Vessel size imaging
Irène Troprès
Unité mixte INSERM/Université Joseph Fourier, Hôpital Albert Michallon, Grenoble, France
Search for more papers by this authorStephan Grimault
Unité mixte INSERM/Université Joseph Fourier, Hôpital Albert Michallon, Grenoble, France
Search for more papers by this authorAlbert Vaeth
Unité mixte INSERM/Université Joseph Fourier, Hôpital Albert Michallon, Grenoble, France
Search for more papers by this authorEmmanuelle Grillon
Unité mixte INSERM/Université Joseph Fourier, Hôpital Albert Michallon, Grenoble, France
Search for more papers by this authorCécile Julien
Unité mixte INSERM/Université Joseph Fourier, Hôpital Albert Michallon, Grenoble, France
Search for more papers by this authorJean-François Payen
Unité mixte INSERM/Université Joseph Fourier, Hôpital Albert Michallon, Grenoble, France
Search for more papers by this authorLaurent Lamalle
Unité mixte INSERM/Université Joseph Fourier, Hôpital Albert Michallon, Grenoble, France
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Michel Décorps
Unité mixte INSERM/Université Joseph Fourier, Hôpital Albert Michallon, Grenoble, France
INSERM U438, Hôpital Michallon, BP 217, 38043, Grenoble cédex 9, France===Search for more papers by this authorIrène Troprès
Unité mixte INSERM/Université Joseph Fourier, Hôpital Albert Michallon, Grenoble, France
Search for more papers by this authorStephan Grimault
Unité mixte INSERM/Université Joseph Fourier, Hôpital Albert Michallon, Grenoble, France
Search for more papers by this authorAlbert Vaeth
Unité mixte INSERM/Université Joseph Fourier, Hôpital Albert Michallon, Grenoble, France
Search for more papers by this authorEmmanuelle Grillon
Unité mixte INSERM/Université Joseph Fourier, Hôpital Albert Michallon, Grenoble, France
Search for more papers by this authorCécile Julien
Unité mixte INSERM/Université Joseph Fourier, Hôpital Albert Michallon, Grenoble, France
Search for more papers by this authorJean-François Payen
Unité mixte INSERM/Université Joseph Fourier, Hôpital Albert Michallon, Grenoble, France
Search for more papers by this authorLaurent Lamalle
Unité mixte INSERM/Université Joseph Fourier, Hôpital Albert Michallon, Grenoble, France
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Michel Décorps
Unité mixte INSERM/Université Joseph Fourier, Hôpital Albert Michallon, Grenoble, France
INSERM U438, Hôpital Michallon, BP 217, 38043, Grenoble cédex 9, France===Search for more papers by this authorAbstract
Vessel size imaging is a new method that is based on simultaneous measurement of the changes ΔR2 and ΔR in relaxation rate constants induced by the injection of an intravascular superparamagnetic contrast agent. Using the static dephasing approximation for ΔR
in relaxation rate constants induced by the injection of an intravascular superparamagnetic contrast agent. Using the static dephasing approximation for ΔR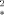 estimation and the slow-diffusion approximation for ΔR2 estimation, it is shown that the ratio ΔR2/ΔR
estimation and the slow-diffusion approximation for ΔR2 estimation, it is shown that the ratio ΔR2/ΔR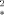 can be expressed as a function of the susceptibility difference between vessels and brain tissue, the brain water diffusion coefficient, and a weighted mean of vessel sizes. Comparison of the results with 1) the Monte Carlo simulations used to quantify the relationship between tissue parameters and susceptibility contrast, 2) the experimental MRI data in the normal rat brain, and 3) the histologic data establishes the validity of this approach. This technique, which allows images of a weighted mean of the vessel size to be obtained, could be useful for in vivo studies of tumor vascularization. Magn Reson Med 45:397–408, 2001. © 2001 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
can be expressed as a function of the susceptibility difference between vessels and brain tissue, the brain water diffusion coefficient, and a weighted mean of vessel sizes. Comparison of the results with 1) the Monte Carlo simulations used to quantify the relationship between tissue parameters and susceptibility contrast, 2) the experimental MRI data in the normal rat brain, and 3) the histologic data establishes the validity of this approach. This technique, which allows images of a weighted mean of the vessel size to be obtained, could be useful for in vivo studies of tumor vascularization. Magn Reson Med 45:397–408, 2001. © 2001 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
REFERENCES
- 1 Ostergaard L, Weisskoff RM, Chesler DA, Gyldensted C, Rosen BR. High resolution measurement of cerebral blood flow using intravascular tracer bolus passages. Part I: mathematical approach and statistical analysis. Magn Reson Med 1996; 36: 715–725.
- 2 Lin W, Paczynski RP, Kuppusamy K, Hsu CY, Haacke EM. Quantitative measurements of regional cerebral blood volume using MRI in rats: effects of arterial carbon dioxide tension and mannitol. Magn Reson Med 1997; 38: 420–428.
- 3 Schwarzbauer C, Morrissey SP, Deichmann R, Hillenbrand C, Syha J, Adolf H, Noth U, Haase A. Quantitative magnetic resonance imaging of capillary water permeability and regional blood volume with an intravascular MR contrast agent. Magn Reson Med 1997; 37: 769–777.
- 4 Boxerman JL, Hamberg LM, Rosen BR, Weisskoff RM. MR contrast due to intravascular magnetic susceptibility perturbations. Magn Reson Med 1995; 34: 555–566.
- 5 Ogawa S, Lee T-M, Nayak AS, Glynn P. Oxygenation-sensitive contrast in magnetic resonance image of rodent brain at high magnetic fields. Magn Reson Med 1990; 14: 68–78.
- 6 Yablonskiy DA, Haacke EM. Theory of NMR signal behavior in magnetically inhomogeneous tissues: the static dephasing regime. Magn Reson Med 1994; 32: 749–763.
- 7 Prinster A, Pierpaoli C, Turner R, Jezzard P. Simultaneous measurement of ΔR2 and ΔR2* in cat brain during hypoxia and hypercapnia. Neuroimage 1997; 6: 191–200.
- 8 Dennie J, Mandeville JB, Boxerman JL, Packard SD, Rosen BR, Weisskoff RM. NMR imaging of changes in vascular morphology due to tumor angiogenesis. Magn Reson Med 1998; 40: 793–799.
- 9 Lin W, Celik A, Paczynski RP, Hsu CY, Powers WJ. Quantitative magnetic resonance imaging in experimental hypercapnia: improvement in the relation between changes in brain R2 and the oxygen saturation of venous blood after correction for changes in cerebral blood volume. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 1999; 19: 853–862.
- 10
Kiselev VG,
Posse S.
Analytical model of susceptibility-induced MR signal dephasing: effect of diffusion in a microvascular network.
Magn Reson Med
1999;
41:
499–509.
10.1002/(SICI)1522-2594(199903)41:3<499::AID-MRM12>3.0.CO;2-O CAS PubMed Web of Science® Google Scholar
- 11 Kiselev V, Posse S. Analytical theory of susceptibility induced NMR signal dephasing in a cerebrovascular network. Phys Rev Lett 1998; 81: 5696–5699.
- 12 Yablonskiy DA. Quantitation of intrinsic magnetic susceptibility-related effects in a tissue matrix. Phantom study. Magn Reson Med 1998; 39: 417–428.
- 13 Fisel CR, Ackerman JL, Buxton RB, Garrido L, Belliveau JW, Rosen BR, Brady TJ. MR contrast due to microscopically heterogeneous magnetic susceptibility: numerical simulations and applications to cerebral physiology. Magn Reson Med 1991; 17: 336–347.
- 14 Kennan RP, Zhong J, Gore JC. Intravascular susceptibility contrast mechanisms in tissues. Magn Reson Med 1994; 31: 9–21.
- 15 Weisskoff RM, Zuo CS, Boxerman JL, Rosen BR. Microscopic susceptibility variation and transverse relaxation: theory and experiment. Magn Reson Med 1994; 31: 601–610.
- 16 Boxerman JL, Bandettini PA, Kwong KK, Baker JR, Davis TL, Rosen BR, Weisskoff RM. The intravascular contribution to fMRI signal change: Monte Carlo modeling and diffusion-weighted studies in vivo. Magn Reson Med 1995; 34: 4–10.
- 17 Berry I, Benderbous S, Ranjeva JP, Gracia-Meavilla D, Manelfe C, Le Bihan D. Contribution of Sinerem used as blood-pool contrast agent: detection of cerebral blood volume changes during apnea in the rabbit. Magn Reson Med 1996; 36: 415–419.
- 18 Jung CW, Jacobs P. Physical and chemical properties of superparamagnetic iron oxide MR contrast agents: ferumoxides, ferumoxtran, ferumoxsil. Magn Reson Imaging 1995; 13: 661–674.
- 19 Weisskoff R, Kiinne S. MR susceptometry: image-based measurement of absolute susceptibility of MR contrast agents and human blood. The magnetic properties and structure of hemoglobin. Magn Reson Med 1992; 24: 375–383.
- 20 Chen Q, Andersen AH, Zhang Z, Ovadia A, Gash DM, Avison MJ. Mapping drug-induced changes in cerebral R2* by multiple gradient recalled echo functional MRI. Magn Reson Imaging 1996; 14: 469–476.
- 21 Ma J, Wehrli FW. Method for image-based measurement of the reversible and irreversible contribution to the transverse-relaxation rate. J Magn Reson B 1996; 111: 61–69.
- 22 Hoehn-Berlage M. Diffusion NMR. NMR Biomed 1995; 8: 279.
- 23 Albert MS, Huang W, Lee JH, Patlak CS, Springer Jr CS. Susceptibility changes following bolus injections. Magn Reson Med 1993; 29: 700–708.
- 24
Jones RA,
Haraldseth O,
Baptista AM,
Muller TB,
Oksendal AN.
A study of the contribution of changes in the cerebral blood volume to the haemodynamic response to anoxia in rat brain.
NMR Biomed
1997;
10:
59–66.
10.1002/(SICI)1099-1492(199704)10:2<59::AID-NBM415>3.0.CO;2-0 CAS PubMed Web of Science® Google Scholar
- 25 Ogawa S, Menon RS, Tank DW, Kim SG, Merkle H, Ellermann JM, Ugurbil K. Functional brain mapping by blood oxygenation level-dependent contrast magnetic resonance imaging. A comparison of signal characteristics with a biophysical model. Biophys J 1993; 64: 803–812.
- 26 Thulborn KR, Waterton JC, Matthews PM, Radda GK. Oxygenation dependence of the transverse relaxation time of water protons in whole blood at high field. Biochim Biophys Acta 1982; 714: 265–270.
- 27 Wright GA, Hu BS, Macovski A. Estimating oxygen saturation of blood in vivo with MR imaging at 1.5 T. J Magn Reson Imaging 1991; 1: 275–283.
- 28 Ye FQ, Allen PS. Relaxation enhancement of the transverse magnetization of water protons in paramagnetic suspensions of red blood cells. Magn Reson Med 1995; 34: 713–720.
- 29 Gillis P, Peto S, Moiny F, Mispelter J, Cuenod CA. Proton transverse nuclear magnetic relaxation in oxidized blood: a numerical approach. Magn Reson Med 1995; 33: 93–100.
- 30 Lee HB, Blaufox MD. Blood volume in the rat. J Nucl Med 1985; 26: 72–76.
- 31 Pouliquen D, Perroud H, Calza F, Jallet P, Le Jeune JJ. Investigation of the magnetic properties of iron oxide nanoparticles used as contrast agent for MRI. Magn Reson Med 1992; 24: 75–84.
- 32 Ogawa S, Lee TM, Barrere B. The sensitivity of magnetic resonance image signals of a rat brain to changes in the cerebral venous blood oxygenation. Magn Reson Med 1993; 29: 205–210.
- 33
Scheffler K,
Seifritz E,
Haselhorst R,
Bilecen D.
Titration of the BOLD effect: separation and quantitation of blood volume and oxygenation changes in the human cerebral cortex during neuronal activation and ferumoxide infusion.
Magn Reson Med
1999;
42:
829–836.
10.1002/(SICI)1522-2594(199911)42:5<829::AID-MRM2>3.0.CO;2-6 CAS PubMed Web of Science® Google Scholar
- 34 Abramovitch R, Frenkiel D, Neeman M. Analysis of subcutaneous angiogenesis by gradient echo magnetic resonance imaging. Magn Reson Med 1998; 39: 813–824.
- 35
Does MD,
Zhong J,
Gore JC.
In vivo measurement of ADC change due to intravascular susceptibility variation.
Magn Reson Med
1999;
41:
236–240.
10.1002/(SICI)1522-2594(199902)41:2<236::AID-MRM4>3.0.CO;2-3 CAS PubMed Web of Science® Google Scholar
- 36 Bereckzi D, Wei L, Otsuka T, Acuff V, Pettigrew K, Patlak C, Fenstermacher J. Hypoxia increases velocity of blood flow through microvascular systems in rat brain. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 1993; 13: 475–486.
- 37 Todd MM, Weeks JB, Warner DS. The influence of intravascular volume expansion on cerebral blood flow and blood volume in normal rats. Anesthesiology 1993; 78: 945–953.
- 38 Weiss HR, Buchweitz E, Murtha TJ, Auletta M. Quantitative regional determination of morphometric indices of the total and perfused capillary network in the rat brain. Circ Res 1982; 51: 494–503.
- 39 Wesseling P, van der Laak JA, de Leeuw H, Ruiter DJ, Burger PC. Quantitative immunohistological analysis of the microvasculature in untreated human glioblastoma multiforme. Computer-assisted image analysis of whole-tumor sections. J Neurosurg 1994; 81: 902–909.
- 40 Wesseling P, van der Laak JA, Link M, Teepen HL, Ruiter DJ. Quantitative analysis of microvascular changes in diffuse astrocytic neoplasms with increasing grade of malignancy. Hum Pathol 1998; 29: 352–358.




