Photofunctional Nanomodulators for Bioexcitation
Corresponding Author
Dr. Eijiro Miyako
Nanotube Research Center (NTRC), National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST), Central 5, 1-1-1 Higashi, Tsukuba 305-8565 (Japan)
Eijiro Miyako, Nanotube Research Center (NTRC), National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST), Central 5, 1-1-1 Higashi, Tsukuba 305-8565 (Japan)
Alberto Bianco, CNRS, Institut de Biologie Moléculaire et Cellulaire, Laboratoire d'Immunopathologie et Chimie Thérapeutique, 15 Rue René Descartes, 67084 Strasbourg (France)
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Julie Russier
CNRS, Institut de Biologie Moléculaire et Cellulaire, Laboratoire d'Immunopathologie et Chimie Thérapeutique, 15 Rue René Descartes, 67084 Strasbourg (France)
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Matteo Mauro
Laboratoire de Chimie et des Biomatériaux Supramoléculaires, Institut de Science et d'Ingénierie Supramoléculaires (ISIS), Université de Strasbourg and CNRS, 8 allée Gaspard Monge, 67083 Strasbourg (France)
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Cristina Cebrian
Laboratoire de Chimie et des Biomatériaux Supramoléculaires, Institut de Science et d'Ingénierie Supramoléculaires (ISIS), Université de Strasbourg and CNRS, 8 allée Gaspard Monge, 67083 Strasbourg (France)
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Hiromu Yawo
Department of Developmental Biology and Neuroscience, Tohoku University, Graduate School of Life Sciences, Sendai 980-8577 (Japan)
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Cécilia Ménard-Moyon
CNRS, Institut de Biologie Moléculaire et Cellulaire, Laboratoire d'Immunopathologie et Chimie Thérapeutique, 15 Rue René Descartes, 67084 Strasbourg (France)
Search for more papers by this authorDr. James A. Hutchison
Laboratoire des Nanostructures, Institut de Science et d'Ingénierie Supramoléculaires (ISIS), Université de Strasbourg and CNRS, 8 allée Gaspard Monge, 67083 Strasbourg (France)
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Masako Yudasaka
Nanotube Research Center (NTRC), National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST), Central 5, 1-1-1 Higashi, Tsukuba 305-8565 (Japan)
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Sumio Iijima
Nanotube Research Center (NTRC), National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST), Central 5, 1-1-1 Higashi, Tsukuba 305-8565 (Japan)
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Luisa De Cola
Laboratoire de Chimie et des Biomatériaux Supramoléculaires, Institut de Science et d'Ingénierie Supramoléculaires (ISIS), Université de Strasbourg and CNRS, 8 allée Gaspard Monge, 67083 Strasbourg (France)
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dr. Alberto Bianco
CNRS, Institut de Biologie Moléculaire et Cellulaire, Laboratoire d'Immunopathologie et Chimie Thérapeutique, 15 Rue René Descartes, 67084 Strasbourg (France)
Eijiro Miyako, Nanotube Research Center (NTRC), National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST), Central 5, 1-1-1 Higashi, Tsukuba 305-8565 (Japan)
Alberto Bianco, CNRS, Institut de Biologie Moléculaire et Cellulaire, Laboratoire d'Immunopathologie et Chimie Thérapeutique, 15 Rue René Descartes, 67084 Strasbourg (France)
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dr. Eijiro Miyako
Nanotube Research Center (NTRC), National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST), Central 5, 1-1-1 Higashi, Tsukuba 305-8565 (Japan)
Eijiro Miyako, Nanotube Research Center (NTRC), National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST), Central 5, 1-1-1 Higashi, Tsukuba 305-8565 (Japan)
Alberto Bianco, CNRS, Institut de Biologie Moléculaire et Cellulaire, Laboratoire d'Immunopathologie et Chimie Thérapeutique, 15 Rue René Descartes, 67084 Strasbourg (France)
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Julie Russier
CNRS, Institut de Biologie Moléculaire et Cellulaire, Laboratoire d'Immunopathologie et Chimie Thérapeutique, 15 Rue René Descartes, 67084 Strasbourg (France)
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Matteo Mauro
Laboratoire de Chimie et des Biomatériaux Supramoléculaires, Institut de Science et d'Ingénierie Supramoléculaires (ISIS), Université de Strasbourg and CNRS, 8 allée Gaspard Monge, 67083 Strasbourg (France)
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Cristina Cebrian
Laboratoire de Chimie et des Biomatériaux Supramoléculaires, Institut de Science et d'Ingénierie Supramoléculaires (ISIS), Université de Strasbourg and CNRS, 8 allée Gaspard Monge, 67083 Strasbourg (France)
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Hiromu Yawo
Department of Developmental Biology and Neuroscience, Tohoku University, Graduate School of Life Sciences, Sendai 980-8577 (Japan)
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Cécilia Ménard-Moyon
CNRS, Institut de Biologie Moléculaire et Cellulaire, Laboratoire d'Immunopathologie et Chimie Thérapeutique, 15 Rue René Descartes, 67084 Strasbourg (France)
Search for more papers by this authorDr. James A. Hutchison
Laboratoire des Nanostructures, Institut de Science et d'Ingénierie Supramoléculaires (ISIS), Université de Strasbourg and CNRS, 8 allée Gaspard Monge, 67083 Strasbourg (France)
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Masako Yudasaka
Nanotube Research Center (NTRC), National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST), Central 5, 1-1-1 Higashi, Tsukuba 305-8565 (Japan)
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Sumio Iijima
Nanotube Research Center (NTRC), National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST), Central 5, 1-1-1 Higashi, Tsukuba 305-8565 (Japan)
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Luisa De Cola
Laboratoire de Chimie et des Biomatériaux Supramoléculaires, Institut de Science et d'Ingénierie Supramoléculaires (ISIS), Université de Strasbourg and CNRS, 8 allée Gaspard Monge, 67083 Strasbourg (France)
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dr. Alberto Bianco
CNRS, Institut de Biologie Moléculaire et Cellulaire, Laboratoire d'Immunopathologie et Chimie Thérapeutique, 15 Rue René Descartes, 67084 Strasbourg (France)
Eijiro Miyako, Nanotube Research Center (NTRC), National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST), Central 5, 1-1-1 Higashi, Tsukuba 305-8565 (Japan)
Alberto Bianco, CNRS, Institut de Biologie Moléculaire et Cellulaire, Laboratoire d'Immunopathologie et Chimie Thérapeutique, 15 Rue René Descartes, 67084 Strasbourg (France)
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
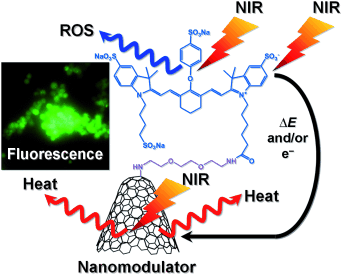
Carbon nanohorns were functionalized with a dye to develop a new type of light-driven nanomodulator. This system generates heat and reactive oxygen species (ROS) under biologically transparent near-infrared (NIR) laser irradiation. These properties can be applied for single-cell analyses and innovative cell therapies.
Abstract
A single organism comprises diverse types of cells. To acquire a detailed understanding of the biological functions of each cell, comprehensive control and analysis of homeostatic processes at the single-cell level are required. In this study, we develop a new type of light-driven nanomodulator comprising dye-functionalized carbon nanohorns (CNHs) that generate heat and reactive oxygen species under biologically transparent near-infrared (NIR) laser irradiation. By exploiting the physicochemical properties of the nanohorns, cellular calcium ion flux and membrane currents were successfully controlled at the single-cell level. In addition, the nanomodulator allows a remote bioexcitation of tissues during NIR laser exposure making this system a powerful tool for single-cell analyses and innovative cell therapies.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie_201407169_sm_1.avi30.8 MB | 1 |
| anie_201407169_sm_2.avi37.2 MB | 2 |
| anie_201407169_sm_3.avi21.9 MB | 3 |
| anie_201407169_sm_4.avi30.7 MB | 4 |
| anie_201407169_sm_miscellaneous_information.pdf1.6 MB | miscellaneous_information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1B. Alberts, D. Bray, K. Hopkin, A. Johnson, J. Lewis, M. Raff, K. Roberts, P. Walter, Essential Cell Biology, 3rd ed., Garland, New York, 2009.
- 2C. Kasper, Eng. Life Sci. 2009, 9, 407.
10.1002/elsc.200990014 Google Scholar
- 3H. Yawo, T. Asano, S. Sakai, T. Ishizuka, Dev. Growth Differ. 2013, 55, 474–490.
- 4V. Gradinaru, M. Mogri, K. R. Thompson, J. M. Henderson, K. Deisseroth, Science 2009, 324, 354–359.
- 5H. Ye, M. D. E. Baba, R.-W. Peng, M. Fussenegger, Science 2011, 332, 1565–1568.
- 6G. Leitz, E. Fällman, S. Tuck, O. Axner, Biophys. J. 2002, 82, 2224–2231.
- 7M. G. Shapiro, K. Homma, S. Villarreal, C.-P. Richter, F. Bezanilla, Nat. Commun. 2011, 3, 736.
- 8R. Weissleder, Nat. Biotechnol. 2001, 19, 316–317.
- 9E. Miyako, K. Kono, E. Yuba, C. Hosokawa, H. Nagai, Y. Hagihara, Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 1226.
- 10E. Miyako, T. Deguchi, Y. Nakajima, M. Yudasaka, Y. Hagihara, M. Horie, M. Shichiri, Y. Higuchi, F. Yamashita, M. Hashida, Y. Shigeri, Y. Yoshida, S. Iijima, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 7523–7528.
- 11K. Kostarelos, L. Lacerda, G. Pastorin, W. Wu, S. Wieckowski, J. Luangsivilay, S. Godefroy, D. Pantarotto, J. P. Briand, S. Muller, M. Prato, A. Bianco, Nat. Nanotechnol. 2007, 2, 108–113.
- 12S. Lacotte, A. García, M. Décossas, W. T. Al-Jamal, S. Li, K. Kostarelos, S. Muller, M. Prato, H. Dumortier, A. Bianco, Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 2421–2426.
- 13M. Zhang, M. Yudasaka, K. Ajima, J. Miyawaki, S. Iijima, ACS Nano 2007, 1, 265–272.
- 14G. Pagona, G. E. Zervaki, A. S. D. Sandanayaka, O. Ito, G. Charalambidis, T. Hasobe, A. G. Coutsolelos, N. Tagmatarchis, J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 9439–9449.
- 15V. L. Colvin, Nat. Biotechnol. 2003, 21, 1166–1170.
- 16A. S. D. Sandanayaka, O. Ito, M. Zhang, K. Ajima, S. Iijima, M. Yudasaka, T. Murakami, K. Tsuchida, Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 4366–4371.
- 17M. Mitsunaga, M. Ogawa, N. Kosaka, L. T. Rosenblum, P. L. Choyke, H. Kobayashi, Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 1685–1691.
- 18X. Peng, D. R. Draney, W. M. Volcheck, G. R. Bashford, D. T. Lamb, D. L. Grone, Y. Zhang, C. M. Johnson, Proc. SPIE-Int. Soc. Opt. Eng. 2006, 6097, 113–124.
- 19J. Yu, D. Javier, M. A. Yaseen, N. Nitin, R. Richards-Kortum, B. Anvari, M. S. Wong, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 1929–1938.
- 20Y. Yan, C.-L. Wei, W.-R. Zhang, H.-P. Cheng, J. Liu, Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2006, 27, 821–826.
- 21R. P. Rastogi, S. P. Singh, D. P. Häder, R. P. Sinha, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 397, 603–607.
- 22K. Mizuno, J. Ishii, H. Kishida, Y. Hayamizu, S. Yasuda, D. N. Futaba, M. Yumura, K. Hata, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 6044–6047.
- 23M. Halasi, M. Wang, T. S. Chavan, V. Gaponenko, N. Hay, A. L. Gartel, Biochem. J. 2013, 454, 201–208.
- 24S. Falk, J. C. Rekling, Neurosci. Lett. 2009, 450, 229–234.
- 25D. Wu, W. Huang, P. M. Richardson, J. V. Priestley, M. Liu, J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 416–426.
- 26M. A. Gandini, A. Sandoval, R. Felix, Cold Spring Harbor Protoc. 2014, 4.
- 27T. Bruegmann, D. Malan, M. Hesse, T. Beiert, C. J. Fuegemann, B. K. Fleischmann, P. Sasse, Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 897–900.
- 28M. Ohkita, S. Saito, T. Imagawa, K. Takahashi, M. Tominaga, T. Ohta, J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 2388–2397.