In vivo measurement of the size of lipid droplets in an intracerebral glioma in the rat
Corresponding Author
Hana Lahrech
Unité mixte INSERM–Université Joseph Fourier, Hôpital Albert Michallon, Grenoble, France
INSERM U438, Centre Hospitalier Universitaire, Pavillon B, BP 217, F 38043 Grenoble cedex 9, France===Search for more papers by this authorSonia Zoula
Unité mixte INSERM–Université Joseph Fourier, Hôpital Albert Michallon, Grenoble, France
Search for more papers by this authorRégine Farion
Unité mixte INSERM–Université Joseph Fourier, Hôpital Albert Michallon, Grenoble, France
Search for more papers by this authorChantal Rémy
Unité mixte INSERM–Université Joseph Fourier, Hôpital Albert Michallon, Grenoble, France
Unité mixte INSERM–Université Joseph Fourier, Hôpital Albert Michallon, Grenoble, France
Search for more papers by this authorMichel Décorps
Unité mixte INSERM–Université Joseph Fourier, Hôpital Albert Michallon, Grenoble, France
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Hana Lahrech
Unité mixte INSERM–Université Joseph Fourier, Hôpital Albert Michallon, Grenoble, France
INSERM U438, Centre Hospitalier Universitaire, Pavillon B, BP 217, F 38043 Grenoble cedex 9, France===Search for more papers by this authorSonia Zoula
Unité mixte INSERM–Université Joseph Fourier, Hôpital Albert Michallon, Grenoble, France
Search for more papers by this authorRégine Farion
Unité mixte INSERM–Université Joseph Fourier, Hôpital Albert Michallon, Grenoble, France
Search for more papers by this authorChantal Rémy
Unité mixte INSERM–Université Joseph Fourier, Hôpital Albert Michallon, Grenoble, France
Unité mixte INSERM–Université Joseph Fourier, Hôpital Albert Michallon, Grenoble, France
Search for more papers by this authorMichel Décorps
Unité mixte INSERM–Université Joseph Fourier, Hôpital Albert Michallon, Grenoble, France
Search for more papers by this authorAbstract
Pulsed field gradient NMR was used to measure the root mean square displacement λ of the NMR visible lipid molecules in C6 brain tumors in the rat at different diffusion times. For a distribution of spherical droplets of diameter with volume fraction ξ(Φi), the mean characteristic droplet diameter Φc = 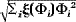 was shown to be related to the root mean square displacement at long diffusion times by the simple relationship Φ
was shown to be related to the root mean square displacement at long diffusion times by the simple relationship Φ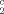 = 10λ2. In the range of diffusion times 100–530 msec, λ was found to be independent of the diffusion time and equal to 1.35 ± 0.22 μm and Φc to 4.27 ± 0.71 μm. The data reinforce the notion that the presence of lipid resonances in NMR spectra of tumors is due to lipid droplets. Light microscopy of histologic slices showed the presence of lipid droplets mainly in the necrotic region and in a layer of tumor cells surrounding the necrosis. Magn Reson Med 45:409–414, 2001. © 2001 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
= 10λ2. In the range of diffusion times 100–530 msec, λ was found to be independent of the diffusion time and equal to 1.35 ± 0.22 μm and Φc to 4.27 ± 0.71 μm. The data reinforce the notion that the presence of lipid resonances in NMR spectra of tumors is due to lipid droplets. Light microscopy of histologic slices showed the presence of lipid droplets mainly in the necrotic region and in a layer of tumor cells surrounding the necrosis. Magn Reson Med 45:409–414, 2001. © 2001 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
REFERENCES
- 1 Barba I, Cabanas ME, Arùs C. The relationship between nuclear magnetic resonance-visible lipids, lipid droplets, and cell proliferation in cultured C6 cells. Cancer Res 1999; 59: 1861–1868.
- 2 Ferretti A, Knijn A, Iorio E, Pulciani S, Giambenedetti M, Molinari A, Meschini S, Stringaro A, Calcabrini A, Freitas I, Strom R, Arancia G, Podo F. Biophysical and structural characterization of 1H-NMR-detectable mobile lipid domains in NIH-3T3 fibroblasts. Biochim Biophys Acta 1999; 1438: 329–348.
- 3 Le Moyec L, Tatoud R, Degeorges A, Calabresse C, Bauza G, Eugène M, Calvo F. Proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy reveals cellular lipids involved in resistance to adriamycin and taxol by the K562 leukemia cell line. Cancer Res 1996; 56: 3461–3467.
- 4 Lean CL, Mackinnon WB, Mountford CE. Fucose in 1H COSY spectra of plasma membrane fragments shed from human malignant colorectal cells. Magn Reson Med 1991; 20: 306–311.
- 5 Mackinnon WB, Dyne M, Holmes KT, Mountford CE. Further evidence that the narrow 1H magnetic resonance signals from malignant cells do not arise from intracellular lipid droplets. NMR Biomed 1989; 2: 161–164.
- 6 Mountford CE, Grossman G, Reid G, Fox RM. Characterization of transformed cells and tumors by proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Cancer Res 1982; 42: 2270–2276.
- 7 Mountford CE, Wright LC. Organization of lipids in the plasma membranes of malignant and stimulated cells: a new model. Trends Biochem Sci 1988; 13: 172–177.
- 8 Hakumäki JM, Poptani H, Sandmair A-M, Ylä-Herttuala S, Kauppinen RA. 1H MRS detects polyunsaturated fatty acid accumulation during gene therapy of glioma: implications for the in vivo detection of apoptosis. Nature Med 1999; 5: 1323–1327.
- 9 Rémy C, Carlès A, Ziegler A, Sam-Lai E, Moreno A, Le Fur Y, Décorps M. In vivo, ex vivo and in vitro one- and two-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of an intracerebral glioma in rat brain: assignment of resonances. J Neurochem 1994; 62: 166–179.
- 10 Rémy C, Von Kienlin M, Lotito S, François A, Benabid AL, Décorps M. In vivo 1H NMR spectroscopy of an intracerebral glioma in the rat. Magn Reson Med 1989; 9: 395–401.
- 11 Kuesel AC, Donnelly MS, Halliday W, Sutherland GR, Smith ICP. Mobile lipids and metabolic heterogeneity of brain tumours as detectable by ex vivo 1H MR spectroscopy. NMR Biomed 1994; 7: 172–180.
- 12 Kuesel AC, Sutherland GR, Halliday W, Smith ICP. 1H MRS of high grade astrocytomas: mobile lipid accumulation in necrotic tissue. NMR Biomed 1994; 7: 149–155.
- 13 Castillo M, Kwock L. Clinical applications of proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy in the evaluation of common intracranial tumors. Top Magn Reson Imaging 1999; 10: 104–113.
- 14 Negendank WG, Sauter R, Brown TR, Evelhoch JL, Falini A, Gotsis ED, Heerschap A, Kamada K, Lee BCP, Mengeot M, Moser E, Padavic-Shaller KA, Sanders JA, Spraggins TA, Stillman AE, Terwey B, Vogl TJ, Wicklow K, Zimmerman RA. Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy in patients with glial tumors: a multicenter study. J Neurosurg 1996; 84: 449–458.
- 15
Sijens PE,
Levendag PC,
Vecht CJ,
Van Dijk P,
Oudkerk M.
1H MR spectroscopy detection of lipids and lactate in metastatic tumors.
NMR Biomed
1996;
9:
65–71.
10.1002/(SICI)1099-1492(199604)9:2<65::AID-NBM397>3.0.CO;2-N CAS PubMed Web of Science® Google Scholar
- 16 Rémy C, Fouilhé N, Ignasi B, Sam-Laï E, Lahrech H, Cucurella MG, Izquierdo M, Moreno A, Ziegler A, Massarelli R, Décorps M, Arùs C. Evidence that mobile lipids detected in rat brain glioma by 1H nuclear magnetic resonance correspond to lipid droplets. Cancer Res 1997; 57: 407–414.
- 17 Stejskal EO, Tanner JE. Spin diffusion measurements: spin echoes in the presence of time-dependent field gradient. J Chem Phys 1965; 42: 288–292.
- 18 Murday JS, Cotts RM. Self-diffusion coefficient of liquid lithium. J Chem Phys 1968; 48: 4938–4945.
- 19 Neuman CH. Spin echo of spins diffusing in a bounded medium. J Chem Phys 1974; 60: 4508–4511.
- 20 Callaghan PT, Jolley KW, Humphrey RS. Diffusion of fat and water in cheese as studied by pulsed field gradient nuclear magnetic resonance. J Colloid Interface Sci 1983; 93: 521–529.
- 21 Packer KJ, Rees C. Pulsed NMR studies of restricted diffusion. Droplet size distribution in emulsions. J Colloid Interface Sci 1972; 40: 206–218.
- 22 Van Den Enden JC, Waddington D, Van Aalst H, Van Kralingen CG, Packer KJ. Rapid determination of water droplet size distributions by PFG-NMR. J Colloid Interface Sci 1990; 140: 105–113.
- 23 Callaghan PT. Pulsed field gradient nuclear magnetic resonance as a probe of liquid state molecular organization. Aust J Phys 1984; 37: 359–387.
- 24 Tanner JE, Stejskal EO. Restricted self-diffusion of protons in colloidal systems by the pulsed-gradient, spin-echo method. J Chem Phys 1968; 49: 1768–1777.
- 25
Le Duc G,
Péoc'h M,
Rémy C,
Charpy O,
Muller RN,
Le Bas JF,
Décorps M.
Use of T2-weighted susceptibility contrast MRI for mapping the blood volume in the glioma-bearing rat brain.
Magn Reson Med
1999;
42:
754–761.
10.1002/(SICI)1522-2594(199910)42:4<754::AID-MRM18>3.0.CO;2-Q CAS PubMed Web of Science® Google Scholar
- 26 Décorps M, Le Bas JF, Leviel JL, Confort S, Rémy C, Benabid AL. Analysis of brain metabolism changes induced by acute potassium cyanide intoxication by 31P NMR in vivo using chronically implanted surface coils. FEBS Lett 1984; 168: 1–6.
- 27 Frahm J, Bruhn H, Gyngell ML, Merboldt K-D, Hänicke W, Sauter R. Localized high-resolution proton NMR spectroscopy using stimulated echoes: initial applications to human brain in vivo. Magn Reson Med 1989; 9: 79–93.
- 28 Granot J. Selected volume excitation using stimulated echoes (VEST). Application to spatially localized spectroscopy and imaging. J Magn Reson 1986; 70: 488–492.
- 29 Kimmich R, Hoepfel D. Volume-selective multipulse spin-echo spectroscopy. J Magn Reson 1987; 72: 379–384.
- 30 Merboldt K-D, Hörstermann D, Hänicke W, Bruhn H, Frahm J. Molecular self-diffusion of intracellular metabolites in rat brain in vivo investigated by localized proton NMR diffusion spectroscopy. Magn Reson Med 1993; 29: 125–129.
- 31 Haase A, Frahm J, Hänicke W, Matthaei D. 1H NMR chemical shift selective (CHESS) imaging. Phys Med Biol 1985; 30: 341–344.
- 32 Wilman AH, Allen PS. An analytical and experimental evaluation of STEAM versus PRESS for the observation of the lactate doublet. J Magn Reson B 1993; 101: 102–105.
- 33 Sotak CH. A method for measuring the apparent self-diffusion coefficient of in vivo lactic acid using double-quantum coherence-transfer spectroscopy. J Magn Reson 1990; 90: 198–204.
- 34 Pfeuffer J, Lin J, Ugurbil K, Garwood M. Diffusion-weighted spectroscopy of 13C-labelled lactate in rat glioma in vivo. In: Proceedings of the 8th Annual Meeting of ISMRM, Denver, 2000. p 475.
- 35 Sijens PE, Knopp MV, Brunetti A, Wicklow K, Alfano B, Bachert P, Sanders JA, Stillman AE, Kett H, Sauter R. 1H MR spectroscopy in patients with metastasis brain tumors: a multicenter study. Magn Reson Med 1995; 33: 818–826.




