Tuning Nanoparticle Catalysis for the Oxygen Reduction Reaction
Dr. Shaojun Guo
Department of Chemistry, Brown University, Providence, RI 02912 (USA)
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorSen Zhang
Department of Chemistry, Brown University, Providence, RI 02912 (USA)
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Shouheng Sun
Department of Chemistry, Brown University, Providence, RI 02912 (USA)
Department of Chemistry, Brown University, Providence, RI 02912 (USA)Search for more papers by this authorDr. Shaojun Guo
Department of Chemistry, Brown University, Providence, RI 02912 (USA)
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorSen Zhang
Department of Chemistry, Brown University, Providence, RI 02912 (USA)
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Shouheng Sun
Department of Chemistry, Brown University, Providence, RI 02912 (USA)
Department of Chemistry, Brown University, Providence, RI 02912 (USA)Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
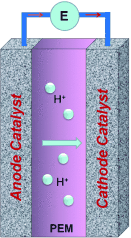
Efforts in searching for efficient nanoparticle catalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) in fuel cells have led to various nanoparticle (NP) systems with precise control of size, shape, composition, and structure. Whereas the traditional Pt-based catalysts are still under heavy investigation, recent studies have led to the emergence of non-Pt systems. This Review highlights the recent efforts in developing Pt- and non-Pt-based NPs into advanced nanocatalysts for the ORR.
Abstract
Advances in chemical syntheses have led to the formation of various kinds of nanoparticles (NPs) with more rational control of size, shape, composition, structure and catalysis. This review highlights recent efforts in the development of Pt and non-Pt based NPs into advanced nanocatalysts for efficient oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) under fuel-cell reaction conditions. It first outlines the shape controlled synthesis of Pt NPs and their shape-dependent ORR. Then it summarizes the studies of alloy and core–shell NPs with controlled electronic (alloying) and strain (geometric) effects for tuning ORR catalysis. It further provides a brief overview of ORR catalytic enhancement with Pt-based NPs supported on graphene and coated with an ionic liquid. The review finally introduces some non-Pt NPs as a new generation of catalysts for ORR. The reported new syntheses with NP parameter-tuning capability should pave the way for future development of highly efficient catalysts for applications in fuel cells, metal-air batteries, and even in other important chemical reactions.
References
- 1R. Borup, J. Meyers, B. Pivovar, Y. S. Kim, R. Mukundan, N. Garland, D. Myers, M. Wilson, F. Garzon, D. Wood, P. Zelenay, K. More, K. Stroh, T. Zawodzinski, J. Boncella, J. E. McGrath, M. Inaba, K. Miyatake, M. Hori, K. Ota, Z. Ogumi, S. Miyata, A. Nishikata, Z. Siroma, Y. Uchimoto, K. Yasuda, K. Kimijima, N. Iwashita, Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 3904–3951.
- 2Y.-J. Wang, D. P. Wilkinson, J. Zhang, Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 7625–7651.
- 3Z. Chen, D. Higgins, A. Yu, L. Zhang, J. Zhang, Energy Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 3167–3192.
- 4Y. Bing, H. Liu, L. Zhang, D. Ghosh, J. Zhang, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 2184–2202.
- 5D. S. Su, G. Sun, Angew. Chem. 2011, 123, 11774–11777; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 11570–11572.
- 6J. Chen, B. Lim, E. P. Lee, Y. Xia, Nano Today 2009, 4, 81–95.
- 7S. Guo, E. Wang, Nano Today 2011, 6, 240–264.
- 8Z. Chen, M. Waje, W. Li, Y. Yan, Angew. Chem. 2007, 119, 4138–4141; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 4060–4063.
- 9C. Koenigsmann, A. C. Santulli, K. Gong, M. B. Vukmirovic, W.-P. Zhou, E. Sutter, S. S. Wong, R. R. Adzic, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 9783–9795.
- 10C. Koenigsmann, E. Sutter, T. A. Chiesa, R. R. Adzic, S. S. Wong, Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 2013–2020.
- 11C. Koenigsmann, E. Sutter, R. R. Adzic, S. S. Wong, J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 15297–15306.
- 12S. Sun, G. Zhang, D. Geng, Y. Chen, R. Li, M. Cai, X. Sun, Angew. Chem. 2011, 123, 442–446; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 422–426.
- 13U.S.D.O. Energy, http://www1.eere.energy.gov/hydrogenandfuelcells/mypp/pdfs/fuel_cells.pdf.
- 14
- 14aM. R. Tarasevich, A. Sadkowski, E. Yeager, Comprehensive Treatise of Electrochemistry, Vol. 7 (Eds.: ), Plenum, New York, 1983, pp. 301;
10.1007/978-1-4613-3584-9_6 Google Scholar
- 14bD. Yu, E. Nagelli, F. Du, L. Dai, J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2010, 1, 2165–2173;
- 14cJ. Zhang, K. Sasaki, E. Sutter, R. R. Adzic, Science 2007, 315, 220–222.
- 15Y. Zheng, Y. Jiao, M. Jaroniec, Y. Jin, S. Z. Qiao, Small 2012, 8, 3550–3566.
- 16J. K. Nørskov, J. Rossmeisl, A. Logadottir, L. Lindqvist, J. R. Kitchin, T. Bligaard, H. Jónsson, J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 17886–17892.
- 17H. A. Gasteiger, S. S. Kocha, B. Sompalli, F. T. Wagner, Appl. Catal. B 2005, 56, 9–35.
- 18“Rotating thin-film method for supported catalysts”: T. J. Schmidt, H. A. Gasteiger, Handbook of Fuel Cells-Fundamentals, Technology and Applications, Vol. 2 (Eds.: ), John Wiley & Sons, New York, 2003, pp. 316–333.
- 19F. Gloaguen, P. Convert, S. Gamburzev, O. A. Velev, S. Srinivasan, Electrochim. Acta 1998, 43, 3767–3772.
- 20J. Perez, E. R. Gonzalez, E. A. Ticianelli, Electrochim. Acta 1998, 44, 1329–1339.
- 21B. Lim, M. Jiang, P. H. C. Camargo, E. C. Cho, J. Tao, X. Lu, Y. Zhu, Y. Xia, Science 2009, 324, 1302–1305.
- 22T. J. Schmidt, H. A. Gasteiger, G. D. Stäb, P. M. Urban, D. M. Kolb, R. J. Behm, J. Electrochem. Soc. 1998, 145, 2354–2358.
- 23S. Wang, D. Yu, L. Dai, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 5182–5185.
- 24S. Wang, D. Yu, L. Dai, D. W. Chang, J.-B. Baek, ACS Nano 2011, 5, 6202–6209.
- 25
- 25aM. L. Sattler, P. N. Ross, Ultramicroscopy 1986, 20, 21–28;
- 25bK. J. Kinoshita, J. Electrochem. Soc. 1990, 137, 845–848.
- 26V. Mazumder, Y. Lee, S. Sun, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2010, 20, 1224–1231.
- 27Y. Xia, Y. Xiong, B. Lim, S. E. Skrabalak, Angew. Chem. 2008, 121, 62–108; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 48, 60–103.
- 28
- 28aT. S. Ahmadi, Z. L. Wang, T. C. Green, A. Henglein, M. A. El-Sayed, Science 1996, 272, 1924–1926;
- 28bJ. M. Petroski, Z. L. Wang, T. C. Green, M. A. El-Sayed, J. Phys. Chem. B 1998, 102, 3316–3320.
- 29C. Wang, H. Daimon, T. Onodera, T. Koda, S. Sun, Angew. Chem. 2008, 120, 3644–3647; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 3588–3591.
- 30C. Wang, H. Daimon, Y. Lee, J. Kim, S. Sun, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 6974–6975.
- 31N. Tian, Z.-Y. Zhou, S.-G. Sun, Y. Ding, Z. L. Wang, Science 2007, 316, 732–735.
- 32T. Yu, D. Y. Kim, H. Zhang, Y. Xia, Angew. Chem. 2011, 123, 2825–2829; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 2773–2777.
- 33B. Lim, X. Lu, M. Jiang, P. H. C. Camargo, E. C. Cho, E. P. Lee, Y. Xia, Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 4043–4047.
- 34V. R. Stamenkovic, B. Fowler, B. S. Mun, G. F. Wang, P. N. Ross, C. A. Lucas, N. M. Markovic, Science 2007, 315, 493–497.
- 35
- 35aC. Wang, N. M. Markovic, V. R. Stamenkovic, ACS Catal. 2012, 2, 891–898;
- 35bJ. Greeley, I. E. L. Stephens, A. S. Bondarenko, T. P. Johansson, H. A. Hansen, T. F. Jaramillo, J. Rossmeisl, I. Chorkendorff, J. K. Nørskov, Nat. Chem. 2009, 1, 552–556.
- 36V. R. Stamenkovic, B. S. Mun, M. Arenz, K. J. J. Mayrhofer, C. A. Lucas, G. F. Wang, P. N. Ross, N. M. Markovic, Nat. Mater. 2007, 6, 241–247.
- 37
- 37aS. H. Sun, C. B. Murray, D. Weller, L. Folks, A. Moser, Science 2000, 287, 1989–1992;
- 37bM. Chen, J. Kim, J. P. Liu, H. Y. Fan, S. H. Sun, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 7132–7133;
- 37cS. Sun, S. Anders, T. Thomson, J. E. E. Baglin, M. F. Toney, H. F. Hamann, C. B. Murray, B. D. Terris, J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 5419–5425;
- 37dC. Liu, X. Wu, T. Klemmer, N. Shukla, X. Yang, D. Weller, J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 6121;
- 37eS. H. Sun, Adv. Mater. 2006, 18, 393–403;
- 37fJ. Kim, C. Rong, J. P. Liu, S. Sun, Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 906–909;
- 37gC. Xu, Z. Yuan, N. Kohler, J. Kim, M. A. Chung, S. Sun, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 15346–15351;
- 37hS. Guo, S. Zhang, X. Sun, S. Sun, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 15354–15357;
- 37iS. Zhang, S. Guo, H. Zhu, D. Su, S. Sun, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 5060–5063.
- 38See Ref. [27].
- 39aE. V. Shevchenko, D. V. Talapin, H. Schnablegger, A. Kornowski, O. Festin, P. Svedlindh, M. Haase, H. Weller, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 9090–9101;
- 39bJ.-I. Park, J. Cheon, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 5743–5746.
- 40aK. Ono, R. Okuda, Y. Ishii, S. Kamimura, M. Oshima, J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 1941–1942;
- 40bD. C. Lee, A. Ghezelbash, C. A. Stowell, B. A. Korgel, J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 20906–20911;
- 40cD. C. Lee, D. K. Smith, A. T. Heitsch, B. A. Korgel, Annu. Rep. Prog. Chem. Sect. C 2007, 103, 351–402;
- 40dY. Kang, C. B. Murray, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 7568–7569.
- 41Y. Liu, D. Li, S. Sun, J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 12579–12587.
- 42
- 42aJ. Wu, A. Gross, H. Yang, Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 798–802;
- 42bJ. Zhang, J. Fang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 18543–18547;
- 42cJ. Zhang, H. Yang, J. Fang, S. Zou, Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 638–644;
- 42dD. Xu, S. Bliznakov, Z. Liu, J. Fang, N. Dimitrov, Angew. Chem. 2010, 122, 1304–1307; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 1282–1285;
- 42eD. Xu, Z. Liu, H. Yang, Q. Liu, J. Zhang, J. Fang, S. Zou, K. Sun, Angew. Chem. 2009, 121, 4281–4285; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 4217–4221;
- 42fH. Yang, J. Zhang, K. Sun, S. Zou, J. Fang, Angew. Chem. 2010, 122, 7000–7003; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 6848–6851.
- 43
- 43aF. J. Perez-Alonso, D. N. McCarthy, A. Nierhoff, P. Hernandez-Fernandez, C. Strebel, I. E. L. Stephens, J. H. Nielsen, I. Chorkendorff, Angew. Chem. 2012, 124, 4719–4721;
10.1002/ange.201200586 Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 4641–4643;
- 43bI. N. Leontyev, S. V. Belenov, V. E. Guterman, P. Haghi-Ashtiani, A. P. Shaganov, B. Dkhil, J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 5429–5434.
- 44C. Wang, D. van der Vliet, K.-C. Chang, H. You, D. Strmcnik, J. A. Schlueter, N. M. Markovic, V. R. Stamenkovic, J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 19365–19368.
- 45C. Wang, G. Wang, D. van der Vliet, K.-C. Chang, N. M. Markovica, V. R. Stamenkovic, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2010, 12, 6933–6939.
- 46C. Wang, M. Chi, D. Li, D. van der Vliet, G. Wang, Q. Lin, J. F. Mitchell, K. L. More, N. M. Markovic, V. R. Stamenkovic, ACS Catal. 2011, 1, 1355–1359.
- 47W. Chen, J. Kim, S. Sun, S. Chen, J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 3891–3898.
- 48C. Wang, M. Chi, G. Wang, D. van der Vliet, D. Li, K. More, H.-H. Wang, J. A. Schlueter, N. M. Markovic, V. R. Stamenkovic, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2011, 21, 147–152.
- 49M. K. Carpenter, T. E. Moylan, R. S. Kukreja, M. H. Atwan, M. M. Tessema, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 8535–8542.
- 50
- 50aY. Wu, S. Cai, D. Wang, W. He, Y. Li, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 8975–8981;
- 50bC. Cui, L. Gan, H.-H. Li, S.-H. Yu, M. Heggen, P. Strasser, Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 5885–5889.
- 51See Ref. [42c].
- 52J. Wu, J. Zhang, Z. Peng, S. Yang, F. T. Wagner, H. Yang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 4984–4985.
- 53J. Wu, L. Qi, H. You, A. Gross, J. Li, H. Yang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 11880–11883.
- 54V. R. Stamenkovic, B. S. Mun, K. J. J. Mayrhofer, P. N. Ross, N. M. Markovic, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 8813–8819.
- 55V. Stamenkovic, B. S. Mun, K. J. J. Mayrhofer, P. N. Ross, N. M. Markovic, J. Rossmeisl, J. Greeley, J. K. Norskov, Angew. Chem. 2006, 118, 2963–2967;
10.1002/ange.200504386 Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 2897–2901.
- 56J. Kim, Y. Lee, S. Sun, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 4996–4997.
- 57J. Zhang, Y. Mo, M. B. Vukmirovic, R. Klie, K. Sasaki, R. R. Adzic, J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 10955–10964.
- 58K. Sasaki, H. Naohara, Y. Cai, Y. M. Choi, P. Liu, M. B. Vukmirovic, J. X. Wang, R. R. Adzic, Angew. Chem. 2010, 122, 8784–8789; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 8602–8607.
- 59
- 59aW.-P. Zhou, K. Sasaki, D. Su, Y. Zhu, J. X. Wang, R. R. Adzic, J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 8950–8957;
- 59bJ. X. Wang, H. Inada, L. Wu, Y. Zhu, Y. Choi, P. Liu, W.-P. Zhou, R. R. Adzic, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 17298–17302;
- 59cD. Wang, H. L. Xin, H. Wang, Y. Yu, E. Rus, D. A. Muller, F. J. DiSalvo, H. D. Abruña, Chem. Mater. 2012, 24, 2274–2281.
- 60K. A. Kuttiyiel, K. Sasaki, Y. Choi, D. Su, P. Liu, R. R. Adzic, Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 5297–5304.
- 61T. Ghosh, M. B. Vukmirovic, F. J. DiSalvo, R. R. Adzic, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 906–907.
- 62H. I. Karan, K. Sasaki, K. Kuttiyiel, C. A. Farberow, M. Mavrikakis, R. R. Adzic, ACS Catal. 2012, 2, 817–824.
- 63K. Gong, D. Su, R. R. Adzic, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 14364–14366.
- 64
- 64aJ. Zhang, M. B. Vukmirovic, K. Sasaki, A. U. Nilekar, M. Mavrikakis, R. R. Adzic, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 12480–12481;
- 64bR. R. Adzic, J. Zhang, K. Sasaki, M. B. Vukmirovic, M. Shao, J. X. Wang, A. U. Nilekar, M. Mavrikakis, J. A. Valerio, F. Uribe, Top. Catal. 2007, 46, 249–262.
- 65V. Mazumder, M. Chi, K. L. More, S. Sun, Angew. Chem. 2010, 122, 9558–9562;
10.1002/ange.201003903 Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 9368–9372.
- 66J. Zhang, Y. Tang, K. Lee, M. Ouyang, Science 2010, 327, 1634–1638.
- 67V. Mazumder, M. Chi, K. L. More, S. Sun, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 7848–7849.
- 68V. Mazumder, S. Sun, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 4588–4589.
- 69C. Wang, D. van der Vliet, K. L. More, N. J. Zaluzec, S. Peng, S. Sun, H. Daimon, G. Wang, J. Greeley, J. Pearson, A. P. Paulikas, G. Karapetrov, D. Strmcnik, N. M. Markovic, V. R. Stamenkovic, Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 919–926.
- 70V. Komanicky, K. C. Chang, A. Menzel, N. M. Markovic, H. You, X. Wang, D. Myers, J. Electrochem. Soc. 2006, 153, B 446–B451.
- 71H. You, D. J. Zurawski, Z. Nagy, R. M. Yonco, J. Chem. Phys. 1994, 100, 4699–4702.
- 72J. Yang, X. Chen, X. Yang, J. Y. Ying, Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 8976–8981.
- 73P. Strasser, S. Koh, T. Anniyev, J. Greeley, K. More, C. Yu, Z. Liu, S. Kaya, D. Nordlund, H. Ogasawara, M. F. Toney, A. Nilsson, Nat. Chem. 2010, 2, 454–460.
- 74R. Srivastava, P. Mani, N. Hahn, P. Strasser, Angew. Chem. 2007, 119, 9146–9149;
10.1002/ange.200703331 Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 8988–8991.
- 75S. Koh, P. Strasser, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 12624–12625.
- 76P. Mani, R. Srivastava, P. Strasser, J. Power Sources 2011, 196, 666–673.
- 77
- 77aC. Wang, M. Chi, D. Li, D. Strmcnik, D. van der Vliet, G. Wang, V. Komanicky, K.-C. Chang, A. P. Paulikas, D. Tripkovic, J. Pearson, K. L. More, N. M. Markovic, V. R. Stamenkovic, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 14396–14403;
- 77bL. Gan, M. Heggen, S. Rudi, P. Strasser, Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 5423–5430.
- 78K. J. J. Mayrhofer, V. Juhart, K. Hartl, M. Hanzlik, M. Zrenz, Angew. Chem. 2009, 121, 3581–3583;
10.1002/ange.200806209 Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 3529–3531.
- 79See Ref. [45].
- 80B. N. Wanjala, B. Fang, J. Luo, Y. Chen, J. Yin, M. H. Engelhard, R. Loukrakpam, C.-J. Zhong, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 12714–12727.
- 81C. Wang, D. Li, M. Chi, J. Pearson, R. B. Rankin, J. Greeley, Z. Duan, G. Wang, D. van der Vliet, K. L. More, N. M. Markovic, V. R. Stamenkovic, J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2012, 3, 1668–1673.
- 82J. Hou, Y. Shao, M. W. Ellis, R. B. Moored, B. Yi, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 15384–15402.
- 83
- 83aS. Guo, S. Dong, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 2644–2672;
- 83bS. Guo, S. Dong, E. Wang, ACS Nano 2010, 4, 547–555.
- 84S. Guo, E. Wang, Acc. Chem. Res. 2011, 44, 491–500.
- 85R. Kou, Y. Shao, D. Wang, M. H. Engelhard, J. H. Kwak, J. Wang, V. V. Viswanathan, C. Wang, Y. Lin, Y. Wang, I. A. Aksay, J. Liu, Electrochem. Commun. 2009, 11, 954–957.
- 86Y. Shao, S. Zhang, C. Wang, Z. Nie, J. Liu, Y. Wang, Y. Lin, J. Power Sources 2010, 195, 4600–4605.
- 87Y. Tan, C. Xu, G. Chen, N. Zheng, Q. Xie, Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 6923–6927.
- 88aR. Kou, Y. Shao, D. Mei, Z. Nie, D. Wang, C. Wang, V. V. Viswanathan, S. Park, I. A. Aksay, Y. Lin, Y. Wang, J. Liu, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 2541–2547;
- 88bY. Li, Y. Li, E. Zhu, T. McLouth, C.-Y. Chiu, X. Huang, Y. Huang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 12326–12329.
- 89B. P. Vinayan, R. Nagar, N. Rajalakshmi, S. Ramaprabhu, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 3519–3526.
- 90C. V. Rao, A. Lee, M. Reddy, Y. Ishikawa, P. M. Ajayan, Carbon 2011, 49, 931–936.
- 91S. Guo, S. Sun, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 2492–2495.
- 92
- 92aY. Zhang, Y. Shen, J. Yuan, D. Han, Z. Wang, Q. Zhang, L. Niu, Angew. Chem. 2006, 118, 5999–6002; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 5867–5870;
- 92bY. F. Shen, Y. J. Zhang, Q. X. Zhang, L. Niu, T. Y. You, A. Ivaska, Chem. Commun. 2005, 4193–4195.
- 93
- 93aS. Guo, S. Dong, E. Wang, Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 1269–1272;
- 93bS. Guo, D. Wen, Y. Zhai, S. Dong, E. Wang, Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 3475–3481.
- 94
- 94aC. S. Shan, H. F. Yang, J. F. Song, D. X. Han, A. Ivaska, L. Niu, Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 2378–2382;
- 94bZ. J. Wang, Q. X. Zhang, D. Kuehner, A. Ivaska, L. Niu, Green Chem. 2008, 10, 907–909;
- 94cZ. Wang, Q. Zhang, D. Kuehner, X. Xu, A. Ivaska, L. Niu, Carbon 2008, 46, 1687–1692;
- 94dB. Wu, D. Hu, Y. Kuang, B. Liu, X. Zhang, J. Chen, Angew. Chem. 2009, 121, 4845–4848; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 4751–4754.
- 95J. Snyder, T. Fujita, M. W. Chen, J. Erlebacher, Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 904–907.
- 96F. Jaouen, E. Proietti, M. Lefevre, R. Chenitz, J.-P. Dodelet, G. Wu, H. T. Chung, C. M. Johnston, P. Zelenay, Energy Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 114–130.
- 97R. Jasinski, Nature 1964, 201, 1212–1213.
- 98H. Jahnke, M. Schonborn, G. Zimmermann, Top. Curr. Chem. 1976, 61, 133–181.
- 99R. Bashyam, P. Zelenay, Nature 2006, 443, 63–66.
- 100G. Wu, K. L. More, C. M. Johnston, P. Zelenay, Science 2011, 332, 443–447.
- 101K. Gong, F. Du, Z. Xia, M. Durstock, L. Dai, Science 2009, 323, 760–764.
- 102
- 102aY. Zhang, K. Fugane, T. Mori, L. Niu, J. Ye, J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 6575–6580;
- 102bL. Qu, Y. Liu, J.-B. Baek, L. Dai, ACS Nano 2010, 4, 1321–1326;
- 102cZ.-H. Sheng, L. Shao, J.-J. Chen, W.-J. Bao, F.-B. Wang, X.-H. Xia, ACS Nano 2011, 5, 4350–4358.
- 103
- 103aY. Zheng, Y. Jiao, J. Chen, J. Liu, J. Liang, A. Du, W. Zhang, Z. Zhu, S. C. Smith, M. Jaroniec, G. Q. Lu, S. Z. Qiao, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 20116–20119;
- 103bY. Sun, C. Li, G. Shi, J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 12810–12816;
- 103cJ. Liang, Y. Zheng, J. Chen, J. Liu, D. Hulicova-Jurcakova, M. Jaroniec, S. Z. Qiao, Angew. Chem. 2012, 124, 3958–3962; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 3892–3896;
- 103dS. Yang, X. Feng, X. Wang, K. Mullen, Angew. Chem. 2011, 123, 5451–5455; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 5339–5343.
- 104S. Shanmugam, T. Osaka, Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 4463–4465.
- 105T. Chen, Z. Cai, Z. Yang, L. Li, X. Sun, T. Huang, A. Yu, H. G. Kia, H. Peng, Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 4620–4625.
- 106Z. Yao, H. Nie, Z. Yang, X. Zhou, Z. Liu, S. Huang, Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 1027–1029.
- 107
- 107aS. Yang, L. Zhi, K. Tang, X. Feng, J. Maier, K. Müllen, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 3634–3640;
- 107bZ. Yang, Z. Yao, G. Li, G. Fang, H. Nie, Z. Liu, X. Zhou, X. Chen, S. Huang, ACS Nano 2012, 6, 205–211.
- 108Z.-W. Liu, F. Peng, H.-J. Wang, H. Yu, W.-X. Zheng, J. Yang, Angew. Chem. 2011, 123, 3315–3319; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 3257–3261.
- 109L. Yang, S. Jiang, Y. Zhao, L. Zhu, S. Chen, X. Wang, Q. Wu, J. Ma, Y. Ma, Z. Hu, Angew. Chem. 2011, 123, 7270–7273; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 7132–7135.
- 110
- 110aS. Wang, L. Zhang, Z. Xia, A. Roy, D. W. Chang, J.-B. Baek, L. Dai, Angew. Chem. 2012, 124, 4285–4288; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 4209–4212;
- 110bS. Wang, E. Iyyamperumal, A. Roy, Y. Xue, D. Yu, L. Dai, Angew. Chem. 2011, 123, 11960–11964; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 11756–11760.
- 111Y. Liang, Y. Li, H. Wang, J. Zhou, J. Wang, T. Regier, H. Dai, Nat. Mater. 2011, 10, 780–786.
- 112Y. Liang, H. Wang, J. Zhou, Y. Li, J. Wang, T. Regier, H. Dai, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 3517–3523.
- 113H. Wang, Y. Liang, Y. Li, H. Dai, Angew. Chem. 2011, 123, 11161–11164; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 10969–10972.
- 114Y. Tan, C. Xu, G. Chen, X. Fang, N. Zheng, Q. Xie, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 4584–4591.
- 115X.-Y. Yan, X.-L. Tong, Y.-F. Zhang, X.-D. Han, Y.-Y. Wang, G.-Q. Jin, Y. Qin, X.-Y. Guo, Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 1892–1894.
- 116Y. Li, Y. Zhao, H. Cheng, Y. Hu, G. Shi, L. Dai, L. Qu, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 15–18.
- 117S. Guo, S. Zhang, L. Wu, S. Sun, Angew. Chem. 2012, 124, 11940–11943; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 11770–11773.
- 118Y. Li, W. Zhou, H. Wang, L. Xie, Y. Liang, F. Wei, J.-C. Idrobo, S. J. Pennycook, H. Dai, Nat. Nanotechnol. 2012, 7, 394–400.