Anti-inflammatory Steroids from the South China Sea Sponge Spongia officinalis
Abstract
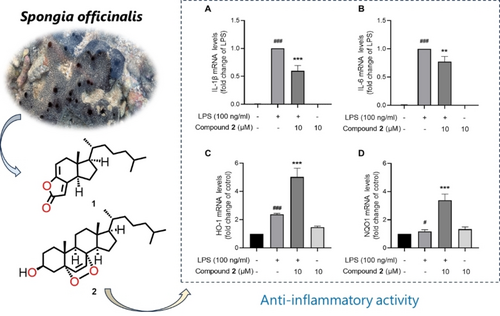
One new highly degraded steroid, namely 21-nor-4-ene-chaxine A (1) furnishing a 5/6/5-tricyclic, along with one known related analogue (2), were isolated from the South China Sea sponge Spongia officinalis. Their structures including absolute configurations were established by extensive spectroscopic data analysis, TDDFT-ECD calculation, and comparison with the spectral data previously reported in the literature. Compound 1 represent the new member of incisterols family with a highly degradation in ring B. In vitro bioassays revealed compound 2 exhibited significant anti-microglial inflammatory effect on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced inflammation in BV-2 microglial cells.
Graphical Abstract
Conflict of interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available in the supplementary material of this article.