Palladium Nanoparticles Embedded in the Inner Surfaces of Carbon Nanotubes: Synthesis, Catalytic Activity, and Sinter Resistance†
This work is financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21203214, 21133010, 21261160487, 51221264), the National Basic Research Program (973 Program, No. 2011CBA00504), the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Grant No. XDA09030103, and the Sinopec China No. 21203214.
Graphical Abstract
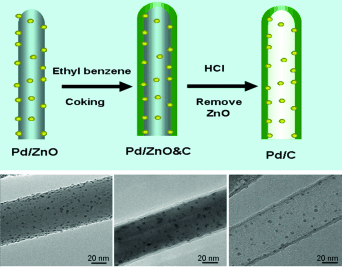
Inside out: A facile and versatile synthesis using a template-based procedure gives Pd nanoparticles uniformly embedded in the inner surfaces of carbon nanotubes (see picture). The nanocomposite is catalytically more active and sinter-resistant, than traditional carbon-nanotube-supported Pd catalysts.
Abstract
The highly efficient preparation of metal nanoparticles embedded in a carbon nanotube remains a considerable challenge. Herein, we report a simple and template-based procedure for the fabrication of carbon nanotubes with Pd nanoparticles uniformly embedded in the inner carbon surfaces. In addition to the novel structure, the sinter-resistance of the as-prepared Pd/C nanocomposite was much better than that of the traditional carbon-nanotube-supported Pd catalysts. The as-prepared Pd/C nanocomposite has a high recyclability in a liquid-phase Suzuki coupling reaction. This strategy may be extended as a general approach to prepare metal nanoparticles supported on carbon-nanotubes.