Using Cusco’s speculum to endoscopically remove a large colonic endoscopic submucosal dissection specimen
Abstract
Watch a video of this article.
Brief Explanation
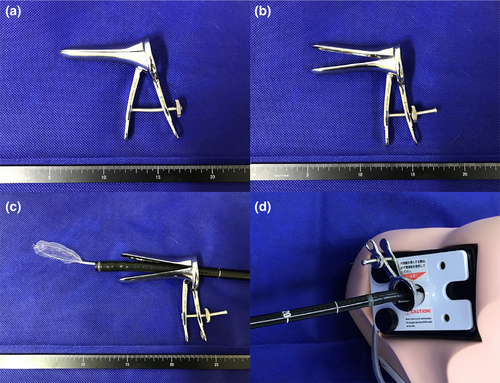
Unlike endoscopic mucosal resection, there is no size limitation for colonic endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD), anticipating en bloc resection.1 If the retrieval net fits well and can grasp the entire collected specimen, the resected specimen can be removed through the anus with minimal resistance. However, it is sometimes difficult to retrieve a large resected specimen after ESD without damage to the specimen by the anal sphincter muscle. Conventional retrieval techniques (e.g., the use of the forefinger-compression method,2 Valsalva maneuver defecation,3 a small plastic bag,4 or sliding tube5) have been suggested, but are often ineffective. We devised a method to collect specimens by widening the inner diameter of the anus sufficiently. This novel technique uses Cusco's speculum. First, after moving the resected specimen to the rectum, only the endoscope was removed. Next, after passing through a Cusco's speculum (SS size, 110 × 90 × 35 mm) (Fig. 1a), an endoscope was reinserted into the anus. Subsequently, the Cusco's speculum was inserted into the anus with an endoscope (Fig. 1b), opened (Fig. 1c), and fixed. Finally, the anus was sufficiently expanded, and the resected specimen grasped by a retrieval net (Roth Net – foreign body – standard. The width is 1.8–3.0 cm, US endoscopy, Mentor, OH, USA) could be collected without resistance through the Cusco’s speculum (Fig. 1d, Video S1). It is a safe and convenient method, and does not require any change in the patient's posture.
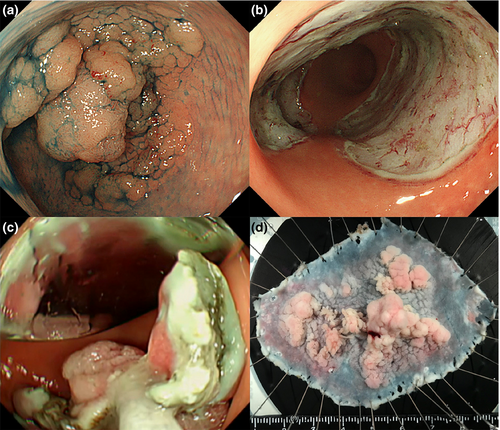
A 50-year-old woman was referred to our department for a laterally spreading rectal tumor measuring approximately 60-mm and occupying approximately 2/3 of the circumference of the rectum (Fig. 2a). An ESD was performed with dissection of the semi-circumference of the rectum (Fig. 2b).1 After ESD, we collected a large colonic ESD specimen without damage, using Cusco’s speculum (Fig. 2c,d, Video S1).
Authors declare no conflicts of interest for this article.
Acknowledgment
Informed consent was obtained from the patient for publication of her information and imaging.