A Selenium Atom Involved Covalent Organic Framework for Window Ledge Photocatalytic Oxidation of Sulfides
Corresponding Author
Fan Yang
College of Chemistry, Chemical Engineering and Materials Science, Collaborative Innovation Center of Functionalized Probes for Chemical Imaging in Universities of Shandong, Key Laboratory of Molecular and Nano Probes, Ministry of Education, Shandong Normal University, Jinan, Shandong, 250014 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
E-mail: [email protected], [email protected], [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorXia Li
College of Chemistry, Chemical Engineering and Materials Science, Collaborative Innovation Center of Functionalized Probes for Chemical Imaging in Universities of Shandong, Key Laboratory of Molecular and Nano Probes, Ministry of Education, Shandong Normal University, Jinan, Shandong, 250014 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorHong-Yan Qu
College of Chemistry, Chemical Engineering and Materials Science, Collaborative Innovation Center of Functionalized Probes for Chemical Imaging in Universities of Shandong, Key Laboratory of Molecular and Nano Probes, Ministry of Education, Shandong Normal University, Jinan, Shandong, 250014 China
Search for more papers by this authorJing-Lan Kan
College of Chemistry, Chemical Engineering and Materials Science, Collaborative Innovation Center of Functionalized Probes for Chemical Imaging in Universities of Shandong, Key Laboratory of Molecular and Nano Probes, Ministry of Education, Shandong Normal University, Jinan, Shandong, 250014 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Yuan Guo
School of Light Industry and Engineering, Qilu University of Technology (Shandong Academy of Sciences), Jinan, Shandong, 250353 China
E-mail: [email protected], [email protected], [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Yu-Bin Dong
College of Chemistry, Chemical Engineering and Materials Science, Collaborative Innovation Center of Functionalized Probes for Chemical Imaging in Universities of Shandong, Key Laboratory of Molecular and Nano Probes, Ministry of Education, Shandong Normal University, Jinan, Shandong, 250014 China
E-mail: [email protected], [email protected], [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Fan Yang
College of Chemistry, Chemical Engineering and Materials Science, Collaborative Innovation Center of Functionalized Probes for Chemical Imaging in Universities of Shandong, Key Laboratory of Molecular and Nano Probes, Ministry of Education, Shandong Normal University, Jinan, Shandong, 250014 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
E-mail: [email protected], [email protected], [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorXia Li
College of Chemistry, Chemical Engineering and Materials Science, Collaborative Innovation Center of Functionalized Probes for Chemical Imaging in Universities of Shandong, Key Laboratory of Molecular and Nano Probes, Ministry of Education, Shandong Normal University, Jinan, Shandong, 250014 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorHong-Yan Qu
College of Chemistry, Chemical Engineering and Materials Science, Collaborative Innovation Center of Functionalized Probes for Chemical Imaging in Universities of Shandong, Key Laboratory of Molecular and Nano Probes, Ministry of Education, Shandong Normal University, Jinan, Shandong, 250014 China
Search for more papers by this authorJing-Lan Kan
College of Chemistry, Chemical Engineering and Materials Science, Collaborative Innovation Center of Functionalized Probes for Chemical Imaging in Universities of Shandong, Key Laboratory of Molecular and Nano Probes, Ministry of Education, Shandong Normal University, Jinan, Shandong, 250014 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Yuan Guo
School of Light Industry and Engineering, Qilu University of Technology (Shandong Academy of Sciences), Jinan, Shandong, 250353 China
E-mail: [email protected], [email protected], [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Yu-Bin Dong
College of Chemistry, Chemical Engineering and Materials Science, Collaborative Innovation Center of Functionalized Probes for Chemical Imaging in Universities of Shandong, Key Laboratory of Molecular and Nano Probes, Ministry of Education, Shandong Normal University, Jinan, Shandong, 250014 China
E-mail: [email protected], [email protected], [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorComprehensive Summary
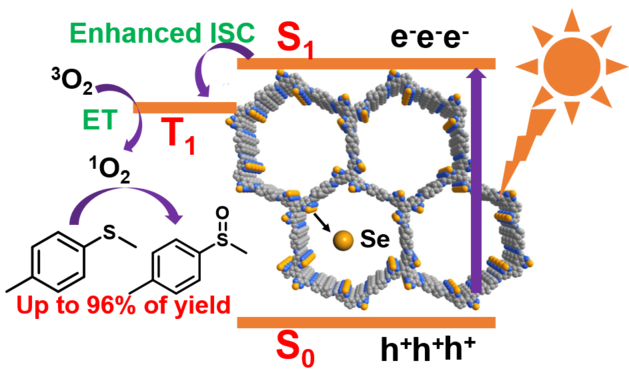
Covalent organic frameworks (COFs) driven photocatalytic organic transformations especially photooxidation reactions have become a fertile topic and attracted numerous research attentions. Boosting the charge generation and transport process is the key factor for achieving high catalytic efficiencies. As one of the most effective strategies, the introduction of “heavy atoms” into the long-range ordered conjugated backbones can effectively facilitate the intersystem crossing (ISC) process and hence improve the generation of active oxygens, which is beneficial for the oxidation. In this work, we designed and synthesized a benzoselenadiazole based covalent organic framework (COF) material, BSe-COF with heavy atom of selenium (Se), and a benzothiadiazole based BT-COF with isomorphic backbone for comparison. Compared to BT-COF, BSe-COF exhibits broader absorption range, stronger photocurrent response and enhanced intersystem crossing (ISC) with higher singlet oxygen (1O2) generation efficiency. When applied in photocatalytic organic transformation, BSe-COF presents remarkably higher photocatalytic activity in the oxidation of sulfides than BT-COF under the irradiation of blue LED lamp. Furthermore, BSe-COF can be used as efficient photocatalyst for the window ledge reaction with high yields (over 84%) of various sulfoxides from a wide range of thioether substrates scope.
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| cjoc202400139-sup-0001-supinfo.pdfPDF document, 2.9 MB |
Appendix S1: Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1(a) Dai, L.; Dong, A.; Meng, X.; Liu, H.; Li, Y.; Li, P.; Wang, B. Enhancement of Visible-Light-Driven Hydrogen Evolution Activity of 2D π-Conjugated Bipyridine-Based Covalent Organic Frameworks via Post-Protonation, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202300224; (b) Fu, Z.; Wang, X.; Gardner, A. M.; Wang, X.; Chong, S. Y.; Neri, G.; Cowan, A. J.; Liu, L.; Li, X.; Vogel, A.; Clowes, R.; Bilton, M.; Chen, L.; Sprick, R. S.; Cooper, A. I. A stable covalent organic framework for photocatalytic carbon dioxide reduction. Chem. Sci. 2020, 11, 543–550; (c) Lu, M.; Liu, J.; Li, Q.; Zhang, M.; Liu, M.; Wang, J.-L.; Yuan, D.-Q.; Lan, Y.-Q. Rational Design of Crystalline Covalent Organic Frameworks for Efficient CO2 Photoreduction with H2O. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 12392–12397; (d) Liu, F.; He, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, Z.; Liu, H.-L.; Zhu, X.; Hou, C.-C.; Weng, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, Y. Regulating Excitonic Effects in Covalent Organic Frameworks to Promote Free Charge Carrier Generation. ACS Catal. 2022, 12, 9494–9502; (e) Wang, J.-l.; Ouyang, G.; Wang, D.; Li, J.; Yao, J.; Li, W.-S.; Li, H. Enhanced Photocatalytic Performance of Donor–Acceptor-Type Polymers Based on a Thiophene-Contained Polycyclic Aromatic Unit. Macromolecules 2021, 54, 2661–2666; (f) Prier, C. K.; Rankic, D. A.; MacMillan, D. W. C. Visible Light Photoredox Catalysis with Transition Metal Complexes: Applications in Organic Synthesis. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 5322–5363.
- 2(a) Dasi, R.; Villinger, A.; Brasholz, M. Photocatalytic Azetidine Synthesis by Aerobic Dehydrogenative [2 + 2] Cycloadditions of Amines with Alkenes. Org. Lett. 2022, 24, 8041–8046; (b) Liu, S.; Pan, W.; Wu, S.; Bu, X.; Xin, S.; Yu, J.; Xu, H.; Yang, X. Visible-light-induced tandem radical addition–cyclization of 2-aryl phenyl isocyanides catalysed by recyclable covalent organic frameworks. Green Chem. 2019, 21, 2905–2910.
- 3(a) Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Lang, X. Symmetry-dependent photocatalysis of conjugated microporous polymers based on pyrene for oxygenation of sulfides with O2. Appl. Catal., B 2024, 340, 123190; (b) Wu, C.-J.; Li, X.-Y.; Li, T.-R.; Shao, M.-Z.; Niu, L.-J.; Lu, X.-F.; Kan, J.-L.; Geng, Y.; Dong, Y.-B. Natural Sunlight Photocatalytic Synthesis of Benzoxazole-Bridged Covalent Organic Framework for Photocatalysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 18750–18755.
- 4(a) Li, Y.-L.; Li, A.-J.; Huang, S.-L.; Vittal, J. J.; Yang, G.-Y. Polypyridyl Ru(II) or cyclometalated Ir(III) functionalized architectures for photocatalysis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2023, 52, 4725–4754; (b) Ma, W.; Xu, L.; Zhang, S.; Li, G.; Ma, T.; Rao, B.; Zhang, M.; He, G. Phosphorescent Bismoviologens for Electrophosphorochromism and Visible Light- Induced Cross-Dehydrogenative Coupling. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 1590–1597; (c) Kang, X.; Wu, X.; Han, X.; Yuan, C.; Liu, Y.; Cui, Y. Rational synthesis of interpenetrated 3D covalent organic frameworks for asymmetric photocatalysis. Chem. Sci. 2020, 11, 1494–1502.
- 5 Dai, C.; Liu, B. Conjugated polymers for visible-light-driven photocatalysis. Energy Environ. Sci. 2020, 13, 24–52.
- 6(a) Xu, Y.; Ren, G.; Zhang, D.; Sun, L.; Zhao, Y. Fully Conjugated Covalent Organic Frameworks: Synthesis, Structures and Applications. Chin. J. Chem. 2023, 41, 3447–3472; (b) Dong, M.; Li, W.; Zhou, J.; You, S.-Q.; Sun, C.-Y.; Yao, X.-H.; Qin, C.; Wang, X.-L.; Su, Z.-M. Microenvironment Modulation of Imine-Based Covalent Organic Frameworks for CO2 Photoreduction. Chin. J. Chem. 2022, 40, 2678–2684.
- 7(a) Huang, N.-Y.; Zheng, Y.-T.; Chen, D.; Chen, Z.-Y.; Huang, C.-Z.; Xu, Q. Reticular framework materials for photocatalytic organic reactions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2023, 52, 7949–8004; (b) Gong, Y.-N.; Guan, X.; Jiang, H.-L. Covalent organic frameworks for photocatalysis: Synthesis, structural features, fundamentals and performance. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2023, 475, 214889; (c) Zhou, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Tian, J.; Nan, N.; Song, R.; Li, J. Recent advances in metal-free covalent organic frameworks for photocatalytic applications in energy and environmental fields. J. Mater. Chem. A 2023, 11, 3245–3261; (d) Wang, G.-B.; Xie, K.-H.; Xu, H.-P.; Wang, Y.-J.; Zhao, F.; Geng, Y.; Dong, Y.-B. Covalent organic frameworks and their composites as multifunctional photocatalysts for efficient visible-light induced organic transformations. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2022, 472, 214774; (e) Basak, A.; Karak, S.; Banerjee, R. Covalent Organic Frameworks as Porous Pigments for Photocatalytic Metal-Free C–H Borylation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 7592–7599.
- 8(a) Nailwal, Y.; Wonanke, A. D. D.; Addicoat, M. A.; Pal, S. K. A Dual-Function Highly Crystalline Covalent Organic Framework for HCl Sensing and Visible-Light Heterogeneous Photocatalysis. Macromolecules 2021, 54, 6595–6604; (b) Yan, X.; Liu, H.; Li, Y.; Chen, W.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, Z.; Xing, G.; Chen, L. Ultrastable Covalent Organic Frameworks via Self-Polycondensation of an A2B2 Monomer for Heterogeneous Photocatalysis. Macromolecules 2019, 52, 7977–7983; (c) Li, Z.; Wang, J.-a.; Ma, S.; Zhang, Z.; Zhi, Y.; Zhang, F.; Xia, H.; Henkelman, G.; Liu, X. 2D covalent organic frameworks for photosynthesis of α-trifluoromethylated ketones from aromatic alkenes, Appl. Catal., B 2022, 310, 121335; (d) Sun, N.; Jin, Y.; Wang, H.; Yu, B.; Wang, R.; Wu, H.; Zhou, W.; Jiang, J. Photoresponsive Covalent Organic Frameworks with Diarylethene Switch for Tunable Singlet Oxygen Generation. Chem. Mater. 2022, 34, 1956–1964.
- 9(a) Shang, P.; Yan, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, G.; Chen, L. Heterogeneous photocatalytic borylation of aryl iodides mediated by isoreticular 2D covalent organic frameworks. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2023, 34, 107584; (b) Li, W.; Huang, X.; Zeng, T.; Liu, Y. A.; Hu, W.; Yang, H.; Zhang, Y.-B.; Wen, K.Thiazolo[5,4-d]thiazole-Based Donor–Acceptor Covalent Organic Framework for Sunlight-Driven Hydrogen Evolution. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 1869–1874; (c) Zhao, C.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, N.; You, S.; Li, W. Diketopyrrolopyrrole-based conjugated materials for non-fullerene organic solar cells. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 10174–10199; (d) Zhao, C.; Yang, F.; Xia, D.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, N.; You, S.; Li, W. Thieno[3,4-c]pyrrole-4,6-dione-based conjugated polymers for organic solar cells. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 10394–10408.
- 10 Xia, Y.; Zhang, W.; Yang, S.; Wang, L.; Yu, G. Research Progress in Donor−Acceptor Type Covalent Organic Frameworks. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2301190.
- 11(a) Mao, Z.; Yang, Z.; Mu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.-F.; Chi, Z.; Lo, C.-C.; Liu, S.; Lien, A.; Xu, J. Linearly Tunable Emission Colors Obtained from a Fluorescent–Phosphorescent Dual-Emission Compound by Mechanical Stimuli. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 6270–6273; (b) Xiao, L.; Wu, Y.; Chen, J.; Yu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Yao, J.; Fu, H. Highly Efficient Room-Temperature Phosphorescence from Halogen-Bonding-Assisted Doped Organic Crystals. J. Phys. Chem. A 2017, 121, 8652–8658; (c) Zou, J.; Yin, Z.; Ding, K.; Tang, Q.; Li, J.; Si, W.; Shao, J.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, W.; Dong, X. BODIPY Derivatives for Photodynamic Therapy: Influence of Configuration versus Heavy Atom Effect. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 32475–32481; (d) Wu, K.; Liu, X.-Y.; Cheng, P.-W.; Huang, Y.-L.; Zheng, J.; Xie, M.; Lu, W.; Li, D. Linker Engineering for Reactive Oxygen Species Generation Efficiency in Ultra-Stable Nickel-Based Metal–Organic Frameworks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 18931–18938.
- 12(a) Sun, P.; Dong, H.; Lv, S.; Yin, Y.; Gong, G.; Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Chen, S. A zinc porphyrin-based halogen-bonded organic framework with the heavy atom effect as a highly efficient photocatalyst for oxidative coupling of amines. J. Mater. Chem. A 2024, 12, 1128–1134; (b) Lee, D. R.; Lee, K. H.; Shao, W.; Kim, C. L.; Kim, J.; Lee, J. Y. Heavy Atom Effect of Selenium for Metal-Free Phosphorescent Light-Emitting Diodes. Chem. Mater. 2020, 32, 2583–2592.
- 13(a) Meng, Y.; Luo, Y.; Shi, J.-L.; Ding, H.; Lang, X.; Chen, W.; Zheng, A.; Sun, J.; Wang, C. 2D and 3D Porphyrinic Covalent Organic Frameworks: The Influence of Dimensionality on Functionality. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 3624–3629; (b) Jiménez-Almarza, A.; López-Magano, A.; Marzo, L.; Cabrera, S.; Mas-Ballesté, R.; Alemán, J. Imine-Based Covalent Organic Frameworks as Photocatalysts for Metal Free Oxidation Processes under Visible Light Conditions. ChemCatChem 2019, 11, 4916–4922; (c) Hao, W.; Chen, D.; Li, Y.; Yang, Z.; Xing, G.; Li, J.; Chen, L. Facile Synthesis of Porphyrin Based Covalent Organic Frameworks via an A2B2 Monomer for Highly Efficient Heterogeneous Catalysis. Chem. Mater. 2019, 31, 8100–8105; (d) Xu, T.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Xing, G.; Chen, L. N,N’-Bicarbazole-Based Covalent Triazine Frameworks as High-Performance Heterogeneous Photocatalysts. Macromolecules 2019, 52, 9786–9791.
- 14 Yang, F.; Qu, H.-Y.; Guo, Y.; Kan, J.-L.; Dong, Y.-B. Boosting the photocatalytic performance via isomeric configuration design in covalent organic frameworks. Chem. Commun. 2022, 58, 13210–13213.
- 15 Wojaczyńska, E.; Wojaczyński, J. Enantioselective Synthesis of Sulfoxides: 2000−2009. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 4303–4356.
- 16(a) Gu, Z.; Wang, J.; Shan, Z.; Wu, M.; Liu, T.; Song, L.; Wang, G.; Ju, X.; Su, J.; Zhang, G. Modulating electronic structure of triazine-based covalent organic frameworks for photocatalytic organic transformations. J. Mater. Chem. A 2022, 10, 17624–17632; (b) Li, Q.; Lan, X.; An, G.; Ricardez-Sandoval, L.; Wang, Z.; Bai, G. Visible-Light-Responsive Anthraquinone Functionalized Covalent Organic Frameworks for Metal-Free Selective Oxidation of Sulfides: Effects of Morphology and Structure. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 6664–6675.
- 17 Wei, H.; Guo, Z.; Liang, X.; Chen, P.; Liu, H.; Xing, H. Selective Photooxidation of Amines and Sulfides Triggered by a Superoxide Radical Using a Novel Visible-Light-Responsive Metal–Organic Framework. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 3016–3023.
- 18 Yue, J.-Y.; Song, L.-P.; Fan, Y.-F.; Pan, Z.-X.; Yang, P.; Ma, Y.; Xu, Q.; Tang, B. Thiophene-Containing Covalent Organic Frameworks for Overall Photocatalytic H2O2 Synthesis in Water and Seawater. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202309624.
- 19(a) de Sousa, L. E.; de Silva, P. Unified Framework for Photophysical Rate Calculations in TADF Molecules. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2021, 17, 5816–5824; (b) An, F.; Zhao, Y.; Li, H.; Meng, J.; Jiao, L.; Zhang, Z.; Li, X.; Sun, X. Intramolecular charge transfer versus intersystem crossing: The way toward super-high photothermal efficiency by thionation. Dyes Pigm. 2023, 217, 111411.
- 20 Gao, X.; Bai, S.; Fazzi, D.; Niehaus, T.; Barbatti, M.; Thiel, W. Evaluation of Spin-Orbit Couplings with Linear-Response Time-Dependent Density Functional Methods. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2017, 13, 515–524.




