.
- 21“Active site of DNA photolyase: tryptophan-306 is the intrinsic hydrogen atom donor essential for flavin radical photoreduction and DNA repair in vitro”: Y. F. Li, P. F. Heelis, A. Sancar, Biochemistry 1991, 30, 6322–6329.
- 22“Determination of rates and yields of interchromophore (folate-flavin) energy transfer and intermolecular (flavin-DNA) electron transfer in Escherichia coli photolyase by time-resolved fluorescence and absorption spectroscopy”: S. T. Kim, P. F. Heelis, T. Okamura, Y. Hirata, N. Mataga, A. Sancar, Biochemistry 1991, 30, 11262–11270.
- 23“Substrate and temperature dependence of DNA Photolyase repair activity examined with ultrafast spectroscopy”: T. Langenbacher, X. D. Zhao, G. Bieser, P. F. Heelis, A. Sancar, E. M. Michel-Beyerle, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997, 119, 10532–10536.
- 24“Absolute action spectrum of E-FADH2 and E-FADH2-MTHF forms of Escherichia coli DNA photolyase”: G. Payne, A. Sancar, Biochemistry 1990, 29, 7715–7727.
- 25“Picosecond Laser Photolysis Studies on the Photorepair of Pyrimidine Dimers by DNA Photolyase.1. Laser Photolysis of Photolyase-2-Deoxyuridine Dinucleotide Photodimer Complex”: T. Okamura, A. Sancar, P. F. Heelis, T. P. Begley, Y. Hirata, N. Mataga, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1991, 113, 3143–3145.
- 26“Analysis of the role of intraprotein electron transfer in photoreactivation by DNA photolyase in vivo”: I. H. Kavakli, A. Sancar, Biochemistry 2004, 43, 15103–15110.
- 27“Structure and function of DNA photolyase and cryptochrome blue-light photoreceptors”: A. Sancar, Chem. Rev. 2003, 103, 2203–2237.
- 28“Structure and function of photolyase and in vivo enzymology: 50th anniversary”: A. Sancar, J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 32153–32157.
- 29“Direct determination of resonance energy transfer in photolyase: structural alignment for the functional state”: C. Tan, L. Guo, Y. Ai, J. Li, L. Wang, A. Sancar, Y. Luo, D. Zhong, J. Phys. Chem. A 2014, 118, 10522–10530.
- 30“Crystal structure of DNA photolyase from Escherichia coli”: H. W. Park, S. T. Kim, A. Sancar, J. Deisenhofer, Science 1995, 268, 1866–1872.
- 31“Electron Transfer Mechanisms of DNA Repair by Photolyase”: P. D. Zhong, Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 2015, 66, 691–715.
- 32“Direct observation of thymine dimer repair in DNA by photolyase”: Y. T. Kao, C. Saxena, L. Wang, A. Sancar, D. Zhong, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 16128–16132.
- 33“Dynamics and mechanism of cyclobutane pyrimidine dimer repair by DNA photolyase”: Z. Liu, C. Tan, X. Guo, Y. T. Kao, J. Li, L. Wang, A. Sancar, D. Zhong, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 14831–14836.
- 34“The molecular origin of high DNA-repair efficiency by photolyase”: C. Tan, Z. Y. Liu, J. Li, X. M. Guo, L. J. Wang, A. Sancar, P. D. Zhong, Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7302.
- 35“Structure and function of DNA photolyase”: A. Sancar, Biochemistry 1994, 33, 2–9.
- 36“Release of Ultraviolet Light-Induced Thymine Dimers from DNA in E. coli K-12”: R. P. Boyce, P. Howard-Flanders, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1964, 51, 293–300.
- 37“Disappearance of Thymine Dimers from DNA. Error-Correcting Mechanism”: R. B. Setlow, L. W. Carrier, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1964, 51, 226–231.
- 38“Overlap of Photoreactivation + Liquid Holding Recovery in Escherichia coli”: B. Castellani, J. Jagger, R. B. Setlow, Science 1964, 143, 1170–1171.
- 39“Evidence for Repair of Ultra-Violet Damaged Deoxyribonucleic Acid in Cultured Mammalian Cells”: R. E. Rasmussen, B. R. Painter, Nature 1964, 203, 1360–1362.
- 40“Evidence for Excision of Ultraviolet-Induced Pyrimidine Dimers from DNA of Human Cells in Vitro”: J. D. Regan, J. E. Trosko, L. W. Carrier, Biophys. J. 1968, 8, 319–325.
- 41“In vivo Excision of Pyrimidine Dimers Is Mediated by a DNA N-Glycosylase in Micrococcus-Luteus but Not in Human-Fibroblasts”: M. La Belle, S. Linn, Photochem. Photobiol. 1982, 36, 319–324.
- 42“Photoreversal-Dependent Release of Thymidine and Thymidine Monophosphate from Pyrimidine Dimer-Containing DNA Excision Fragments Isolated from Ultraviolet-Damaged Human-Fibroblasts”: M. Weinfeld, N. E. Gentner, L. D. Johnson, C. M. Paterson, Biochemistry 1986, 25, 2656–2664.
- 43“Three Loci in Escherichia Coli K-12 That Control Excision of Pyrimidine Dimers and Certain Other Mutagen Products from DNA”: P. Howard-Flanders, R. P. Boyce, L. Theriot, Genetics 1966, 53, 1119–1136.
- 44“Defective Repair Replication of DNA in Xeroderma Pigmentosum”: E. J. Cleaver, Nature 1968, 218, 652–656.
- 45“Xeroderma Pigmentosum – Biochemical and Genetic Characteristics”: J. E. Cleaver, D. Bootsma, Annu. Rev. Genet. 1975, 9, 19–38.
- 46“Evidence for Repair-Replication of Ultraviolet Damaged DNA in Bacteria”: D. E. Pettijohn, P. Hanawalt, J. Mol. Biol. 1964, 9, 395–410.
- 47“Ultraviolet-Light Repair and Mutagenesis Revisited”: A. W. Haseltine, Cell 1983, 33, 13–17.
- 48“Simple Method for Identification of Plasmid-Coded Proteins”: A. Sancar, A. M. Hack, D. W. Rupp, J. Bacteriol. 1979, 137, 692–693.
- 49“Identification of the UvrA-Gene Product”: A. Sancar, R. P. Wharton, S. Seltzer, B. M. Kacinski, N. D. Clarke, D. W. Rupp, J. Mol. Biol. 1981, 148, 45–62.
- 50“Identification of the UvrB-Gene Product”: A. Sancar, N. D. Clarke, J. Griswold, W. J. Kennedy, D. W. Rupp, J. Mol. Biol. 1981, 148, 63–76.
- 51“Identification of the UvrC-Gene Product”: A. Sancar, B. M. Kacinski, D. L. Mott, D. W. Rupp, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1981, 78, 5450–5454.
- 52“A Novel Repair Enzyme – UvrABC Excision Nuclease of Escherichia coli Cuts a DNA Strand on Both Sides of the Damaged Region”: A. Sancar, D. W. Rupp, Cell 1983, 33, 249–260.
- 53“Amplification and Purification of Uvra, Uvrb, and Uvrc Proteins of Escherichia coli”: D. C. Thomas, M. Levy, A. Sancar, J. Biol. Chem. 1985, 260, 9875–9883.
- 54“Effect of DNA Polymerase I and DNA Helicase II on the Turnover Rate of UvrABC Excision Nuclease”: I. Husain, B. Van Houten, D. C. Thomas, M. Abdelmonem, A. Sancar, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1985, 82, 6774–6778.
- 55“Construction of DNA Substrates Modified with Psoralen at a Unique Site and Study of the Action Mechanism of ABC Excinuclease on These Uniformly Modified Substrates”: B. Van Houten, H. Gamper, J. E. Hearst, A. Sancar, J. Biol. Chem. 1986, 261, 14135–14141.
- 56“Action Mechanism of ABC Excision Nuclease on a DNA Substrate Containing a Psoralen Cross-Link at a Defined Position”: B. Van Houten, H. Gamper, S. R. Holbrook, J. E. Hearst, A. Sancar, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1986, 83, 8077–8081.
- 57“Dnase-I Footprint of ABC Excinuclease”: B. Van Houten, H. Gamper, A. Sancar, E. J. Hearst, J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 13180–13187.
- 58“Analysis of sequential steps of nucleotide excision repair in Escherichia coli using synthetic substrates containing single psoralen adducts”: B. Van Houten, H. Gamper, J. E. Hearst, A. Sancar, J. Biol. Chem. 1988, 263, 16553–16560.
- 59“The (A)BC Excinuclease of Escherichia coli Has Only the Uvrb and Uvrc Subunits in the Incision Complex”: D. K. Orren, A. Sancar, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 5237–5241.
- 60“Formation and enzymatic properties of the UvrB.DNA complex”: D. K. Orren, A. Sancar, J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 15796–15803.
- 61“Post-Incision Steps of Nucleotide Excision Repair in Escherichia coli. Disassembly of the UvrBC-DNA Complex by Helicase II and DNA-Polymerase I”: D. K. Orren, C. P. Selby, J. E. Hearst, A. Sancar, J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 780–788.
- 62“A New Mechanism for Repairing Oxidative Damage to DNA – (A)BC Excinuclease Removes AP Sites and Thymine Glycols from DNA”: J. J. Lin, A. Sancar, Biochemistry 1989, 28, 7979–7984.
- 63“Active-Site of (A)BC Excinuclease. 1. Evidence for 5′ Incision by UvrC through a Catalytic Site Involving Asp 399, Asp 438, Asp 466, and His 538 Residues”: J. J. Lin, A. Sancar, J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 17688–17692.
- 64“Active-Site of (A)BC Excinuclease. 2. Binding, Bending, and Catalysis Mutants of Uvrb Reveal a Direct Role in 3′ and an Indirect Role in 5′ Incision”: J. J. Lin, A. M. Phillips, J. E. Hearst, A. Sancar, J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 17693–17700.
- 65“(A)BC Excinuclease – the Escherichia coli Nucleotide Excision Repair Enzyme”: J. J. Lin, A. Sancar, Mol. Microbiol. 1992, 6, 2219–2224.
- 66“Molecular Matchmakers”: A. Sancar, E. J. Hearst, Science 1993, 259, 1415–1420.
- 67“The repair patch of E. coli (A)BC excinuclease”: Sibghat-Ullah, A. Sancar, E. J. Hearst, Nucleic Acids Res. 1990, 18, 5051–5053.
- 68“DNA-Repair Enzymes”: A. Sancar, B. G. Sancar, Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1988, 57, 29–67.
- 69“Catalytic sites for 3′ and 5′ incision of Escherichia coli nucleotide excision repair are both located in UvrC”: E. E. A. Verhoeven, M. van Kesteren, G. F. Moolenaar, R. Visse, N. Goosen, J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 5120–5123.
- 70“Conserved domains in DNA repair proteins and evolution of repair systems”: L. Aravind, D. R. Walker, V. E. Koonin, Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 1223–1242.
- 71“DNA-Repair in an Active Gene – Removal of Pyrimidine Dimers from the Dhfr Gene of Cho Cells Is Much More Efficient Than in the Genome Overall”: V. A. Bohr, C. A. Smith, D. S. Okumoto, C. P. Hanawalt, Cell 1985, 40, 359–369.
- 72“Selective Removal of Transcription-Blocking DNA Damage from the Transcribed Strand of the Mammalian Dhfr Gene”: I. Mellon, G. Spivak, C. P. Hanawalt, Cell 1987, 51, 241–249.
- 73“Induction of the Escherichia coli Lactose Operon Selectively Increases Repair of Its Transcribed DNA Strand”: I. Mellon, C. P. Hanawalt, Nature 1989, 342, 95–98.
- 74“Transcription preferentially inhibits nucleotide excision repair of the template DNA strand in vitro”: C. P. Selby, A. Sancar, J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 21330–21336.
- 75“Gene- and strand-specific repair in vitro: partial purification of a transcription-repair coupling factor”: C. P. Selby, A. Sancar, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 8232–8236.
- 76“Escherichia coli mfd mutant deficient in ”mutation frequency decline“ lacks strand-specific repair: in vitro complementation with purified coupling factor”: C. P. Selby, E. M. Witkin, A. Sancar, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 11574–11578.
- 77“Molecular Mechanism of Transcription-Repair Coupling”: C. P. Selby, A. Sancar, Science 1993, 260, 53–58.
- 78“Mechanisms of transcription-repair coupling and mutation frequency decline”: C. P. Selby, A. Sancar, Microbiol. Rev. 1994, 58, 317–329.
- 79“Structure and Function of Transcription-Repair Coupling Factor. 1. Structural Domains and Binding Properties”: C. P. Selby, A. Sancar, J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 4882–4889.
- 80“Structure and Function of Transcription-Repair Coupling Factor. 2. Catalytic Properties”: C. P. Selby, A. Sancar, J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 4890–4895.
- 81“RNA polymerase II, stalled at a thymine dimer: footprint and effect on excision repair”: C. P. Selby, R. Drapkin, D. Reinberg, A. Sancar, Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 787–793.
- 82“Mechanisms of DNA excision repair”: A. Sancar, Science 1994, 266, 1954–1956.
- 83“Nucleotide Excision Repair”:A. Sancar, S. M. Tang, Photochem. Photobiol. 1993, 57, 905–921.
- 84“Radiation-Induced Mutations and Their Repair”: M. E. Witkin, Science 1966, 152, 1345–1353.
- 85“Human Nucleotide Excision Repair In vitro – Repair of Pyrimidine Dimers, Psoralen and Cisplatin Adducts by Hela Cell-Free Extract”: Sibghat-Uullah, I. Husain, W. Carlton, A. Sancar, Nucleic Acids Res. 1989, 17, 4471–4484.
- 86“Human nucleotide excision nuclease removes thymine dimers from DNA by incising the 22nd phosphodiester bond 5′ and the 6th phosphodiester bond 3′ to the photodimer”: J. C. Huang, D. L. Svoboda, J. T. Reardon, A. Sancar, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 3664–3668.
- 87“Purification of PCNA as a Nucleotide Excision Repair Protein”: A. F. Nichols, A. Sancar, Nucleic Acids Res. 1992, 20, 2441–2446.
- 88“Excision Repair in Man and the Molecular Basis of Xeroderma Pigmentosum Syndrome”: J. T. Reardon, L. H. Thompson, A. Sancar, Cold Spring Harbor Symp. Quant. Biol. 1993, 58, 605–617.
- 89“DNA Repair by Eukaryotic Nucleotide Excision Nuclease – Removal of Thymine Dimer and Psoralen Monoadduct by Hela Cell-Free Extract and of Thymine Dimer by Xenopus laevis Oocytes”: D. L. Svoboda, J. S. Taylor, J. E. Hearst, A. Sancar, J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 1931–1936.
- 90“HMG-domain proteins specifically inhibit the repair of the major DNA adduct of the anticancer drug cisplatin by human excision nuclease”: J. C. Huang, D. B. Zamble, J. T. Reardon, S. J. Lippard, A. Sancar, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 10394–10398.
- 91“Substrate spectrum of human excinuclease: repair of abasic sites, methylated bases, mismatches, and bulky adducts”: J. C. Huang, D. S. Hsu, A. Kazantsev, A. Sancar, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 12213–12217.
- 92“Dual role of TFIIH in DNA excision repair and in transcription by RNA polymerase II”: R. Drapkin, J. T. Reardon, A. Ansari, J. C. Huang, L. Zawel, K. Ahn, A. Sancar, D. Reinberg, Nature 1994, 368, 769–772.
- 93“Reconstitution of human DNA repair excision nuclease in a highly defined system”: D. Mu, C. H. Park, T. Matsunaga, D. S. Hsu, J. T. Reardon, A. Sancar, J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 2415–2418.
- 94“Formation of a ternary complex by human XPA, ERCC1, and ERCC4(XPF) excision repair proteins”: C. H. Park, A. Sancar, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 5017–5021.
- 95“Human DNA-Repair Excision Nuclease – Analysis of the Roles of the Subunits Involved in Dual Incisions by Using Anti-XPG and Anti-ERCC1 Antibodies”: T. Matsunaga, D. Mu, C. H. Park, J. T. Reardon, A. Sancar, J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 20862–20869.
- 96“Purification and Characterization of the XPF ERCC1 Complex of Human DNA Repair Excision Nuclease”: C. H. Park, T. Bessho, T. Matsunaga, A. Sancar, J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 22657–22660.
- 97“Reaction mechanism of human DNA repair excision nuclease”: D. Mu, D. S. Hsu, A. Sancar, J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 8285–8294.
- 98“Replication protein A confers structure-specific endonuclease activities to the XPF-ERCC1 and XPG subunits of human DNA repair excision nucleases”: T. Matsunaga, C. H. Park, T. Bessho, D. Mu, A. Sancar, J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 11047–11050.
- 99“Overproduction, purification, and characterization of the XPC subunit of the human DNA repair excision nuclease”: J. T. Reardon, D. Mu, A. Sancar, J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 19451–19456.
- 100“Recognition and repair of compound DNA lesions (base damage and mismatch) by human mismatch repair and excision repair systems”: D. Mu, M. Tursun, D. R. Duckett, J. T. Drummond, P. Modrich, A. Sancar, Mol. Cell. Biol. 1997, 17, 760–769.
- 101“Reconstitution of human excision nuclease with recombinant XPF-ERCC1 complex”: T. Bessho, A. Sancar, L. H. Thompson, P. M. Thelen, J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 3833–3837.
- 102“Rodent UV-sensitive mutant cell lines in complementation groups 6–10 have normal general excision repair activity”: J. T. Reardon, L. H. Thompson, A. Sancar, Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 1015–1021.
- 103“Characterization of reaction intermediates of human excision repair nuclease”: D. Mu, M. Wakasugi, D. S. Hsu, A. Sancar, J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 28971–28979.
- 104“The non-catalytic function of XPG protein human nucleotide excision repair”: M. Wakasugi, J. T. Reardon, A. Sancar, J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 16030–16034.
- 105“Assembly, subunit composition, and footprint of human DNA repair excision nuclease”: M. Wakasugi, A. Sancar, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 6669–6674.
- 106“Order of assembly of human DNA repair excision nuclease”: M. Wakasugi, A. Sancar, J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 18759–18768.
- 107“Efficient nucleotide excision repair of cisplatin, oxaliplatin, and Bis-aceto-ammine-dichloro-cyclohexylamine-platinum(IV) (JM216) platinum intrastrand DNA diadducts”: J. T. Reardon, A. Vaisman, S. G. Chaney, A. Sancar, Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 3968–3971.
- 108“Initiation of DNA interstrand cross-link repair in humans: the nucleotide excision repair system makes dual incisions 5′ to the cross-linked base and removes a 22- to 28-nucleotide-long damage-free strand”: T. Bessho, D. Mu, A. Sancar, Mol. Cell. Biol. 1997, 17, 6822–6830.
- 109“DNA interstrand cross-links induce futile repair synthesis in mammalian cell extracts”: D. Mu, T. Bessho, L. V. Nechev, D. J. Chen, T. M. Harris, J. E. Hearst, A. Sancar, Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000, 20, 2446–2454.
- 110“DNA damage in the nucleosome core is refractory to repair by human excision nuclease”: R. Hara, J. Y. Mo, A. Sancar, Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000, 20, 9173–9181.
- 111“The SWI/SNF chromatin-remodeling factor stimulates repair by human excision nuclease in the mononucleosome core particle”: R. Hara, A. Sancar, Mol. Cell. Biol. 2002, 22, 6779–6787.
- 112“Effect of damage type on stimulation of human excision nuclease by SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling factor”: R. Hara, A. Sancar, Mol. Cell. Biol. 2003, 23, 4121–4125.
- 113“Nucleotide excision repair from site-specifically platinum-modified nucleosomes”: D. Wang, R. Hara, G. Singh, A. Sancar, J. S. Lippard, Biochemistry 2003, 42, 6747–6753.
- 114“DNA repair excision nuclease attacks undamaged DNA – A potential source of spontaneous mutations”: M. E. Branum, J. T. Reardon, A. Sancar, J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 25421–25426.
- 115“Recognition and repair of the cyclobutane thymine dimer, a major cause of skin cancers, by the human excision nuclease”: J. T. Reardon, A. Sancar, Genes Dev. 2003, 17, 2539–2551.
- 116“Thermodynamic cooperativity and kinetic proofreading in DNA damage recognition and repair”: J. T. Reardon, A. Sancar, Cell Cycle 2004, 3, 139–142.
- 117“A mathematical model for human nucleotide excision repair: damage recognition by random order assembly and kinetic proofreading”: K. J. Kesseler, W. K. Kaufmann, J. T. Reardon, T. C. Elston, A. Sancar, J. Theor. Biol. 2007, 249, 361–375.
- 118“Xeroderma pigmentosum complementation group E protein (XPE/DDB2): Purification of various complexes of XPE and analyses of their damaged DNA binding and putative DNA repair properties”: G. Kulaksiz, J. T. Reardon, A. Sancar, Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005, 25, 9784–9792.
- 119“Characterization of transcription-repair coupling factors in E. coli and humans”: C. P. Selby, A. Sancar, Methods Enzymol. 2003, 371, 300–324.
- 120“DNA excision repair”: A. Sancar, Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1996, 65, 43–81.
- 121“Nucleotide excision repair: From E coli to man”: C. Petit, A. Sancar, Biochimie 1999, 81, 15–25.
- 122“Molecular mechanisms of mammalian DNA repair and the DNA damage checkpoints”: A. Sancar, L. A. Lindsey-Boltz, K. Unsal-Kacmaz, S. Linn, Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2004, 73, 39–85.
- 123“Nucleotide excision repair in E coli and man”: A. Sancar, T. J. Reardon, DNA Repair Replication 2004, 69, 43–71.
- 124“Nucleotide excision repair”: J. T. Reardon, A. Sancar, Prog. Nucleic Acid Res. Mol. Biol. 2005, 79, 183–235.
- 125“Purification and characterization of Escherichia coli and human nucleotide excision repair enzyme systems”: J. T. Reardon, A. Sancar, DNA Repair Part A 2006, 408, 189–213.
- 126“Repair of DNA-polypeptide crosslinks by human excision nuclease”: J. T. Reardon, A. Sancar, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 4056–4061.
- 127“Purification and characterization of human DNA damage checkpoint Rad complexes”: L. A. Lindsey-Boltz, V. P. Bermudez, J. Hurwitz, A. Sancar, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 11236–11241.
- 128“Loading of the human 9-1-1 checkpoint complex onto DNA by the checkpoint clamp loader hRad17-replication factor C complex in vitro”: V. P. Bermudez, L. A. Lindsey-Boltz, A. J. Cesare, Y. Maniwa, J. D. Griffith, J. Hurwitz, A. Sancar, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 1633–1638.
- 129“Reconstitution of RPA-covered single-stranded DNA-activated ATR-Chk1 signaling”: J. H. Choi, L. A. Lindsey-Boltz, M. Kemp, A. C. Mason, M. S. Wold, A. Sancar, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 13660–13665.
- 130“Coupling of human DNA excision repair and the DNA damage checkpoint in a defined in vitro system”: L. A. Lindsey-Boltz, M. G. Kemp, J. T. Reardon, V. DeRocco, R. R. Iyer, P. Modrich, A. Sancar, J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 5074–5082.
- 131“Mechanism of release and fate of excised oligonucleotides during nucleotide excision repair”: M. G. Kemp, J. T. Reardon, L. A. Lindsey-Boltz, A. Sancar, J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 22889–22899.
- 132“DNA excision repair: where do all the dimers go?”: M. G. Kemp, A. Sancar, Cell Cycle 2012, 11, 2997–3002.
- 133“Nucleotide excision repair in human cells: fate of the excised oligonucleotide carrying DNA damage in vivo”: J. Hu, J. H. Choi, S. Gaddameedhi, M. G. Kemp, J. T. Reardon, A. Sancar, J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 20918–20926.
- 134“Highly specific and sensitive method for measuring nucleotide excision repair kinetics of ultraviolet photoproducts in human cells”: J. H. Choi, S. Gaddameedhi, S. Y. Kim, J. Hu, M. G. Kemp, A. Sancar, Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, e 29.
- 135“DNA repair synthesis and ligation affect the processing of excised oligonucleotides generated by human nucleotide excision repair”: M. G. Kemp, S. Gaddameedhi, J. H. Choi, J. Hu, A. Sancar, J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 26574–26583.
- 136“An Integrated Approach for Analysis of the DNA Damage Response in Mammalian Cells: Nucleotide Excision Repair, DNA Damage Checkpoint, and Apoptosis”: J. H. Choi, S. Y. Kim, S. K. Kim, M. G. Kemp, A. Sancar, J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 28812–28821.
- 137“Analysis of Ribonucleotide Removal from DNA by Human Nucleotide Excision Repair”: L. A. Lindsey-Boltz, M. G. Kemp, J. Hu, A. Sancar, J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 29801–29807.
- 138“Genome-wide analysis of human global and transcription-coupled excision repair of UV damage at single-nucleotide resolution”: J. Hu, S. Adar, C. P. Selby, J. D. Lieb, A. Sancar, Genes Dev. 2015, 29, 948–960.
- 139“Evidence for lack of DNA photoreactivating enzyme in humans”: Y. F. Li, S. T. Kim, A. Sancar, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 4389–4393.
- 140“Photoreactivating enzyme from human leukocytes”: M. B. Sutherland, Nature 1974, 248, 109–112.
- 141“Initial assessment of human gene diversity and expression patterns based upon 83 million nucleotides of cDNA sequence”: M. D. Adams, A. R. Kerlavage, R. D. Fleischmann, R. A. Fuldner, C. J. Bult, N. H. Lee, E. F. Kirkness, K. G. Weinstock, J. D. Gocayne, O. White, et al., Nature 1995, 377, 3–174.
- 142“Internal timekeeping”: J. W. Schwartz, Sci. Med. 1996, 3, 44–53.
- 143“Putative blue-light photoreceptors from Arabidopsis thaliana and Sinapis alba with a high degree of sequence homology to DNA photolyase contain the two photolyase cofactors but lack DNA repair activity”: K. Malhotra, S. T. Kim, A. Batschauer, L. Dawut, A. Sancar, Biochemistry 1995, 34, 6892–6899.
- 144“Putative human blue-light photoreceptors hCRY1 and hCRY2 are flavoproteins”: D. S. Hsu, X. Zhao, S. Zhao, A. Kazantsev, R. P. Wang, T. Todo, Y. F. Wei, A. Sancar, Biochemistry 1996, 35, 13871–13877.
- 145“Vitamin B2-based blue-light photoreceptors in the retinohypothalamic tract as the photoactive pigments for setting the circadian clock in mammals”: Y. Miyamoto, A. Sancar, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 6097–6102.
- 146“A web of circadian pacemakers”: U. Schibler, P. Sassone-Corsi, Cell 2002, 111, 919–922.
- 147“Coordination of circadian timing in mammals”: S. M. Reppert, R. D. Weaver, Nature 2002, 418, 935–941.
- 148“A clockwork web: circadian timing in brain and periphery, in health and disease”: M. H. Hastings, A. B. Reddy, S. E. Maywood, Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2003, 4, 649–661.
- 149“Molecular architecture of the mammalian circadian clock”: C. L. Partch, C. B. Green, S. J. Takahashi, Trends Cell Biol. 2014, 24, 90–99.
- 150“Role of mouse cryptochrome blue-light photoreceptor in circadian photoresponses”: R. J. Thresher, M. H. Vitaterna, Y. Miyamoto, A. Kazantsev, D. S. Hsu, C. Petit, C. P. Selby, L. Dawut, O. Smithies, J. S. Takahashi, A. Sancar, Science 1998, 282, 1490–1494.
- 151“Differential regulation of mammalian period genes and circadian rhythmicity by cryptochromes 1 and 2”: M. H. Vitaterna, C. P. Selby, T. Todo, H. Niwa, C. Thompson, E. M. Fruechte, K. Hitomi, R. J. Thresher, T. Ishikawa, J. Miyazaki, J. S. Takahashi, A. Sancar, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 12114–12119.
- 152“Circadian regulation of cryptochrome genes in the mouse”: Y. Miyamoto, A. Sancar, Mol. Brain Res. 1999, 71, 238–243.
- 153“Cryptochrome: the second photoactive pigment in the eye and its role in circadian photoreception”: A. Sancar, Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2000, 69, 31–67.
- 154“Functional redundancy of cryptochromes and classical photoreceptors for nonvisual ocular photoreception in mice”: C. P. Selby, C. Thompson, T. M. Schmitz, R. N. Van Gelder, A. Sancar, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 14697–14702.
- 155“Photolyase/cryptochrome family blue-light photoreceptors use light energy to repair DNA or set the circadian clock”: A. Sancar, C. Thompson, R. J. Thresher, F. Araujo, J. Mo, S. Ozgur, E. Vagas, L. Dawut, P. C. Selby, Cold Spring Harbor Symp. Quant. Biol. 2000, 65, 157–171.
- 156“Expression of the blue-light receptor cryptochrome in the human retina”: C. L. Thompson, C. Bowes Rickman, S. J. Shaw, J. N. Ebright, U. Kelly, A. Sancar, W. D. Rickman, Invest. Ophthalmol. Visual Sci. 2003, 44, 4515–4521.
- 157“Further evidence for the role of cryptochromes in retinohypothalamic photoreception/phototransduction”: C. L. Thompson, C. P. Selby, C. L. Partch, D. T. Plante, R. J. Thresher, F. Araujo, A. Sancar, Mol. Brain Res. 2004, 122, 158–166.
- 158“Regulation of the mammalian circadian clock by cryptochrome”: A. Sancar, J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 34079–34082.
- 159“Effect of vitamin A depletion on nonvisual phototransduction pathways in cryptochromeless mice”: C. L. Thompson, C. P. Selby, R. N. Van Gelder, W. S. Blaner, J. Lee, L. Quadro, K. Lai, M. E. Gottesman, A. Sancar, J. Biol. Rhythms 2004, 19, 504–517.
- 160“Role of structural plasticity in signal transduction by the cryptochrome blue-light photoreceptor”: C. L. Partch, M. W. Clarkson, S. Ozgur, A. L. Lee, A. Sancar, Biochemistry 2005, 44, 3795–3805.
- 161“Cryptochromes and circadian photoreception in animals”: C. L. Partch, A. Sancar, Methods Enzymol. 2005, 393, 726–745.
- 162“Cryptochrome, circadian cycle, cell cycle checkpoints, and cancer”: M. A. Gauger, A. Sancar, Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 6828–6834.
- 163“Analysis of autophosphorylating kinase activities of Arabidopsis and human cryptochromes”: S. Özgür, A. Sancar, Biochemistry 2006, 45, 13369–13374.
- 164“Formation and function of flavin anion radical in cryptochrome 1 blue-light photoreceptor of monarch butterfly”: S. H. Song, N. Ozturk, T. R. Denaro, N. O. Arat, Y. T. Kao, H. Zhu, D. Zhong, S. M. Reppert, A. Sancar, J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 17608–17612.
- 165“Structure and function of animal cryptochromes”: N. Öztürk, S. H. Song, S. Özgür, C. P. Selby, L. Morrison, C. Partch, D. Zhong, A. Sancar, Cold Spring Harbor Symp. Quant. Biol. 2007, 72, 119–131.
- 166“Reaction mechanism of Drosophila cryptochrome”: N. Ozturk, C. P. Selby, Y. Annayev, D. Zhong, A. Sancar, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 516–521.
- 167“Loss of cryptochrome reduces cancer risk in p53 mutant mice”: N. Ozturk, J. H. Lee, S. Gaddameedhi, A. Sancar, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 2841–2846.
- 168“Circadian clock disruption improves the efficacy of chemotherapy through p73-mediated apoptosis”: J. H. Lee, A. Sancar, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 10668–10672.
- 169“Circadian clock, cancer, and chemotherapy”: A. Sancar, L. A. Lindsey-Boltz, S. Gaddameedhi, C. P. Selby, R. Ye, Y. Y. Chiou, M. G. Kemp, J. Hu, J. H. Lee, N. Ozturk, Biochemistry 2015, 54, 110–123.
- 170“Circadian clock control of the cellular response to DNA damage”: A. Sancar, L. A. Lindsey-Boltz, T. H. Kang, J. T. Reardon, J. H. Lee, N. Ozturk, FEBS Lett. 2010, 584, 2618–2625.
- 171“Biochemical analysis of the canonical model for the mammalian circadian clock”: R. Ye, C. P. Selby, N. Ozturk, Y. Annayev, A. Sancar, J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 25891–25902.
- 172“Dual modes of CLOCK:BMAL1 inhibition mediated by Cryptochrome and Period proteins in the mammalian circadian clock”: R. Ye, C. P. Selby, Y. Y. Chiou, I. Ozkan-Dagliyan, S. Gaddameedhi, A. Sancar, Genes Dev. 2014, 28, 1989–1998.
- 173“Circadian oscillation of nucleotide excision repair in mammalian brain”: T. H. Kang, J. T. Reardon, M. Kemp, A. Sancar, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 2864–2867.
- 174“Circadian control of XPA and excision repair of cisplatin-DNA damage by cryptochrome and HERC2 ubiquitin ligase”: T. H. Kang, L. A. Lindsey-Boltz, J. T. Reardon, A. Sancar, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 4890–4895.
- 175“Regulation of nucleotide excision repair activity by transcriptional and post-transcriptional control of the XPA protein”: T. H. Kang, J. T. Reardon, A. Sancar, Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 3176–3187.
- 176“Control of skin cancer by the circadian rhythm”: S. Gaddameedhi, C. P. Selby, W. K. Kaufmann, R. C. Smart, A. Sancar, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 18790–18795.
- 177“The circadian clock controls sunburn apoptosis and erythema in mouse skin”: S. Gaddameedhi, C. P. Selby, M. G. Kemp, R. Ye, A. Sancar, J. Invest. Dermatol. 2015, 135, 1119–1127.
- 178J. Buckingham, Chasing the Molecule, Sutton Publishing, England, 2004.
- 179“Watching DNA repair in real time”: A. Stuchebrukhov, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 19445–19446.