Angiopep-Conjugated Electro-Responsive Hydrogel Nanoparticles: Therapeutic Potential for Epilepsy†
This study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81202478, 91332202, 81221003), the Program for Zhejiang Leading Team of S&T Innovation (2011R50014), the Public Welfare Project of the Zhejiang province (2013C33G2010274), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, China (2013QNA7013).
Graphical Abstract
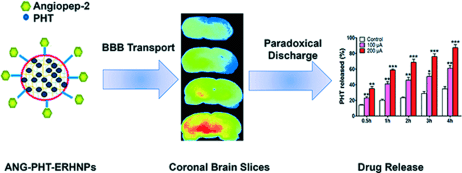
Smart vesicles: Electro-responsive hydrogel nanoparticles (ERHNPs) modified with angiopep-2 (ANG) were loaded with the antiepileptic drug phenytoin sodium (PHT). The complex ANG-PHT-ERHNPs can easily transport the drug into the brain and a fast release could be achieved by the application of an electric field, leading to a reduction of the severity of the seizure onset.
Abstract
A safe and effective therapy for epilepsy requires a drug delivery system that can penetrate the blood–brain barrier and subsequently release antiepileptic drugs rapidly to suppress neuronal discharges in a timely manner. We have developed electro-responsive hydrogel nanoparticles (ERHNPs) modified with angiopep-2 (ANG) to facilitate the delivery of the antiepileptic drug phenytoin sodium. The resulting ANG-ERHNPs had an average diameter of (102.3±16.8) nm and were electro-sensitive with regard to particle size and drug release in vitro. ANG-ERHNPs have the characteristics of penetrate the BBB easily, resulting in a higher distribution in the central system. The improved antiepileptic effects were investigated with the amygdala kindling model. The results demonstrate that the ANG-ERHNPs were able to transport antiepileptic drugs into the brain and release them under electroencephalograph epileptiform abnormalities to greatly improve the therapeutic index of existing drugs in clinical use.