Hydrogel-Assisted Electrokinetics for High-Resolution and Non-invasive Flow Monitoring in Microfluidic Chips†
Na Zhao
MOE Key Laboratory of Hydraulic Machinery Transients, School of Power and Mechanical Engineering, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430072 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorYanni Ma
MOE Key Laboratory of Hydraulic Machinery Transients, School of Power and Mechanical Engineering, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430072 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorZehua Yu
MOE Key Laboratory of Hydraulic Machinery Transients, School of Power and Mechanical Engineering, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430072 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Jun Huang
MOE Key Laboratory of Hydraulic Machinery Transients, School of Power and Mechanical Engineering, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430072 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorXiangqian Fu
MOE Key Laboratory of Hydraulic Machinery Transients, School of Power and Mechanical Engineering, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430072 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Tao Qiu
Department of Urology, Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430072 China
Department of Organ Transplantation, Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430072 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Kang Liu
MOE Key Laboratory of Hydraulic Machinery Transients, School of Power and Mechanical Engineering, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430072 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorNa Zhao
MOE Key Laboratory of Hydraulic Machinery Transients, School of Power and Mechanical Engineering, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430072 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorYanni Ma
MOE Key Laboratory of Hydraulic Machinery Transients, School of Power and Mechanical Engineering, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430072 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorZehua Yu
MOE Key Laboratory of Hydraulic Machinery Transients, School of Power and Mechanical Engineering, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430072 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Jun Huang
MOE Key Laboratory of Hydraulic Machinery Transients, School of Power and Mechanical Engineering, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430072 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorXiangqian Fu
MOE Key Laboratory of Hydraulic Machinery Transients, School of Power and Mechanical Engineering, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430072 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Tao Qiu
Department of Urology, Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430072 China
Department of Organ Transplantation, Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430072 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Kang Liu
MOE Key Laboratory of Hydraulic Machinery Transients, School of Power and Mechanical Engineering, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430072 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorDedicated to the 130th Anniversary of Wuhan University.
Comprehensive Summary
Convenient non-invasive flow monitoring would facilitate the operation and control in microfluidic chips, but is challenging due to the small space of microchannels and complex operation required in traditional optical methods. In this work, we propose a novel non-invasive strategy to probe microfluidic flows via streaming potential phenomenon. By sealing one side of the microchannel with a piece of hydrogel film, streaming potential inside the channel can be clearly detected by electrodes at outer surface of the hydrogel due to ion diffusion in the hydrogel. Flow is detected without sensors contacting with the internal liquid. Moreover, the electrodes shape like a tiny probe, which can move around mapping the flow distribution in a chip with the spatial resolution of 1 mm and flow rate detection limit of 3 μL·min–1. Bubbles inside the channels can also be detected, due to the fluctuation of streaming voltage when gas-liquid interface flows through the electrode, showing an easy and potential way for multi-functional flow monitoring in microfluidic chips.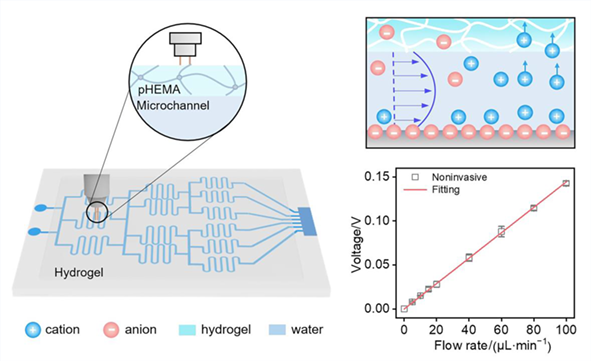
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| cjoc202300582-sup-0001-supinfo.pdfPDF document, 644.5 KB |
Appendix S1: Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1 Low, L. A.; Mummery, C.; Berridge, B. R.; Austin, C. P.; Tagle, D. A. Organs-on-Chips: Into the Next Decade. Nat. Rev. Drug discov. 2020, 20, 345–361.
- 2 Wang, X.; Jia, J.; Niu, M.; Li, W.; Zhao, Y. J. Living Chinese Herbal Scaffolds from Microfluidic Bioprinting for Wound Healing. Research 2023, 6, 0138.
- 3 Kashaninejad, N.; Nguyen, N. T. Microfluidic Solutions for Biofluids Handling in on-Skin Wearable Systems. Lab Chip 2023, 23, 913–937.
- 4 Liu, Y.; Sun, L.; Zhang, H.; Shang, L.; Zhao, Y. Microfluidics for Drug Development: From Synthesis to Evaluation. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 7468–7529.
- 5 Zhang, Q.; Kuang, G.; Yu, Y.; Ding, X.; Ren, H.; Sun, W.; Zhao, Y. J. Hierarchical Microparticles Delivering Oxaliplatin and Nlg919 Nanoprodrugs for Local Chemo-Immunotherapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 48527–48539.
- 6 Liu, K.; Ding, T. P.; Mo, X.; Chen, Q.; Yang, P. H.; Li, J.; Xie, W.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, J. Flexible Microfluidics Nanogenerator Based on the Electrokinetic Conversion. Nano Energy 2016, 30, 684–690.
- 7 Liu, Y. X.; Yu, Z. H.; Liu, X. W.; Cheng, P.; Zhao, Y. F.; Ma, Y. N.; Yang, P. H.; Liu, K. Negative Pressure in Water for Efficient Heat Utilization and Transfer. Nano Lett. 2023, 23, 6651–6657.
- 8 Su, L.; Xiong, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Zi, Y. A Liquid–Solid Contact Electrification Based All-Optical Liquid Flow Sensor for Microfluidic Analysis in Biomedical Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2207096.
- 9
Chen, H.; Guo, J.; Bian, F.; Zhao, Y. Microfluidic Technologies for Cell Deformability Cytometry. Smart Med. 2022, 1, e20220001.
10.1002/SMMD.20220001 Google Scholar
- 10 Sanfilippo, J. E.; Lorestani, A.; Koch, M. D.; Bratton, B. P.; Siryaporn, A.; Stone, H. A.; Gitai, Z. Microfluidic-Based Transcriptomics Reveal Force-Independent Bacterial Rheosensing. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 1274–1281.
- 11 Wu, C. H.; Kang, D.; Chen, P. H.; Tai, Y. C. Mems Thermal Flow Sensors. Sens. Actuators A 2016, 241, 135–144.
- 12 Ejeian, F.; Azadi, S.; Razmjou, A.; Orooji, Y.; Kottapalli, A.; Ebrahimi Warkiani, M.; Asadnia, M. Design and Applications of Mems Flow Sensors: A Review. Sens. Actuators A 2019, 295, 483–502.
- 13 Abolpour Moshizi, S.; Moradi, H.; Wu, S.; Han, Z. J.; Razmjou, A.; Asadnia, M. Biomimetic Ultraflexible Piezoresistive Flow Sensor Based on Graphene Nanosheets and Pva Hydrogel. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2021, 7, 2100783.
- 14 Kwon, K.; Kim, J. U.; Deng, Y.; Krishnan, S. R.; Choi, J.; Jang, H.; Lee, K.; Su, C. J.; Yoo, I.; Wu, Y.; Lipschultz, L.; Kim, J. H.; Chung, T. S.; Wu, D.; Park, Y.; Kim, T. i.; Ghaffari, R.; Lee, S.; Huang, Y.; Rogers, J. A. An on-Skin Platform for Wireless Monitoring of Flow Rate, Cumulative Loss and Temperature of Sweat in Real Time. Nat. Electron. 2021, 4, 302–312.
- 15 Zhang, R.; Ye, Z.; Gao, M.; Gao, C.; Zhang, X.; Li, L.; Gui, L. Liquid Metal Electrode-Enabled Flexible Microdroplet Sensor. Lab Chip 2020, 20, 496–504.
- 16 Shinohara, K.; Sugii, Y.; Aota, A.; Hibara, A.; Tokeshi, M.; Kitamori, T.; Okamoto, K. High-Speed Micro-Piv Measurements of Transient Flow in Microfluidic Devices. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2004, 15, 1965–1970.
- 17 König, J.; Voigt, A.; Büttner, L.; Czarske, J. Precise Micro Flow Rate Measurements by a Laser Doppler Velocity Profile Sensor with Time Division Multiplexing, Meas. Sci. Technol. 2010, 21, 074005.
- 18 Cavaniol, C.; Cesar, W.; Descroix, S.; Viovy, J. L. Flowmetering for Microfluidics. Lab Chip 2022, 22, 3603–3617.
- 19 Sadegh Cheri, M.; Latifi, H.; Sadeghi, J.; Salehi Moghaddam, M.; Shahraki, H.; Hajghassem, H. Real-Time Measurement of Flow Rate in Microfluidic Devices Using a Cantilever-Based Optofluidic Sensor. Analyst 2014, 139, 431–438.
- 20 Xu, S. H.; Liu, X. Y.; Yu, Z.; Liu, K. Non-Contact Optical Characterization of Negative Pressure in Hydrogel Voids and Microchannels. Front. Optoelectron. 2022, 15, 10.
- 21 van der Heyden, F. H. J.; Bonthuis, D. J.; Stein, D.; Meyer, C.; Dekker, C. Electrokinetic Energy Conversion Efficiency in Nanofluidic Channels. Nano Lett. 2006, 6, 2232–2237.
- 22 Xiao, K.; Jiang, L.; Antonietti, M. Ion Transport in Nanofluidic Devices for Energy Harvesting. Joule 2019, 3, 2364–2380.
- 23 Newaz, A. K. M.; Markov, D. A.; Prasai, D.; Bolotin, K. I. Graphene Transistor as a Probe for Streaming Potential. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 2931–2935.
- 24 Zhao, N.; Yu, Z. H.; Huang, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y. F.; Fu, X.; Yang, P. H.; Liu, K. Non-Invasive Monitoring of Biochemicals in Hydrogel-Assisted Microfluidic Chips. Nanoscale 2023, 15, 6179–6186.
- 25 Pozuelo, J.; Compañ, V.; González-Méijome, J. M.; González, M.; Mollá, S. Oxygen and Ionic Transport in Hydrogel and Silicone-Hydrogel Contact Lens Materials: An Experimental and Theoretical Study. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 452, 62–72.




