Tuning Spin Crossover Properties in Hofmann-Type Framework by Guest-Adaptive Deformation
Corresponding Author
Kai-Ping Xie
School of Chemistry and Materials Engineering, Huizhou University, Huizhou, Guangdong, 516007 China
Key Laboratory of Bioinorganic and Synthetic Chemistry of Ministry of Education, School of Chemistry, IGCME, GBRCE for Functional Molecular Engineering, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, 510275 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorHai-Ling Wang
School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Guangxi Key Laboratory of Electrochemical Energy Materials, Guangxi Colleges and Universities Key Laboratory of Applied Chemistry Technology and Resource Development, Guangxi University, Nanning, Guangxi, 530004 China
Search for more papers by this authorZe-Yu Ruan
Key Laboratory of Bioinorganic and Synthetic Chemistry of Ministry of Education, School of Chemistry, IGCME, GBRCE for Functional Molecular Engineering, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, 510275 China
Search for more papers by this authorPei-Yu Liao
Key Laboratory of Bioinorganic and Synthetic Chemistry of Ministry of Education, School of Chemistry, IGCME, GBRCE for Functional Molecular Engineering, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, 510275 China
Search for more papers by this authorGuang Yang
Key Laboratory of Bioinorganic and Synthetic Chemistry of Ministry of Education, School of Chemistry, IGCME, GBRCE for Functional Molecular Engineering, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, 510275 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Zi-Cheng Xiao
School of Chemistry and Materials Engineering, Huizhou University, Huizhou, Guangdong, 516007 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Yi-Fei Deng
Department of Chemistry, Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen, Guangdong, 518055 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Si-Guo Wu
Key Laboratory of Bioinorganic and Synthetic Chemistry of Ministry of Education, School of Chemistry, IGCME, GBRCE for Functional Molecular Engineering, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, 510275 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorYan Shi
School of Chemistry and Materials Engineering, Huizhou University, Huizhou, Guangdong, 516007 China
Search for more papers by this authorMing-Liang Tong
Key Laboratory of Bioinorganic and Synthetic Chemistry of Ministry of Education, School of Chemistry, IGCME, GBRCE for Functional Molecular Engineering, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, 510275 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Kai-Ping Xie
School of Chemistry and Materials Engineering, Huizhou University, Huizhou, Guangdong, 516007 China
Key Laboratory of Bioinorganic and Synthetic Chemistry of Ministry of Education, School of Chemistry, IGCME, GBRCE for Functional Molecular Engineering, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, 510275 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorHai-Ling Wang
School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Guangxi Key Laboratory of Electrochemical Energy Materials, Guangxi Colleges and Universities Key Laboratory of Applied Chemistry Technology and Resource Development, Guangxi University, Nanning, Guangxi, 530004 China
Search for more papers by this authorZe-Yu Ruan
Key Laboratory of Bioinorganic and Synthetic Chemistry of Ministry of Education, School of Chemistry, IGCME, GBRCE for Functional Molecular Engineering, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, 510275 China
Search for more papers by this authorPei-Yu Liao
Key Laboratory of Bioinorganic and Synthetic Chemistry of Ministry of Education, School of Chemistry, IGCME, GBRCE for Functional Molecular Engineering, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, 510275 China
Search for more papers by this authorGuang Yang
Key Laboratory of Bioinorganic and Synthetic Chemistry of Ministry of Education, School of Chemistry, IGCME, GBRCE for Functional Molecular Engineering, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, 510275 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Zi-Cheng Xiao
School of Chemistry and Materials Engineering, Huizhou University, Huizhou, Guangdong, 516007 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Yi-Fei Deng
Department of Chemistry, Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen, Guangdong, 518055 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Si-Guo Wu
Key Laboratory of Bioinorganic and Synthetic Chemistry of Ministry of Education, School of Chemistry, IGCME, GBRCE for Functional Molecular Engineering, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, 510275 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorYan Shi
School of Chemistry and Materials Engineering, Huizhou University, Huizhou, Guangdong, 516007 China
Search for more papers by this authorMing-Liang Tong
Key Laboratory of Bioinorganic and Synthetic Chemistry of Ministry of Education, School of Chemistry, IGCME, GBRCE for Functional Molecular Engineering, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, 510275 China
Search for more papers by this authorComprehensive Summary
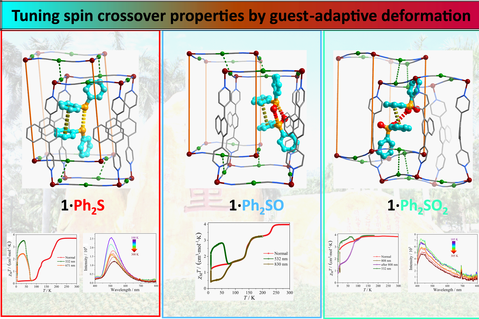
Three three-dimensional Hofmann-type metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) [Fe(bpn){Ag(CN)2}2]·Ph2S (1·Ph2S, bpn = 1,4-di(pyridin-4-yl)naphthalene, Ph2S = diphenylsulfide), [Fe(bpn){Ag(CN)2}2]·Ph2SO (1·Ph2SO, Ph2SO = diphenylsulfoxide) and [Fe(bpn){Ag(CN)2}2]·Ph2SO2 (1·Ph2SO2, Ph2SO2 = diphenylsulfone) were synthesized by employing sulfur-containing aromatic guests varying in oxidation states. 1·Ph2S performed a complete four-step spin crossover (SCO) behavior with the sequence of HS↔~LS1/3HS2/3↔~LS1/2HS1/2↔ ~LS2/3HS1/3↔LS, while an incomplete two-step SCO profile with the sequence of HS↔~LS1/3HS2/3↔~LS2/3HS1/3 and a faint SCO behavior at low temperature for 1·Ph2SO and 1·Ph2SO₂. Photomagnetic experiments indicate the light-induced excited spin-state trapping (LIESST) effect in 1·Ph2S and the bi-directional LIESST effect for 1·Ph2SO and 1·Ph2SO₂. Variable-temperature structural analyses reveal the evolution of host-guest synergy and highlight the mechanism of adaptive deformation of guests mediated by phenyl rotation amid spin transition. As the oxidation state of sulfur-containing guests increases, the host-guest cooperation within the lattice is limited by the steric effect, which stabilizes the high-spin state and consequently diminishes the SCO capability in this system. These results demonstrated herein open a new perspective on host-guest chemistry within SCO frameworks.
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| cjoc202500033-sup-0001-supinfo.pdfPDF document, 3.2 MB |
Appendix S1: Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1 Konig, E.; Ritter, G.; Kulshreshtha, S. K. The nature of spin-state transitions in solid complexes of iron(II) and the interpretation of some associated phenomena. Chem. Rev. 1985, 85, 219–234.
- 2 Gütlich, P.; Garcia, Y.; Goodwin, H. A. Spin crossover phenomena in Fe(II) complexes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2000, 29, 419–427.
- 3 Bousseksou, A.; Molnár, G.; Salmon, L.; Nicolazzi, W. Molecular spin crossover phenomenon: recent achievements and prospects. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 3313–3335.
- 4 Brooker, S. Spin crossover with thermal hysteresis: practicalities and lessons learnt. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 2880–2892.
- 5
Ye, Y.-S.; Chen, X.-Q.; Shen, K.-Y.; Tong, M.-L.; Bao, X. Acidity-Driven Bidirectional Room-Temperature Spin-State Switch and Fluorescence Modulation of a Mononuclear Fe(II) Complex. CCS Chem. 2020, 3, 2350–2358.
10.31635/ccschem.020.202000452 Google Scholar
- 6 Sun, Y.-C.; Li, Y.-L.; Zhang, C.-C.; Chen, F.-L.; Shao, D.; Zhao, Y.; Wei, H.-Y.; Wang, X.-Y. Gradual or Hysteretic Transition: Anion Effects on Cobalt(II) Spin Crossover Complexes. Chin. J. Chem. 2024, 42, 2381–2390.
- 7 Liu, Z.-K.; Ji, X.-Y.; Yu, M.; Li, Y.-X.; Hu, J.-S.; Zhao, Y.-M.; Yao, Z.-S.; Tao, J. Proton-Induced Reversible Spin-State Switching in Octanuclear FeIII Spin-Crossover Metal–Organic Cages. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 22036–22046.
- 8 Peng, S.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, Z.-Y.; Xu, G.-Y.; Zheng, W.-J.; Yang, F.-L.; Dai, J.-W.; Li, Z.-Y. Spin Crossover OFF/ON Triggered by Ligand Chemical Doping in an Fe(III) Solid Solution. Chin. J. Chem. 2025, 43, 90–96.
- 9 Yi, C.; Meng, Y.-S.; Zhao, L.; Yao, N.-T.; Liu, Q.; Wen, W.; Li, R.-X.; Zhu, Y.-Y.; Oshio, H.; Liu, T. A Smart Molecule Showing Spin Crossover Responsive Aggregation-Induced Emission. CCS Chem. 2022, 5, 915–924.
- 10 Javed, M. K.; Sulaiman, A.; Yamashita, M.; Li, Z.-Y. Shedding light on bifunctional luminescent spin crossover materials. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2022, 467, 214625.
- 11 Du, S.-N.; Yao, C.-Y.; Liu, J.-L.; Tong, M.-L. Magnetic Switchability via Thermal-Induced Structural Phase Transitions in Molecular Solids. Magnetochemistry 2023, 9, 80.
- 12 Liu, C.; Li, Y.; Tang, Z.; Gao, K.-G.; Xie, J.; Tao, J.; Yao, Z.-S. High-performance Pyroelectric Property Accompanied by Spin Crossover in a Single Crystal of Fe(II) Complex. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202405514.
- 13 Zakrzewski, J. J.; Liberka, M.; Wang, J.; Chorazy, S.; Ohkoshi, S.-i. Optical Phenomena in Molecule-Based Magnetic Materials. Chem. Rev. 2024, 124, 5930–6050.
- 14 Ai, Y.; Hu, Z.-B.; Weng, Y.-R.; Peng, H.; Qi, J.-C.; Chen, X.-G.; Lv, H.-P.; Song, X.-J.; Ye, H.-Y.; Xiong, R.-G. A Multiferroic Spin-Crossover Molecular Crystal. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2407822.
- 15 Wu, X.-R.; Wu, S.-Q.; Liu, Z.-K.; Chen, M.-X.; Tao, J.; Sato, O.; Kou, H.-Z. Integrating spin-dependent emission and dielectric switching in FeII catenated metal-organic frameworks. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 3961.
- 16 Charytanowicz, T.; Wang, J.; Tokoro, H.; Tran, K.; Renz, F.; Ohkoshi, S.-i.; Chorazy, S.; Sieklucka, B. Thermal Bistability of Magnetic Susceptibility, Light Absorption, Second Harmonic Generation, and Dielectric Properties in a Polar Spin-Crossover Iron–Rhenium Chain Material. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2025, 64, e202419242.
- 17 Zhao, X.-H.; Deng, Y.-F.; Xi, J.; Huang, J.-Q.; Zhang, Y.-Z. Supramolecular Spring-Like Fe(II) Spin-Crossover Complexes Experiencing Giant and Anisotropic Thermal Expansion Across Two Distinct Temperature Regimes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2025, 64, e202414826.
- 18 Getzner, L.; Paliwoda, D.; Vendier, L.; Lawson-Daku, L. M.; Rotaru, A.; Molnár, G.; Cobo, S.; Bousseksou, A. Combining electron transfer, spin crossover, and redox properties in metal-organic frameworks. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 7192.
- 19 Murphy, M. J.; Zenere, K. A.; Ragon, F.; Southon, P. D.; Kepert, C. J.; Neville, S. M. Guest Programmable Multistep Spin Crossover in a Porous 2-D Hofmann-Type Material. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 1330–1335.
- 20 Cruddas, J.; Powell, B. J. Spin-State Ice in Elastically Frustrated Spin-Crossover Materials. J. Am. Chem. Soc.2019, 141, 19790–19799.
- 21 Cruddas, J.; Powell, B. J. Structure–property relationships and the mechanisms of multistep transitions in spin crossover materials and frameworks. Inorg. Chem. Front.2020, 7, 4424–4437.
- 22 Natt, N.; Powell, B. J. Complex relaxation of trapped spin-states in spin crossover materials. Chem. Sci. 2024, 15, 17862–17872.
- 23 Decurtins, S.; Gütlich, P.; Köhler, C. P.; Spiering, H.; Hauser, A. Light-induced excited spin state trapping in a transition-metal complex: The hexa-1-propyltetrazole-iron(II) tetrafluoroborate spin- crossover system. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1984, 105, 1–4.
- 24 Létard, J.-F.; Real, J. A.; Moliner, N.; Gaspar, A. B.; Capes, L.; Cador, O.; Kahn, O. Light Induced Excited Pair Spin State in an Iron(II) Binuclear Spin-Crossover Compound. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999, 121, 10630–10631.
- 25 Sun, H.-Y.; Meng, Y.-S.; Liu, T. Photo-switched magnetic coupling in spin-crossover complexes. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 8359–8373.
- 26 Gakiya-Teruya, M.; Jiang, X.; Le, D.; Üngör, Ö.; Durrani, A. J.; Koptur-Palenchar, J. J.; Jiang, J.; Jiang, T.; Meisel, M. W.; Cheng, H.-P. Asymmetric Design of Spin-Crossover Complexes to Increase the Volatility for Surface Deposition. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 14563–14572.
- 27 Yan, F.-F.; Jiang, W.-J.; Yao, N.-T.; Mao, P.-D.; Zhao, L.; Sun, H.-Y.; Meng, Y.-S.; Liu, T. Manipulating fluorescence by photo-switched spin-state conversions in an iron(ii)-based SCO-MOF. Chem. Sci. 2023, 14, 6936–6942.
- 28 Milin, E.; Patinec, V.; Triki, S.; Bendeif, E.-E.; Pillet, S.; Marchivie, M.; Chastanet, G.; Boukheddaden, K. Elastic Frustration Triggering Photoinduced Hidden Hysteresis and Multistability in a Two-Dimensional Photoswitchable Hofmann-Like Spin-Crossover Metal–Organic Framework. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 55, 11652–11661.
- 29 Ye, Y.-S.; Chen, X.-Q.; De, C.-Y.; Fei, B.; Dechambenoit, P.; Rouzières, M.; Mathonière, C.; Clérac, R.; Bao, X. Slow Dynamics of the Spin-Crossover Process in an Apparent High-Spin Mononuclear FeII Complex. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 18888–18891.
- 30 Mondal, D. J.; Kumar, B.; Shome, S.; Konar, S. Observation of TLIESST above Liquid Nitrogen Temperature and Disclosure of Hidden Hysteresis in Multiresponsive Hofmann-type Coordination Polymers. Inorg. Chem. 2024, 63, 15752–15761.
- 31 Chen, Y.-R.; Ying, T.-T.; Chen, Y.-C.; Liao, P.-Y.; Ni, Z.-P.; Tong, M.-L. Bidirectional photomagnetism, exciplex fluorescence and dielectric anomalies in a spin crossover Hofmann-type coordination polymer. Chem. Sci. 2024, 15, 9240–9248,
- 32 Li, G.; Stefanczyk, O.; Kumar, K.; Guérin, L.; Okuzono, K.; Tran, K.; Seydi Kilic, M.; Nakabayashi, K.; Imoto, K.; Namai, A. Near-Infrared Light-Induced Spin-State Switching Based on Fe(II)−Hg(II) Spin- Crossover Network. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, e202423095.
- 33 Xu, M.-X.; Liu, Z.; Dong, B.-W.; Cui, H.-H.; Wang, Y.-X.; Su, J.; Wang, Z.; Song, Y.; Chen, X.-T.; Jiang, S.-D.; Gao, S. Single-Crystal Study of a Low Spin Co(II) Molecular Qubit: Observation of Anisotropic Rabi Cycles. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 58, 2330–2335.
- 34 Xie, K.-P.; Ruan, Z.-Y.; Chen, X.-X.; Yang, J.; Wu, S.-G.; Ni, Z.-P.; Tong, M.-L. Light-induced hidden multistability in a spin crossover metal–organic framework. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2022, 9, 1770–1776
- 35 Cui, W.; Wu, W.-W.; Ruan, Z.-Y.; Chen, Y.-C.; Zeng, G.-J.; Chen, G.-X.; Wu, S.-G.; Ni, Z.-P.; Tong, M.-L. Light-induced stepped thermal relaxation in a Hofmann-type metal-organic framework. Sci. China Chem. 2024, 67, 1983–1989.
- 36 Niel, V.; Martinez-Agudo, J. M.; Muñoz, M. C.; Gaspar, A. B.; Real, J. A. Cooperative Spin Crossover Behavior in Cyanide-Bridged Fe(II)−M(II) Bimetallic 3D Hofmann-like Networks (M = Ni, Pd, and Pt). Inorg. Chem. 2001, 40, 3838–3839.
- 37
Niel, V.; Muñoz, M. C.; Gaspar, A. B.; Galet, A.; Levchenko, G.; Real, J. A. Thermal-, Pressure-, and Light-Induced Spin Transition in Novel Cyanide-Bridged FeII-AgI Bimetallic Compounds with Three-Dimensional Interpenetrating Double Structures {FeIIL[Ag(CN)2]2}·G. Chem. Eur. J. 2002, 8, 2446–2453.
10.1002/1521-3765(20020603)8:11<2446::AID-CHEM2446>3.0.CO;2-K CAS PubMed Web of Science® Google Scholar
- 38 Muñoz, M. C.; Real, J. A. Thermo-, piezo-, photo- and chemo- switchable spin crossover iron(II)-metallocyanate based coordination polymers. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2011, 255, 2068–2093.
- 39 Ni, Z.-P.; Liu, J.-L.; Hoque, M. N.; Liu, W.; Li, J.-Y.; Chen, Y.-C.; Tong, M.-L. Recent advances in guest effects on spin-crossover behavior in Hofmann-type metal-organic frameworks. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2017, 335, 28–43.
- 40 Ahmed, M.; Zenere, K. A.; Sciortino, N. F.; Arachchige, K. S. A.; Turner, G. F.; Cruddas, J.; Hua, C.; Price, J. R.; Clegg, J. K.; Valverde-Muñoz, F. J. Regulation of Multistep Spin Crossover Across Multiple Stimuli in a 2-D Framework Material. Inorg. Chem. 2022, 61, 6641–6649.
- 41 Xue, J.-P.; Hu, Y.; Zhao, B.; Liu, Z.-K.; Xie, J.; Yao, Z.-S.; Tao, J. A spin-crossover framework endowed with pore-adjustable behavior by slow structural dynamics. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3510.
- 42 Wu, X.-R.; Wu, S.-Q.; Liu, Z.-K.; Chen, M.-X.; Tao, J.; Sato, O.; Kou, H.-Z. Manipulating guest-responsive spin transition to achieve switchable fluorescence in a Hofmann-type framework. Sci. China Chem. 2024, 67, 3339–3346.
- 43 Sciortino, N. F.; Zenere, K. A.; Corrigan, M. E.; Halder, G. J.; Chastanet, G.; Létard, J.-F.; Kepert, C. J.; Neville, S. M. Four-step iron(II) spin state cascade driven by antagonistic solid state interactions. Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 701–707
- 44 Clements, J. E.; Price, J. R.; Neville, S. M.; Kepert, C. J. Hysteretic Four-Step Spin Crossover within a Three-Dimensional Porous Hofmann-like Material. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 15105–15109.
- 45 Liu, W.; Peng, Y.-Y.; Wu, S.-G.; Chen, Y.-C.; Hoque, M. N.; Ni, Z.-P.; Chen, X.-M.; Tong, M.-L. Guest-Switchable Multi-Step Spin Transitions in an Amine-Functionalized Metal–Organic Framework. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 14982–14986.
- 46 Peng, Y.-Y.; Wu, S.-G.; Chen, Y.-C.; Liu, W.; Huang, G.-Z.; Ni, Z.-P.; Tong, M.-L. Asymmetric seven-/eight-step spin-crossover in a three- dimensional Hofmann-type metal–organic framework. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2020, 7, 1685–1690.
- 47 Delgado, T.; Meneses-Sánchez, M.; Piñeiro-López, L.; Bartual-Murgui, C.; Muñoz, M. C.; Real, J. A. Thermo- and photo-modulation of exciplex fluorescence in a 3D spin crossover Hofmann-type coordination polymer. Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 8446–8452.
- 48 Zhang, C.-J.; Lian, K.-T.; Wu, S.-G.; Liu, Y.; Huang, G.-Z.; Ni, Z.-P.; Tong, M.-L. The substituent guest effect on four-step spin-crossover behavior. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2020, 7, 911–917.
- 49 Piñeiro-López, L.; Valverde-Muñoz, F.-J.; Trzop, E.; Muñoz, M. C.; Seredyuk, M.; Castells-Gil, J.; da Silva, I.; Martí-Gastaldo, C.; Collet, E.; Real, J. A. Guest induced reversible on–off switching of elastic frustration in a 3D spin crossover coordination polymer with room temperature hysteretic behaviour. Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 1317–1326.
- 50 Xie, K.-P.; Ruan, Z.-Y.; Lyu, B.-H.; Chen, X.-X.; Zhang, X.-W.; Huang, G.-Z.; Chen, Y.-C.; Ni, Z.-P.; Tong, M.-L. Guest-Driven Light-Induced Spin Change in an Azobenzene Loaded Metal–Organic Framework. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 27144–27150.
- 51 Yao, N.-T.; Zhao, L.; Sun, H.-Y.; Yi, C.; Guan, Y.-H.; Li, Y.-M.; Oshio, H.; Meng, Y.-S.; Liu, T. Simultaneous Photo-Induced Magnetic and Dielectric Switching in an Iron(II)-Based Spin-Crossover Hofmann-Type Metal-Organic Framework. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202208208.
- 52 Ohba, M.; Yoneda, K.; Agustí, G.; Muñoz, M. C.; Gaspar, A. B.; Real, J. A.; Yamasaki, M.; Ando, H.; Nakao, Y.; Sakaki, S. Bidirectional Chemo- Switching of Spin State in a Microporous Framework. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 4767–4771.
- 53 Sheldrick, G. M. SHELXT - integrated space-group and crystal-structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. A Found. Adv. 2015, 71, 3–8.
- 54 Sheldrick, G. M. A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. A Found. Adv. 2008, 64, 112–122.
- 55 Dolomanov, O. V.; Bourhis, L. J.; Gildea, R. J.; Howard, J. A. K.; Puschmann, H. OLEX2: a complete structure solution, refinement and analysis program. J. Appl. Cryst. 2009, 42, 339–341.