Mature CD8+ T-cell clonal expansion in the oral cavity and digestive tract: a severe lymphoid malignancy that mimics Crohn's disease
Key Clinical Message
In patients with atypical Crohn's disease features, including severe oral ulcerations and resistance to standard treatment, the possibility of a mature clonal CD8+ T-cell lymphoproliferative disorder should be investigated. Clinicians should be aware of this differential diagnosis because CD8+ T-cell lymphoma prognosis can be remarkably favorable upon oral treatment with cyclophosphamide.
Introduction
Mature digestive CD8+ T-cell lymphomas are rare entities of variable severity (from indolent to aggressive and destructive disease) 1-3. Despite their severity, their prognosis may be favorable if adapted treatment is provided 1. We report here an unusual case of severe mature CD8+ T-cell lymphoma with digestive infiltration that mimicked Crohn's disease, but with favorable outcome upon oral treatment with cyclophosphamide.
Case History
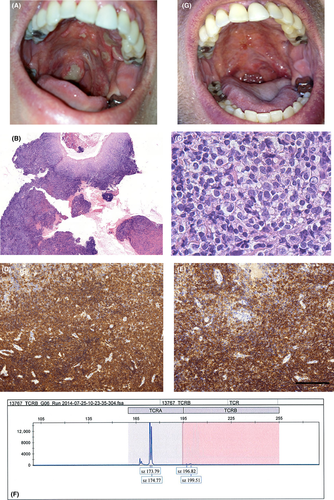
A 37-year-old male with a history of pancolitis consistent with Crohn's disease was successively treated with azathioprine and antitumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha antibodies (adalimumab and infliximab) with limited results. After 8 years of follow-up, he developed persistent buccal ulcerations. Examination of the oral cavity highlighted the presence of palatal and mucosal ulcerations with fibrin deposits, gingivitis, periodontitis, osteolysis, and total destruction of the uvula (Fig. 1A). The patient was treated with mesalamine, methotrexate, and ustekinumab (anti-interleukin 12 antibody), without long-lasting effects. Diarrhea and oral ulcerations progressively worsened, leading to a weight loss of 8 kg. Multiple ulcerations, consistent with pancolitis, were found mainly in the right colon and cecum by endoscopic exploration of the digestive tract. Histopathological analysis of the palatal ulcerations showed a diffuse mucosal lymphoid infiltration made of small- to medium-sized lymphoid cells (Fig. 1B) with large cytoplasm. At the ulcer surface, necrosis and leukocytes were observed (Fig. 1C). These cells expressed the CD3 (Fig. 1D), CD8 (Fig. 1E), CD2, CD5, and CD7 antigens. Conversely, they were negative for CD56, Epstein–Barr-encoded small RNAs (EBERs), and CD30. The proliferation index, assessed by Ki67 staining, was low to moderate (not shown). These findings were consistent with a mature CD8+ T-cell lymphoproliferative disorder. Review of historical colonic biopsies showed the same lymphoid mucosal infiltration with superficial ulcerations without crypt distortion and absence of granuloma. Clonal CD8+ T-cell expansion was assessed by T-cell receptor-γ locus rearrangement analysis and was detected in lymphoid cells from the oral cavity and colon (Fig. 1F), but not in blood. A computerized tomodensitometry of thorax and abdomen found no additional organ involvement. No somatic STAT3 exon 21 mutation was detected in this lymphoproliferative malignancy with expansion of mature and CD8+ lymphoid cells 4.
Treatment and Outcome
On the basis of the diagnosis of mature CD8+ T-cell lymphoproliferative disorder, oral treatment with 150 mg cyclophosphamide per day was started. Diarrhea rapidly disappeared and oral ulcerations improved. After 4 months, the patient had already recovered his baseline weight and the oral cavity lesions had completely healed (Fig. 1G). After 8 months, he is still in remission with normal physical activity.
Discussion
We report a very unusual case of mature CD8+ T-cell lymphoma with digestive infiltration that mimics Crohn's disease. Literature reports on this malignancy are very rare and treatment remains unknown. Our finding suggests that in patients with atypical features of Crohn's disease, including severe oral ulcerations, and who are refractory to standard treatment, the alternative diagnosis of clonal CD8+ T-cell lymphoproliferative disorder should be considered. Its prognosis can be remarkably favorable upon oral treatment with cyclophosphamide, as observed for our patient. Clinicians should therefore be aware of this possible differential diagnosis.
Conflict of Interest
None declared.




