A Co-catalyst-Loaded Ta3N5 Photoanode with a High Solar Photocurrent for Water Splitting upon Facile Removal of the Surface Layer†
Mingxue Li
Ecomaterials and Renewable Energy Research Center, National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures, Department of Physics, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093 (P. R. China)
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dr. Wenjun Luo
Ecomaterials and Renewable Energy Research Center, National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures, Department of Physics, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093 (P. R. China)
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Ecomaterials and Renewable Energy Research Center, National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures, Department of Physics, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093 (P. R. China)Search for more papers by this authorDapeng Cao
College of Engineering and Applied Science, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093 (P. R. China)
Search for more papers by this authorXin Zhao
Ecomaterials and Renewable Energy Research Center, National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures, Department of Physics, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093 (P. R. China)
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Zhaosheng Li
College of Engineering and Applied Science, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093 (P. R. China)
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Tao Yu
Ecomaterials and Renewable Energy Research Center, National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures, Department of Physics, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093 (P. R. China)
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Zhigang Zou
Ecomaterials and Renewable Energy Research Center, National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures, Department of Physics, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093 (P. R. China)
Ecomaterials and Renewable Energy Research Center, National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures, Department of Physics, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093 (P. R. China)Search for more papers by this authorMingxue Li
Ecomaterials and Renewable Energy Research Center, National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures, Department of Physics, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093 (P. R. China)
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Dr. Wenjun Luo
Ecomaterials and Renewable Energy Research Center, National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures, Department of Physics, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093 (P. R. China)
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Ecomaterials and Renewable Energy Research Center, National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures, Department of Physics, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093 (P. R. China)Search for more papers by this authorDapeng Cao
College of Engineering and Applied Science, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093 (P. R. China)
Search for more papers by this authorXin Zhao
Ecomaterials and Renewable Energy Research Center, National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures, Department of Physics, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093 (P. R. China)
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Zhaosheng Li
College of Engineering and Applied Science, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093 (P. R. China)
Search for more papers by this authorProf. Tao Yu
Ecomaterials and Renewable Energy Research Center, National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures, Department of Physics, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093 (P. R. China)
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Zhigang Zou
Ecomaterials and Renewable Energy Research Center, National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures, Department of Physics, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093 (P. R. China)
Ecomaterials and Renewable Energy Research Center, National Laboratory of Solid State Microstructures, Department of Physics, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210093 (P. R. China)Search for more papers by this authorThis work is supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program, 2013CB632404) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 50902068, 51272101, 11174129). M. Li. is also supported by the Science Research Foundation of Graduate School of Nanjing University. We thank Mr. Robert Rozansky of Brown University for his editing of English.
Graphical Abstract
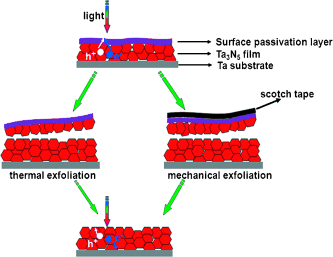
Surface exfoliation: A Ta3N5 photoanode prepared by a thermal oxidation and nitridation method shows a high solar photocurrent. This photocurrent is currently the highest achieved by a Ta3N5 photoanode. The photocurrent is obtained mainly because of facile thermal and mechanical exfoliation of the surface passivation layer of the Ta3N5 photoanode (see picture).
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie_201305350_sm_miscellaneous_information.pdf1,008.4 KB | miscellaneous_information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1G. W. Crabtree, M. S. Dresselhaus, M. V. Buchanan, Phys. Today 2004, 57, 39–44.
- 2A. Fujishima, K. Honda, Nature 1972, 238, 37–38.
- 3A. B. Murphy, P. R. F. Barnes, L. K. Randeniya, I. C. Plumb, I. E. Grey, M. D. Horne, J. A. Glasscock, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2006, 31, 1999–2017.
- 4W. Shockley, H. J. Queisser, J. Appl. Phys. 1961, 32, 510–519.
- 5M. G. Walter, E. L. Warren, J. R. McKone, S. W. Boettcher, Q. Mi, E. A. Santori, N. S. Lewis, Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 6446–6473.
- 6A. J. Nozik, Appl. Phys. Lett. 1976, 29, 150–153.
- 7Y. Hou, B. L. Abrams, P. C. K. Vesborg, M. E. Björketun, K. Herbst, L. Bech, A. M. Setti, C. D. Damsgaard, T. Pedersen, O. Hansen, J. Rossmeisl, S. Dahl, J. K. Nørskov, I. Chorkendorff, Nat. Mater. 2011, 10, 434–438.
- 8S. W. Boettcher, E. L. Warren, M. C. Putnam, E. A. Santori, D. Tuner-Evans, M. D. Kelzenberg, M. G. Walter, J. R. McKone, B. S. Brunschwig, H. A. Atwater, N. S. Lewis, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 1216–1219.
- 9B. Seger, A. B. Laursen, P. C. K. Vesborg, T. Pedersen, O. Hansen, S. Dahl, I. Chorkendoff, Angew. Chem. 2012, 124, 9262–9265; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 9128–9131.
- 10M. H. Lee, K. Takei, J. Zhang, R. Kapadia, M. Zheng, Y. Chen, J. Nah, T. S. Matthews, Y. Chueh, J. W. Ager, A. Javey, Angew. Chem. 2012, 124, 10918–10922; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 10760–10764.
- 11B. D. Alexander, P. J. Kulesza, I. Rutkowska, R. Solarska, J. Augustynski, J. Mater. Chem. 2008, 18, 2298–2303.
- 12N. Gaillard, B. Cole, J. Kaneshiro, E. L. Miller, B. Marsen, L. Weinhardt, M. Bär, C. Heske, K.-S. Ahn, Y. Yan, M. M. Al-Jassim, J. Mater. Res. 2010, 25, 45–51.
- 13W. Luo, Z. Yang, Z. Li, J. Zhang, J. Liu, Z. Zhao, Z. Wang, S. Yan, T. Yu, Z. Zou, Energy Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 4046–4051.
- 14Y. Park, K. J. McDonald, K. S. Choi, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 2321–2337.
- 15Z. S. Li, W. J. Luo, M. L. Zhang, J. Y. Feng, Z. G. Zou, Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 347–370.
- 16S. D. Tilley, M. Cornuz, K. Sivula, M. Grätzel, Angew. Chem. 2010, 122, 6549–6552;
10.1002/ange.201003110 Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 6405–6408.
- 17K. Sivula, F. L. Formal, M. Grätzel, ChemSusChem 2011, 4, 432–449.
- 18A. Ishikawa, T. Takata, J. N. Kondo, M. Hara, K. Domen, J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 11049–11053.
- 19M. Higashi, K. Domen, R. Abe, Energy Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 4138–4147.
- 20M. Liao, J. Feng, W. Luo, Z. Wang, J. Zhang, Z. Li, T. Yu, Z. Zou, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 3066–3074.
- 21B. A. Pinaud, P. C. K. Vesborg, T. F. Jaramillo, J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 15918–15924.
- 22Y. Cong, H. S. Park, H. X. Dang, F. F. Fan, A. J. Bard, C. B. Mullins, Chem. Mater. 2012, 24, 579–586.
- 23Y. Cong, H. S. Park, S. Wang, H. X. Dang, F.-R. F. Fan, C. B. Mullins, A. J. Bard, J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 14541–14550.
- 24Y. Li, T. Takata, D. Cha, K. Takanabe, T. Minegishi, J. Kubota, K. Domen, Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 125–131.
- 25Y. Lin, Y. Xu, M. T. Mayer, Z. I. Simpson, G. McMahon, S. Zhou, D. Wang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 5508–5511.
- 26S. J. Moon, W. W. So, H.-Y. Chang, J. Electrochem. Soc. 2001, 148, E 378–E381.
- 27Y. Jin, J. Y. Song, S.-H. Jeong, J. W. Kim, T. G. Lee, J. H. Kim, J. Hahn, J. Mater. Res. 2010, 25, 1080–1086.
- 28F. Le Formal, N. Tétreault, M. Cornuz, T. Moehl, M. Grätzel, K. Sivula, Chem. Sci. 2011, 2, 737–743.
- 29B. Klahr, S. Gimenez, F. Fabregat-Santiago, T. Hamann, J. Bisquert, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 4294–4302.
- 30H. Shin, S. Y. Park, S. T. Bae, S. Lee, K. S. Hong, H. S. Jung, J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 104, 116108.
- 31M. Li, W. Luo, B. Liu, X. Zhao, Z. Li, D. Chen, T. Yu, Z. Xie, R. Zhang, Z. Zou, Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 99, 112108.
- 32W. J. Luo, Z. S. Li, T. Yu, Z. G. Zou, J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 5076–5081.
- 33C. Zhen, L. Wang, G. Liu, G. Q. Lu, H. Cheng, Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 3019–3021.
- 34R. Saito, Y. Miseki, K. Sayama, Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 3833.
- 35J. A. Seabold, K. Choi, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 2186.