Internal Magnetic Fields of Dianions of Fullerene C60 and Its Cage-Opened Derivatives Studied with Encapsulated H2 as an NMR Probe†
Michihisa Murata Dr.
Institute for Chemical Research, Kyoto University, Uji, Kyoto 611-0011, Japan, Fax: (+81) 774-38-3178
Search for more papers by this authorYuta Ochi
Institute for Chemical Research, Kyoto University, Uji, Kyoto 611-0011, Japan, Fax: (+81) 774-38-3178
Search for more papers by this authorFumiyuki Tanabe
Institute for Chemical Research, Kyoto University, Uji, Kyoto 611-0011, Japan, Fax: (+81) 774-38-3178
Search for more papers by this authorKoichi Komatsu Prof. Dr.
Department of Environmental and Biotechnological, Frontier Engineering, Fukui University of Technology, Gakuen, Fukui 910-8505, Japan, Fax: (+81) 776-29-7891
Search for more papers by this authorYasujiro Murata Prof. Dr.
Institute for Chemical Research, Kyoto University, Uji, Kyoto 611-0011, Japan, Fax: (+81) 774-38-3178
Search for more papers by this authorMichihisa Murata Dr.
Institute for Chemical Research, Kyoto University, Uji, Kyoto 611-0011, Japan, Fax: (+81) 774-38-3178
Search for more papers by this authorYuta Ochi
Institute for Chemical Research, Kyoto University, Uji, Kyoto 611-0011, Japan, Fax: (+81) 774-38-3178
Search for more papers by this authorFumiyuki Tanabe
Institute for Chemical Research, Kyoto University, Uji, Kyoto 611-0011, Japan, Fax: (+81) 774-38-3178
Search for more papers by this authorKoichi Komatsu Prof. Dr.
Department of Environmental and Biotechnological, Frontier Engineering, Fukui University of Technology, Gakuen, Fukui 910-8505, Japan, Fax: (+81) 776-29-7891
Search for more papers by this authorYasujiro Murata Prof. Dr.
Institute for Chemical Research, Kyoto University, Uji, Kyoto 611-0011, Japan, Fax: (+81) 774-38-3178
Search for more papers by this authorThis research was supported by KAKENHI from MEXT/JSPS and the PRESTO program sponsored by JST.
Graphical Abstract
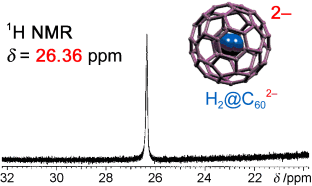
Inside information: The NMR signal of the molecular hydrogen in H2@C602− appears at extraordinarily low field (δ=26.36 ppm) relative to that of neutral H2@C60. This can be explained by the decrease in aromaticity of the C60 cage upon 2 e reduction. Spherical delocalization of the added two electrons over the π system of the fullerene cage is thought to be responsible for the drastic change in fullerene aromaticity.
Supporting Information
Supporting information for this article is available on the WWW under http://www.wiley-vch.de/contents/jc_2002/2008/z705285_s.pdf or from the author.
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1
- 1aV. Elser, R. C. Haddon, Nature 1987, 325, 792–794;
- 1bA. Pasquarello, M. Schlüter, R. C. Haddon, Science 1992, 257, 1660–1661;
- 1cR. C. Haddon, Science 1993, 261, 1545–1550;
- 1dA. Pasquarello, M. Schlüter, R. C. Haddon, Phys. Rev. A 1993, 47, 1783–1789;
- 1eM. Bühl, Chem. Eur. J. 1998, 4, 734–739;
- 1fA. Hirsch, Z. Chen, H. Jiao, Angew. Chem. 2000, 112, 4079–4081;
10.1002/1521-3757(20001103)112:21<4079::AID-ANGE4079>3.0.CO;2-H Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2000, 39, 3915–3917;10.1002/1521-3773(20001103)39:21<3915::AID-ANIE3915>3.0.CO;2-O CAS PubMed Web of Science® Google Scholar
- 1gM. Bühl, A. Hirsch, Chem. Rev. 2001, 101, 1153–1183.
- 2M. Saunders, R. J. Cross, H. A. Jiménez-Vázquez, R. Shimshi, A. Khong, Science 1996, 271, 1693–1697.
- 3
- 3aM. Saunders, H. A. Jiménez-Vázquez, B. W. Bangerter, R. J. Cross, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1994, 116, 3621–3622;
- 3bA. B. Smith III, R. M. Strongin, L. Brard, W. J. Romanow, M. Saunders, H. A. Jiménez-Vázquez, R. J. Cross, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1994, 116, 10831–10832;
- 3cM. Rüttimann, R. F. Haldimann, L. Isaacs, F. Diederich, A. Khong, H. A. Jiménez-Vázquez, R. J. Cross, M. Saunders, Chem. Eur. J. 1997, 3, 1071–1076;
- 3dO. V. Boltalina, M. Bühl, A. Khong, M. Saunders, J. M. Street, R. Taylor, J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2 1999, 1475–1479.
- 4
- 4aE. Shabtai, A. Weitz, R. C. Haddon, R. E. Hoffman, M. Rabinovitz, A. Khong, R. J. Cross, M. Saunders, P.-C. Cheng, L. T. Scott, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 6389–6393;
- 4bT. Sternfeld, F. Wudl, K. Hummelen, A. Weizt, R. C. Haddon, M. Rabinovitz, Chem. Commun. 1999, 2037–2039;
- 4cT. Sternfeld, R. E. Hoffman, M. Saunders, R. J. Cross, S. Syamala, M. Rabinovitz, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 8786–8787.
- 5
- 5aR. Subramanian, K. M. Kadish, M. N. Vijayashree, X. Gao, M. T. Jones, J. Phys. Chem. 1996, 100, 16327–16335;
- 5bS. Fukuzumi, T. Suenobu, T. Hirasaka, R. Arakawa, K. M. Kadish, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 9220–9227;
- 5cY.-H. Zhu, L.-C. Song, Q.-M. Hu, C.-M. Li, Org. Lett. 1999, 1, 1693–1695.
- 6
- 6aE. Allard, L. Riviere, J. Delaunay, D. Dubois, J. Cousseau, Tetrahedron Lett. 1999, 40, 7223–7226;
- 6bE. Allard, J. Delaunay, F. Cheng, J. Cousseau, J. Ordúna, G. Javier, Org. Lett. 2001, 3, 3503–3506;
- 6cF. Cheng, Y. Murata, K. Komatsu, Org. Lett. 2002, 4, 2541–2544.
- 7P. C. Trulove, R. T. Carlin, G. R. Eaton, S. S. Eaton, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 6265–6272.
- 8
- 8aY. Murata, M. Murata, K. Komatsu, Chem. Eur. J. 2003, 9, 1600–1609;
- 8bY. Murata, M. Murata, K. Komatsu, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 7152–7153;
- 8cK. Komatsu, M. Murata, Y. Murata, Science 2005, 307, 238–240;
- 8dK. Komatsu, Y. Murata, Chem. Lett. 2005, 34, 886–891.
- 9M. Murata, Y. Murata, K. Komatsu, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 8024–8033.
- 10R. Subramanian, P. Boulas, M. N. Vijayashree, F. D'Souza, M. T. Jones, K. M. Kadish, J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1994, 1847–1848.
- 11P. D. W. Boyd, P. Bhyrappa, P. Paul, J. Stinchcombe, R. D. Bolskar, Y. Sun, C. A. Reed, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 2907–2914.
- 12
- 12aY. Matsuo, H. Isobe, T. Tanaka, Y. Murata, M. Murata, K. Komatsu, E. Nakamura, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 17148–17149;
- 12bY. Rubin, T. Jarrosson, G.-W. Wang, M. D. Bartberger, K. N. Houk, G. Schick, M. Saunders, R. J. Cross, Angew. Chem. 2001, 113, 1591–1594;
10.1002/1521-3757(20010417)113:8<1591::AID-ANGE1591>3.0.CO;2-V Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2001, 40, 1543–1546;10.1002/1521-3773(20010417)40:8<1543::AID-ANIE1543>3.0.CO;2-6 CAS PubMed Web of Science® Google Scholar
- 12cS.-i. Iwamatsu, S. Murata, Y. Andoh, M. Minoura, K. Kobayashi, N. Mizorogi, S. Nagase, J. Org. Chem. 2005, 70, 4820–4825.
- 13K. Wolinski, J. F. Hinton, P. Pulay, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1990, 112, 8251–8260.
- 14Gaussian03 (Revision D.02): M. J. Frisch et al., see the Supporting Information.
- 15P. v. R. Schleyer, C. Maerker, A. Dransfeld, H. Jiao, N. J. R. v. E. Hommes, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 6317–6318.
- 16We could not observe any 13C NMR signals for H2@12−-H2@32− most likely because of thermal population of the triplet excited states,[11] although the possibility of formation of radical trianions cannot be rigorously ruled out.