TiO2 Hollow Spheres Composed of Highly Crystalline Nanocrystals Exhibit Superior Lithium Storage Properties†
This work was financially supported by the Singapore National Research Foundation under its Campus for Research Excellence and Technological Enterprise (CREATE) program.
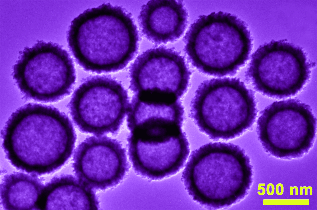
Graphical Abstract
Empty vessels: Anatase TiO2 hollow spheres composed of highly crystalline nanocrystals are prepared by a simple two-step template strategy. They exhibit superior lithium storage properties in terms of long-term cycling stability and an excellent rate capability which benefits from many structural features, including a hollow interior, small size, high crystallinity of primary nanocrystals, and shell robustness.
Abstract
While the synthesis of TiO2 hollow structures is well-established, in most cases it is particularly difficult to control the crystallization of TiO2 in solution or by calcination. As a result, TiO2 hollow structures do not really exhibit enhanced lithium storage properties. Herein, we report a simple and cost-effective template-assisted method to synthesize anatase TiO2 hollow spheres composed of highly crystalline nanocrystals, in which carbonaceous (C) spheres are chosen as the removable template. The release of gaseous species from the combustion of C spheres may inhibit the growth of TiO2 crystallites so that instead small TiO2 nanocrystals are generated. The small size and high crystallinity of primary TiO2 nanoparticles and the high structural integrity of the hollow spheres gives rise to significant improvements in the cycling stability and rate performance of the TiO2 hollow spheres.