Clinicopathological analysis of low-grade papillary Schneiderian carcinoma: report of five new cases and review of the literature
C.Z. and H.W. contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
Aims
Low-grade papillary Schneiderian carcinoma (LGPSC) is a rare and newly described entity of the sinonasal tract. The aim of this study was to evaluate the clinicopathological and molecular characteristics in order to identify typical features for differential diagnosis.
Methods and results
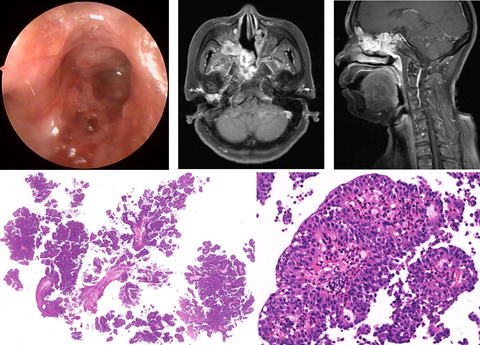
Of the 3000 cases of sinonasal tumour studied during a period of 6 years, five cases were reviewed and diagnosed as LGPSC. All five patients were female (mean age, 47.8 years; range, 18–64 years) and had undergone multiple surgeries (3–10 surgeries). Both the sinonasal tract and the middle ear were involved in four patients. Nodal metastasis occurred in two patients, and one patient developed a distant metastasis to the left lung. Histologically, tumours had branched and crowded papillae with pushing boundaries. Tumour epithelia were multilayered and arranged in an orderly pattern without cilia. No malignant cytological features were observed in any of the cases. Immunohistochemical findings revealed a scattered distribution of Ki67-positive cells and positive staining for epithelial membrane antigen, mainly in the outermost-layer cells. Human papillomavirus (HPV) DNA was found in two patients and genotyped as HPV type 16. Sanger sequencing did not reveal any epidermal growth factor receptor or Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homologue gene mutation in the five cases.
Conclusions
We report on five new cases of LGPSC, and confirm LGPSC as a new sinonasal carcinoma that behaves aggressively with metastatic potential. The combination of clinical behaviour and typical histological features can distinguish LGPSC from sinonasal papilloma and other carcinomas.
Graphical Abstract
Conflict of interest
All authors have approved this manuscript. No author has financial or other contractual agreements that might cause conflicts of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analysed during the study are included in this published article.