New Hydroxyphenylacetic Acids and α-Pyrone Derivative from the Deep-Sea Cold Seep Sediment-Derived Fungus Penicillium corylophilum CS-682
Chi-Sheng Zhu
CAS and Shandong Province Key Laboratory of Experimental Marine Biology, Center for Ocean Mega-Science, Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Nanhai Road 7, Qingdao, 266071 China Tel.
University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Yuquan Road 19 A, Beijing, 100049 China
Contribution: Investigation (lead), Writing - original draft (lead)
Search for more papers by this authorXiao-Ming Li
CAS and Shandong Province Key Laboratory of Experimental Marine Biology, Center for Ocean Mega-Science, Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Nanhai Road 7, Qingdao, 266071 China Tel.
Contribution: Investigation (lead)
Search for more papers by this authorSui-Qun Yang
CAS and Shandong Province Key Laboratory of Experimental Marine Biology, Center for Ocean Mega-Science, Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Nanhai Road 7, Qingdao, 266071 China Tel.
University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Yuquan Road 19 A, Beijing, 100049 China
Contribution: Resources (equal)
Search for more papers by this authorYi-Wei Liu
CAS and Shandong Province Key Laboratory of Experimental Marine Biology, Center for Ocean Mega-Science, Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Nanhai Road 7, Qingdao, 266071 China Tel.
University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Yuquan Road 19 A, Beijing, 100049 China
Contribution: Investigation (supporting)
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Bin-Gui Wang
- [email protected]
- +86-532-8289-8553 (B.-G.W.) +86-532-8289-8890 (X.L.
CAS and Shandong Province Key Laboratory of Experimental Marine Biology, Center for Ocean Mega-Science, Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Nanhai Road 7, Qingdao, 266071 China Tel.
University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Yuquan Road 19 A, Beijing, 100049 China
Laboratory of Marine Biology and Biotechnology, Qingdao National Laboratory for Marine Science and Technology, Wenhai Road 1, Qingdao, 266237 China
Contribution: Funding acquisition (equal), Supervision (equal), Writing - review & editing (equal)
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Xin Li
CAS and Shandong Province Key Laboratory of Experimental Marine Biology, Center for Ocean Mega-Science, Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Nanhai Road 7, Qingdao, 266071 China Tel.
University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Yuquan Road 19 A, Beijing, 100049 China
Laboratory of Marine Biology and Biotechnology, Qingdao National Laboratory for Marine Science and Technology, Wenhai Road 1, Qingdao, 266237 China
Contribution: Funding acquisition (lead), Supervision (lead), Writing - review & editing (lead)
Search for more papers by this authorChi-Sheng Zhu
CAS and Shandong Province Key Laboratory of Experimental Marine Biology, Center for Ocean Mega-Science, Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Nanhai Road 7, Qingdao, 266071 China Tel.
University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Yuquan Road 19 A, Beijing, 100049 China
Contribution: Investigation (lead), Writing - original draft (lead)
Search for more papers by this authorXiao-Ming Li
CAS and Shandong Province Key Laboratory of Experimental Marine Biology, Center for Ocean Mega-Science, Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Nanhai Road 7, Qingdao, 266071 China Tel.
Contribution: Investigation (lead)
Search for more papers by this authorSui-Qun Yang
CAS and Shandong Province Key Laboratory of Experimental Marine Biology, Center for Ocean Mega-Science, Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Nanhai Road 7, Qingdao, 266071 China Tel.
University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Yuquan Road 19 A, Beijing, 100049 China
Contribution: Resources (equal)
Search for more papers by this authorYi-Wei Liu
CAS and Shandong Province Key Laboratory of Experimental Marine Biology, Center for Ocean Mega-Science, Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Nanhai Road 7, Qingdao, 266071 China Tel.
University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Yuquan Road 19 A, Beijing, 100049 China
Contribution: Investigation (supporting)
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Bin-Gui Wang
- [email protected]
- +86-532-8289-8553 (B.-G.W.) +86-532-8289-8890 (X.L.
CAS and Shandong Province Key Laboratory of Experimental Marine Biology, Center for Ocean Mega-Science, Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Nanhai Road 7, Qingdao, 266071 China Tel.
University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Yuquan Road 19 A, Beijing, 100049 China
Laboratory of Marine Biology and Biotechnology, Qingdao National Laboratory for Marine Science and Technology, Wenhai Road 1, Qingdao, 266237 China
Contribution: Funding acquisition (equal), Supervision (equal), Writing - review & editing (equal)
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Xin Li
CAS and Shandong Province Key Laboratory of Experimental Marine Biology, Center for Ocean Mega-Science, Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Nanhai Road 7, Qingdao, 266071 China Tel.
University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Yuquan Road 19 A, Beijing, 100049 China
Laboratory of Marine Biology and Biotechnology, Qingdao National Laboratory for Marine Science and Technology, Wenhai Road 1, Qingdao, 266237 China
Contribution: Funding acquisition (lead), Supervision (lead), Writing - review & editing (lead)
Search for more papers by this authorAbstract
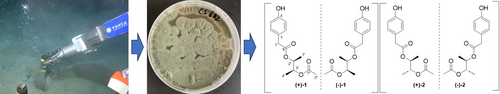
Two pairs of new enantiomeric hydroxyphenylacetic acid derivatives, (±)-corylophenols A and B ((±)-1 and (±)-2), a new α-pyrone analogue, corylopyrone A (3), and six andrastin-type meroterpenoids (4–9) were isolated and identified from the deep-sea cold-seep sediment-derived fungus Penicillium corylophilum CS-682. Their structures and stereo configurations were determined by detailed spectroscopic analysis of NMR and MS data, chiral HPLC analysis, J-based configuration analysis, and quantum chemical calculations of ECD, specific rotation, and NMR (with DP4+ probability analysis). Compound 3 showed inhibitory activity against some strains of pathogenic bacteria.
Graphical Abstract
Conflict of interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available in the supplementary material of this article.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| cbdv202400584-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf4 MB | Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1A. R. Carroll, B. R. Copp, T. Grkovic, R. A. Keyzers, M. R. Prinsep, Nat. Prod. Rep. 2024, 41, 162–207.
- 2A. R. Carroll, B. R. Copp, R. A. Davis, R. A. Keyzers, M. R. Prinsep, Nat. Prod. Rep. 2023, 40, 275–325.
- 3L. I. Pilkington, Molecules 2019, 24, 3942.
- 4D. Skropeta, L. Wei, Nat. Prod. Rep. 2014, 31, 999–1025.
- 5E. Shekarriz, J. Chen, Z. Xu, H. Liu, Microbiol Spectr 2023, 11, e0197822.
- 6M. Cong, Y. Zhang, X. Feng, X. Pang, Y. Liu, X. Zhang, Z. Yang, J. Wang, J. Biotechnol. 2022, 12, 161.
- 7Q. Song, S. Q. Yang, X. M. Li, X. Y. Hu, X. Li, B. G. Wang, Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 529.
- 8Y. Li, X. Li, X. Li, S. Yang, B. Wang, H. Li, Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5567.
- 9L. P. Chi, X. M. Li, Y. P. Wan, Y. H. Li, X. Li, B. G. Wang, Chem. Biodiversity 2021, 18, e2100512.
- 10Y. P. Liu, S. T. Fang, Z. Z. Shi, B. G. Wang, X. N. Li, N. Y. Ji, Mar. Drugs 2020, 19, 9.
- 11X. Y. Hu, C. Y. Wang, X. M. Li, S. Q. Yang, X. Li, B. G. Wang, S. Y. Si, L. H. Meng, J. Nat. Prod. 2021, 84, 3122–3130.
- 12Y. J. Hao, Z. B. Zou, M. M. Xie, Y. Zhang, L. Xu, H. Y. Yu, H. B. Ma, X. W. Yang, Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 234.
- 13L. H. Yan, P. H. Li, X. M. Li, S. Q. Yang, K. C. Liu, B. G. Wang, X. Li, Org. Lett. 2022, 24, 2684–2688.
- 14L. P. Chi, X. M. Li, Y. P. Wan, X. Li, B. G. Wang, J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 3652–3660.
- 15Y. H. Li, X. M. Li, X. Li, S. Q. Yang, X. S. Shi, H. L. Li, B. G. Wang, Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 553.
- 16L. P. Chi, X. M. Li, L. Li, X. Li, Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 160.
- 17D. R. McMullin, T. K. Nsiama, J. D. Miller, J. Nat. Prod. 2014, 77, 206–212.
- 18D. R. McMullin, T. K. Nsiama, J. D. Miller, Mycologia 2014, 106, 621–628.
- 19L. Xu, H. B. Ma, T. Wu, L. F. Liu, M. M. Xie, M. Y. Hu, Y. B. Gai, T. H. Zhong, X. W. Yang, Chem. Biodiversity 2023, 20, e202300753.
- 20G. Bifulco, P. Dambruoso, L. Gomez-Paloma, R. & Riccio, Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 3744–3779.
- 21J. Chang, Q. Ouyang, X. Peng, J. Pei, L. Zhang, Y. Gan, H. Ruan, Bioorg. Chem. 2023, 139, 106745.
- 22F. C. Özkaya, W. Ebrahim, M. Klopotowski, Z. Liu, C. Janiak, P. Proksch, Nat. Prod. Res. 2018, 32, 840–843.
- 23J. Ren, R. Huo, G. Liu, L. Liu, Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 189–197.
- 24C. L. Xie, Q. Liu, Z. H. He, Y. B. Gai, Z. B. Zou, Z. Z. Shao, G. M. Liu, H. F. Chen, X. W. Yang, Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 108, 104671–104679.
- 25L. H. Meng, X. M. Li, F. Z. Zhang, Y. N. Wang, B. G. Wang, J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 2528–2536.
- 26X. Y. Hu, X. M. Li, B. G. Wang, L. H. Meng, J. Nat. Prod. 2022, 85, 1398–1406.
- 27Y. H. Li, S. Q. Yang, X. M. Li, X. Li, B. G. Wang, H. L. Li, B. ‘Cyclopiumolides A, Bioorg. Chem. 2022, 128, 106104.
- 28M. J. Frisch, G. W. Trucks, H. B. Schlegel, G. E. Scuseria, M. A. Robb, J. R. Cheeseman, G. Scalmani, V. Barone, B. Mennucci, G. A. Petersson, ‘Gaussian 09, Revision D.01’, Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, UK, 2013.
- 29N. Grimblat, M. M. Zanardi, A. M. Sarotti, J. Org. Chem. 2015, 80, 12526–12534.
- 30S. K. S. Al-Burtamani, M. O. Fatope, R. G. Marwah, A. K. Onifade, S. H. Al-Saidi, J. Ethnopharmacol. 2005, 96, 107–112.