Converting Molecular Monolayers into Functional Membranes
Graphical Abstract
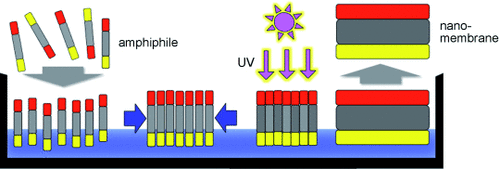
Carbon nanomembranes are constructed from monolayers of molecular amphiphiles assembled on a water surface. The floating molecular film is cross-linked to form a mechanically stable nanomembrane. By varying the type of molecules, the surface area, and the exposure condition, the membrane's stiffness, thickness, and permeability can be tailored.