Protecting-Group-Free One-Step Palladium-Catalyzed Coupling on C25 of Cucurbitacin B Expands Chemical Diversity with Improved Cytotoxicity against A549 Cells
Ning Zhuo
University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, No. 19A Yuquan Road, Beijing, 100049 China
State Key Laboratory of Drug Research, Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai, 201203 China
Search for more papers by this authorJie Ma
State Key Laboratory of Drug Research, Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai, 201203 China
Search for more papers by this authorLei Cao
State Key Laboratory of Drug Research, Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai, 201203 China
School of Chinese Materia Medica, Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing, Jiangsu, 210046 China
Search for more papers by this authorLinhai Chen
State Key Laboratory of Drug Research, Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai, 201203 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Fajun Nan
University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, No. 19A Yuquan Road, Beijing, 100049 China
State Key Laboratory of Drug Research, Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai, 201203 China
Drug Discovery Shandong Laboratory, Bohai Rim Advanced Research Institute for Drug Discovery, Yantai, Shandong, 264117 China
E-mail: [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorNing Zhuo
University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, No. 19A Yuquan Road, Beijing, 100049 China
State Key Laboratory of Drug Research, Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai, 201203 China
Search for more papers by this authorJie Ma
State Key Laboratory of Drug Research, Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai, 201203 China
Search for more papers by this authorLei Cao
State Key Laboratory of Drug Research, Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai, 201203 China
School of Chinese Materia Medica, Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing, Jiangsu, 210046 China
Search for more papers by this authorLinhai Chen
State Key Laboratory of Drug Research, Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai, 201203 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Fajun Nan
University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, No. 19A Yuquan Road, Beijing, 100049 China
State Key Laboratory of Drug Research, Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai, 201203 China
Drug Discovery Shandong Laboratory, Bohai Rim Advanced Research Institute for Drug Discovery, Yantai, Shandong, 264117 China
E-mail: [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorComprehensive Summary
The natural product cucurbitacin B has been widely studied because of its multiple biological activities, especially its potent antitumor effects. However, modifications of cucurbitacin B are mainly focused on the C2 and C16 site, studies on the C25 acetoxy group are still limited. We successfully developed a palladium-catalyzed allylic coupling of cucurbitacin B with boronic acids, providing a one-step approach to expand the chemical diversity of the C25 position. Our method was protecting-group-free, showing a good functional group tolerance and a wide substrate scope under mild reaction conditions. A library of 29 derivatives was prepared, compounds 2q and 2u showed higher cytotoxicity against A549 cells than cucurbitacin B, compounds 2n and 2o maintained potency, and the introduced hydroxyl and amino groups could be further derived.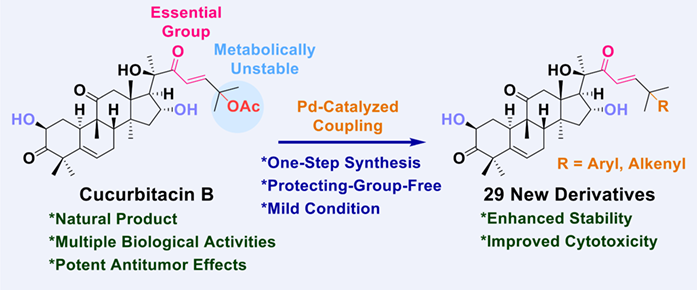
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| cjoc202200106-sup-0001-Supinfo.pdfPDF document, 8.4 MB |
Appendix S1 Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1 Kaushik, U.; Aeri, V.; Mir, S. R. Cucurbitacins - An insight into medicinal leads from nature. Pharmacogn. Rev. 2015, 9, 12–18.
- 2 Chen, J. C.; Chiu, M. H.; Nie, R. L.; Cordell, G. A.; Qiu, S. X. Cucurbitacins and cucurbitane glycosides: structures and biological activities. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2005, 22, 386–399.
- 3 Hussain, A. I.; Rathore, H. A.; Sattar, M. Z.; Chatha, S. A.; Sarker, S. D.; Gilani, A. H. Citrullus colocynthis (L.) Schrad (bitter apple fruit): a review of its phytochemistry, pharmacology, traditional uses and nutritional potential. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 155, 54–66.
- 4 Jayaprakasam, B.; Seeram, N. P.; Nair, M. G. Anticancer and antiinflammatory activities of cucurbitacins from Cucurbita andreana. Cancer Lett. 2003, 189, 11–16.
- 5 Garg, S.; Kaul, S. C.; Wadhwa, R. Cucurbitacin B and cancer intervention: Chemistry, biology and mechanisms (Review). Int. J. Oncol. 2018, 52, 19–37.
- 6 Silvestre, G.; de Lucena, R. P.; da Silva Alves, H. Cucurbitacins and the Immune System: Update in Research on Anti-inflammatory, Antioxidant, and Immunomodulatory Mechanisms. Curr. Med. Chem. 2022, 29, 3774–3789.
- 7(a) Kim, K. H.; Lee, I. S.; Park, J. Y.; Kim, Y.; An, E. J.; Jang, H. J. Cucurbitacin B Induces Hypoglycemic Effect in Diabetic Mice by Regulation of AMP-Activated Protein Kinase Alpha and Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 via Bitter Taste Receptor Signaling. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1071; (b) Dwijayanti, D. R.; Shimada, T.; Ishii, T.; Okuyama, T.; Ikeya, Y.; Mukai, E.; Nishizawa, M. Bitter melon fruit extract has a hypoglycemic effect and reduces hepatic lipid accumulation in ob/ob mice. Phytother. Res. 2020, 34, 1338–1346.
- 8 Chen, J. C.; Zhang, G. H.; Zhang, Z. Q.; Qiu, M. H.; Zheng, Y. T.; Yang, L. M.; Yu, K. B. Octanorcucurbitane and cucurbitane triterpenoids from the tubers of Hemsleya endecaphylla with HIV-1 inhibitory activity. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 153–155.
- 9 El Naggar el, M. B.; Chalupová, M.; Pražanová, G.; Parák, T.; Švajdlenka, E.; Žemlička, M.; Suchý, P. Hepatoprotective and proapoptotic effect of Ecballium elaterium on CCl4-induced hepatotoxicity in rats. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2015, 8, 526-531.
- 10 Schlegel, W.; Melera, A.; Noller, C. R. Reduction and Oxidation Products of Cucurbitacin B. J. Org. Chem. 1961, 26, 1206–1210.
- 11 Kupchan, S. M.; Tsou, G. Tumor inhibitors. LXXXI. Structure and partial synthesis of fabacein. J. Org. Chem. 1973, 38, 1055–1056.
- 12 Ryu, S. Y.; Choi, S. U.; Lee, S. H.; Lee, C. O.; No, Z.; Ahn, J. W. Cytotoxicity of Cucurbitacins in vitro. Arch. Pharm. Res. 1995, 18, 60–61.
- 13 Lang, K. L.; Silva, I. T.; Zimmermann, L. Z.; Machado, V. R.; Teixeira, M. R.; Lapuh, M. I.; Galetti, M. A.; Palermo, J. A.; Cabrera, G. M.; Bernardes, L. S. C.; Simões, C. M. O.; Schenkel, E. P.; Caro, M. S. B.; Durán, F. J. Synthesis and cytotoxic activity evaluation of dihydrocucurbitacin B and cucurbitacin B derivatives. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2012, 20, 3016–3030.
- 14 Ge, W.; Chen, X.; Han, F.; Liu, Z.; Wang, T.; Wang, M.; Chen, Y.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, Q. Synthesis of Cucurbitacin B Derivatives as Potential Anti-Hepatocellular Carcinoma Agents. Molecules 2018, 23, 3345.
- 15 Suebsakwong, P.; Wang, J.; Khetkam, P.; Weerapreeyakul, N.; Wu, J.; Du, Y.; Yao, Z. J.; Li, J. X.; Suksamrarn, A. A Bioreductive Prodrug of Cucurbitacin B Significantly Inhibits Tumor Growth in the 4T1 Xenograft Mice Model. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 10, 1400–1406.
- 16 Chen, C.; Qiang, S.; Lou, L.; Zhao, W. Cucurbitane-type triterpenoids from the stems of Cucumis melo. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 824–829.
- 17(a) Whitehouse, M. W.; Doskotch, R. W. Selective inhibition of thymidine incorporation into lymphocytes by cucurbitacins B and D. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1969, 18, 1790–1793; (b) Kausar, H.; Munagala, R.; Bansal, S. S.; Aqil, F.; Vadhanam, M. V.; Gupta, R. C. Cucurbitacin B potently suppresses non-small-cell lung cancer growth: identification of intracellular thiols as critical targets. Cancer Lett. 2013, 332, 35–45.
- 18 Bartalis, J.; Halaweish, F. T. Relationship between cucurbitacins reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography hydrophobicity index and basal cytotoxicity on HepG2 cells. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2005, 818, 159–166.
- 19 Meng, D.; Qiang, S.; Lou, L.; Zhao, W. Cytotoxic cucurbitane-type triterpenoids from Elaeocarpus hainanensis. Planta Med. 2008, 74, 1741–1744.
- 20 Saade, M.; Magdalou, J.; Ouaini, N.; Greige-Gerges, H. Stability of cucurbitacin E in human plasma: chemical hydrolysis and role of plasma esterases. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 2009, 30, 389–397.
- 21 Abbas, S.; Vincourt, J. B.; Habib, L.; Netter, P.; Greige-Gerges, H.; Magdalou, J. The cucurbitacins E, D and I: investigation of their cytotoxicity toward human chondrosarcoma SW 1353 cell line and their biotransformation in man liver. Toxicol. Lett. 2013, 216, 189–199.
- 22 Hunsakunachai, N.; Nuengchamnong, N.; Jiratchariyakul, W.; Kummalue, T.; Khemawoot, P. Phar-macokinetics of cucurbitacin B from Trichosanthes cucumerina L. in rats. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2019, 19, 157.
- 23 Liaw, M. W.; Cheng, W. F.; Tong, R. C-Aryl Glycosylation: Palladium- Catalyzed Aryl-Allyl Coupling of Achmatowicz Rearrangement Products with Arylboronic Acids. J. Org. Chem. 2020, 85, 6663–6674.




